Theo van Walsum
OccluNet: Spatio-Temporal Deep Learning for Occlusion Detection on DSA
Aug 19, 2025Abstract:Accurate detection of vascular occlusions during endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) is critical in acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Interpretation of digital subtraction angiography (DSA) sequences poses challenges due to anatomical complexity and time constraints. This work proposes OccluNet, a spatio-temporal deep learning model that integrates YOLOX, a single-stage object detector, with transformer-based temporal attention mechanisms to automate occlusion detection in DSA sequences. We compared OccluNet with a YOLOv11 baseline trained on either individual DSA frames or minimum intensity projections. Two spatio-temporal variants were explored for OccluNet: pure temporal attention and divided space-time attention. Evaluation on DSA images from the MR CLEAN Registry revealed the model's capability to capture temporally consistent features, achieving precision and recall of 89.02% and 74.87%, respectively. OccluNet significantly outperformed the baseline models, and both attention variants attained similar performance. Source code is available at https://github.com/anushka-kore/OccluNet.git
An automated framework for brain vessel centerline extraction from CTA images
Jan 13, 2024Abstract:Accurate automated extraction of brain vessel centerlines from CTA images plays an important role in diagnosis and therapy of cerebrovascular diseases, such as stroke. However, this task remains challenging due to the complex cerebrovascular structure, the varying imaging quality, and vessel pathology effects. In this paper, we consider automatic lumen segmentation generation without additional annotation effort by physicians and more effective use of the generated lumen segmentation for improved centerline extraction performance. We propose an automated framework for brain vessel centerline extraction from CTA images. The framework consists of four major components: (1) pre-processing approaches that register CTA images with a CT atlas and divide these images into input patches, (2) lumen segmentation generation from annotated vessel centerlines using graph cuts and robust kernel regression, (3) a dual-branch topology-aware UNet (DTUNet) that can effectively utilize the annotated vessel centerlines and the generated lumen segmentation through a topology-aware loss (TAL) and its dual-branch design, and (4) post-processing approaches that skeletonize the predicted lumen segmentation. Extensive experiments on a multi-center dataset demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of average symmetric centerline distance (ASCD) and overlap (OV). Subgroup analyses further suggest that the proposed framework holds promise in clinical applications for stroke treatment. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/Liusj-gh/DTUNet.
AngioMoCo: Learning-based Motion Correction in Cerebral Digital Subtraction Angiography
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Cerebral X-ray digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is the standard imaging technique for visualizing blood flow and guiding endovascular treatments. The quality of DSA is often negatively impacted by body motion during acquisition, leading to decreased diagnostic value. Time-consuming iterative methods address motion correction based on non-rigid registration, and employ sparse key points and non-rigidity penalties to limit vessel distortion. Recent methods alleviate subtraction artifacts by predicting the subtracted frame from the corresponding unsubtracted frame, but do not explicitly compensate for motion-induced misalignment between frames. This hinders the serial evaluation of blood flow, and often causes undesired vasculature and contrast flow alterations, leading to impeded usability in clinical practice. To address these limitations, we present AngioMoCo, a learning-based framework that generates motion-compensated DSA sequences from X-ray angiography. AngioMoCo integrates contrast extraction and motion correction, enabling differentiation between patient motion and intensity changes caused by contrast flow. This strategy improves registration quality while being substantially faster than iterative elastix-based methods. We demonstrate AngioMoCo on a large national multi-center dataset (MR CLEAN Registry) of clinically acquired angiographic images through comprehensive qualitative and quantitative analyses. AngioMoCo produces high-quality motion-compensated DSA, removing motion artifacts while preserving contrast flow. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/RuishengSu/AngioMoCo.
Comparison of different retinal regions-of-interest imaged by OCT for the classification of intermediate AMD
May 04, 2023



Abstract:To study whether it is possible to differentiate intermediate age-related macular degeneration (AMD) from healthy controls using partial optical coherence tomography (OCT) data, that is, restricting the input B-scans to certain pre-defined regions of interest (ROIs). A total of 15744 B-scans from 269 intermediate AMD patients and 115 normal subjects were used in this study (split on subject level in 80% train, 10% validation and 10% test). From each OCT B-scan, three ROIs were extracted: retina, complex between retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and Bruch membrane (BM), and choroid (CHO). These ROIs were obtained using two different methods: masking and cropping. In addition to the six ROIs, the whole OCT B-scan and the binary mask corresponding to the segmentation of the RPE-BM complex were used. For each subset, a convolutional neural network (based on VGG16 architecture and pre-trained on ImageNet) was trained and tested. The performance of the models was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC), accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity. All trained models presented an AUROC, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity equal to or higher than 0.884, 0.816, 0.685, and 0.644, respectively. The model trained on the whole OCT B-scan presented the best performance (AUROC = 0.983, accuracy = 0.927, sensitivity = 0.862, specificity = 0.913). The models trained on the ROIs obtained with the cropping method led to significantly higher outcomes than those obtained with masking, with the exception of the retinal tissue, where no statistically significant difference was observed between cropping and masking (p = 0.47). This study demonstrated that while using the complete OCT B-scan provided the highest accuracy in classifying intermediate AMD, models trained on specific ROIs such as the RPE-BM complex or the choroid can still achieve high performance.
Label Refinement Network from Synthetic Error Augmentation for Medical Image Segmentation
Sep 14, 2022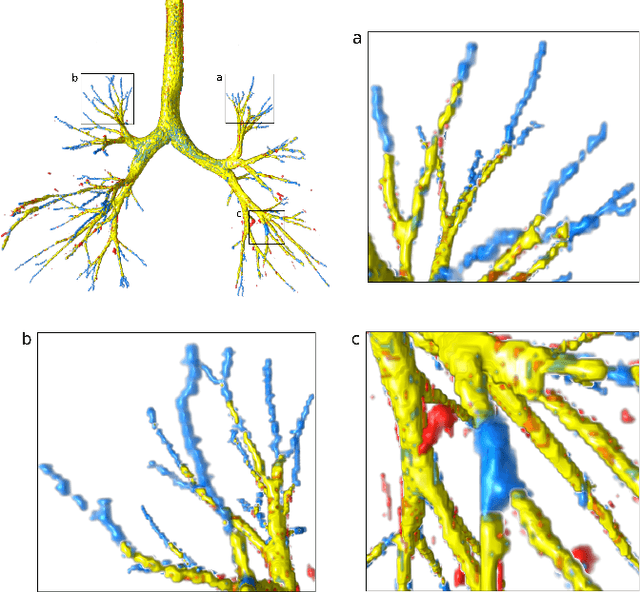
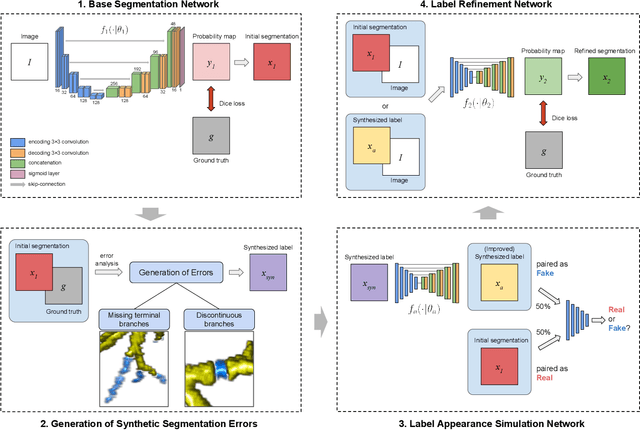
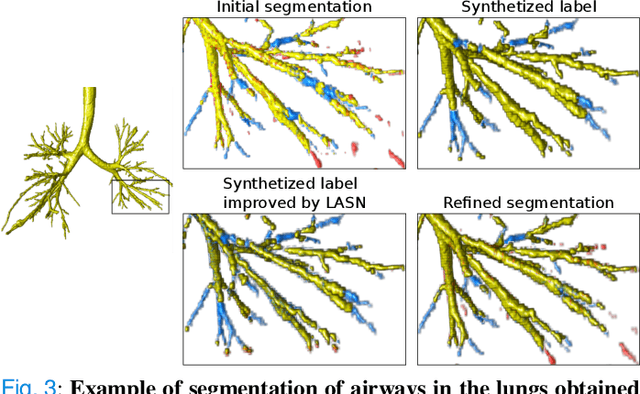
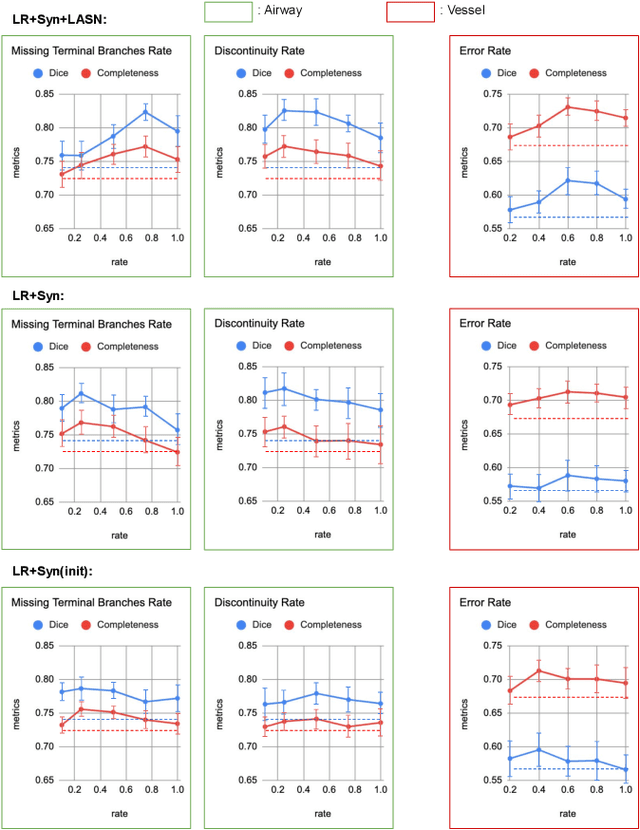
Abstract:Deep convolutional neural networks for image segmentation do not learn the label structure explicitly and may produce segmentations with an incorrect structure, e.g., with disconnected cylindrical structures in the segmentation of tree-like structures such as airways or blood vessels. In this paper, we propose a novel label refinement method to correct such errors from an initial segmentation, implicitly incorporating information about label structure. This method features two novel parts: 1) a model that generates synthetic structural errors, and 2) a label appearance simulation network that produces synthetic segmentations (with errors) that are similar in appearance to the real initial segmentations. Using these synthetic segmentations and the original images, the label refinement network is trained to correct errors and improve the initial segmentations. The proposed method is validated on two segmentation tasks: airway segmentation from chest computed tomography (CT) scans and brain vessel segmentation from 3D CT angiography (CTA) images of the brain. In both applications, our method significantly outperformed a standard 3D U-Net and other previous refinement approaches. Improvements are even larger when additional unlabeled data is used for model training. In an ablation study, we demonstrate the value of the different components of the proposed method.
Spatio-Temporal U-Net for Cerebral Artery and Vein Segmentation in Digital Subtraction Angiography
Aug 03, 2022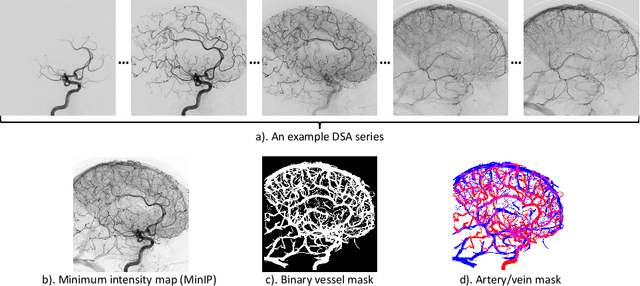
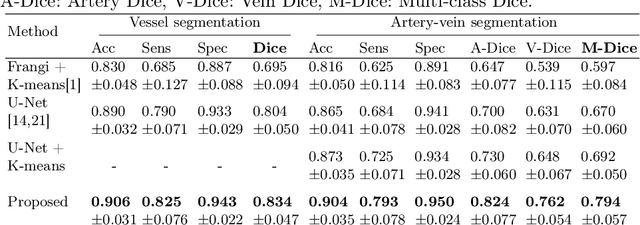
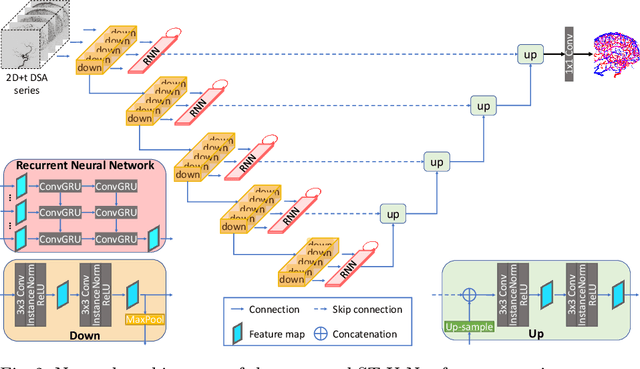
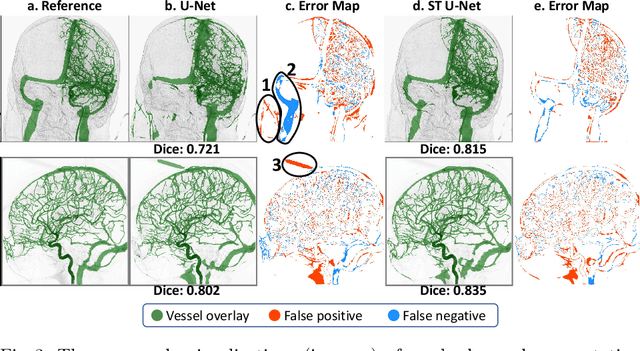
Abstract:X-ray digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is widely used for vessel and/or flow visualization and interventional guidance during endovascular treatment of patients with a stroke or aneurysm. To assist in peri-operative decision making as well as post-operative prognosis, automatic DSA analysis algorithms are being developed to obtain relevant image-based information. Such analyses include detection of vascular disease, evaluation of perfusion based on time intensity curves (TIC), and quantitative biomarker extraction for automated treatment evaluation in endovascular thrombectomy. Methodologically, such vessel-based analysis tasks may be facilitated by automatic and accurate artery-vein segmentation algorithms. The present work describes to the best of our knowledge the first study that addresses automatic artery-vein segmentation in DSA using deep learning. We propose a novel spatio-temporal U-Net (ST U-Net) architecture which integrates convolutional gated recurrent units (ConvGRU) in the contracting branch of U-Net. The network encodes a 2D+t DSA series of variable length and decodes it into a 2D segmentation image. On a multi-center routinely acquired dataset, the proposed method significantly outperformed U-Net (P<0.001) and traditional Frangi-based K-means clustering (P$<$0.001). Particularly in artery-vein segmentation, ST U-Net achieved a Dice coefficient of 0.794, surpassing the existing state-of-the-art methods by a margin of 12\%-20\%. Code will be made publicly available upon acceptance.
Automatic Segmentation of the Optic Nerve Head Region in Optical Coherence Tomography: A Methodological Review
Sep 06, 2021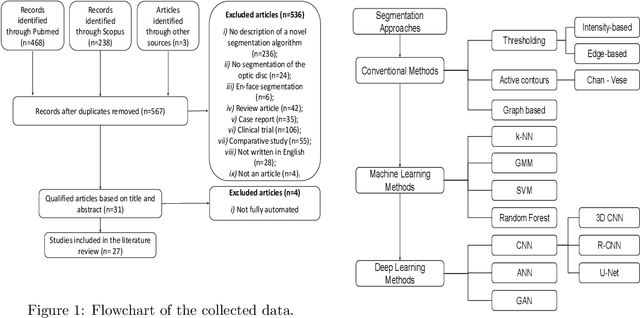
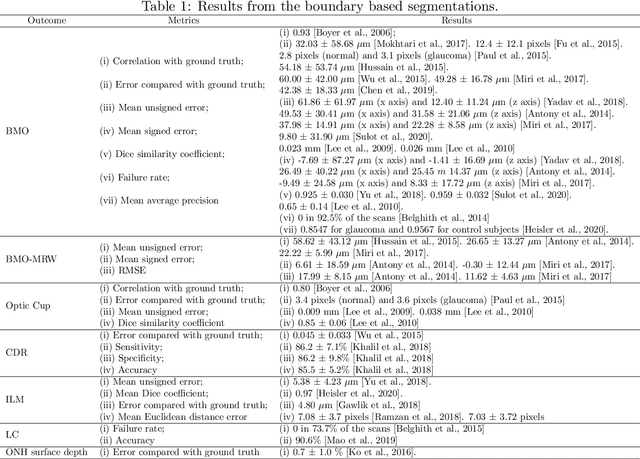
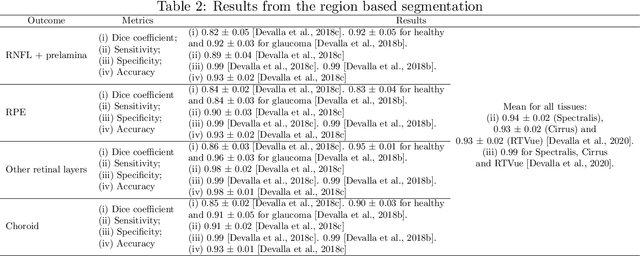
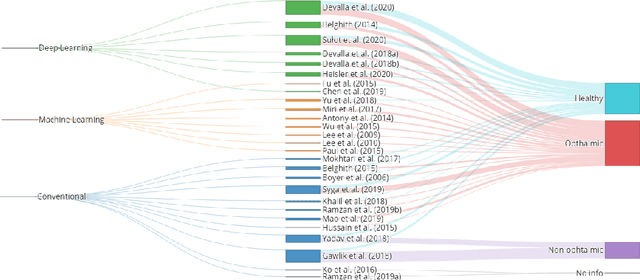
Abstract:The optic nerve head represents the intraocular section of the optic nerve (ONH), which is prone to damage by intraocular pressure. The advent of optical coherence tomography (OCT) has enabled the evaluation of novel optic nerve head parameters, namely the depth and curvature of the lamina cribrosa (LC). Together with the Bruch's membrane opening minimum-rim-width, these seem to be promising optic nerve head parameters for diagnosis and monitoring of retinal diseases such as glaucoma. Nonetheless, these optical coherence tomography derived biomarkers are mostly extracted through manual segmentation, which is time-consuming and prone to bias, thus limiting their usability in clinical practice. The automatic segmentation of optic nerve head in OCT scans could further improve the current clinical management of glaucoma and other diseases. This review summarizes the current state-of-the-art in automatic segmentation of the ONH in OCT. PubMed and Scopus were used to perform a systematic review. Additional works from other databases (IEEE, Google Scholar and ARVO IOVS) were also included, resulting in a total of 27 reviewed studies. For each algorithm, the methods, the size and type of dataset used for validation, and the respective results were carefully analyzed. The results show that deep learning-based algorithms provide the highest accuracy, sensitivity and specificity for segmenting the different structures of the ONH including the LC. However, a lack of consensus regarding the definition of segmented regions, extracted parameters and validation approaches has been observed, highlighting the importance and need of standardized methodologies for ONH segmentation.
Signal-carrying speckle in Optical Coherence Tomography: a methodological review on biomedical applications
Aug 30, 2021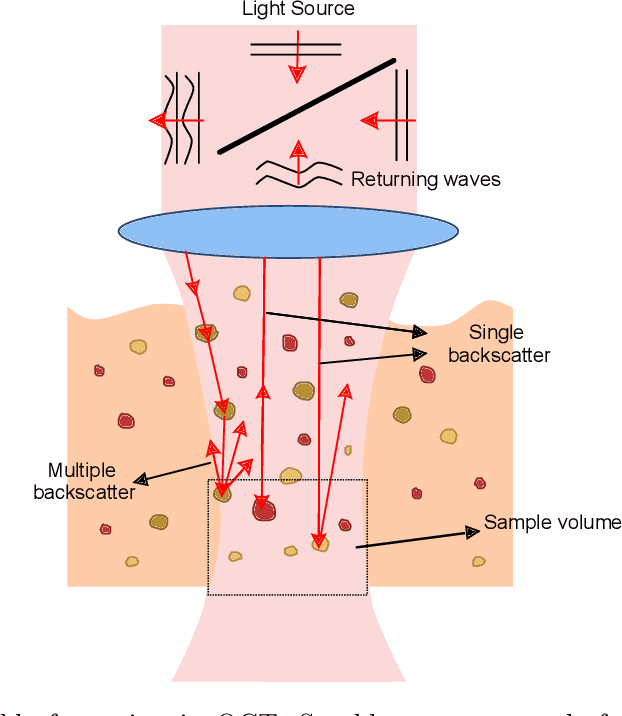
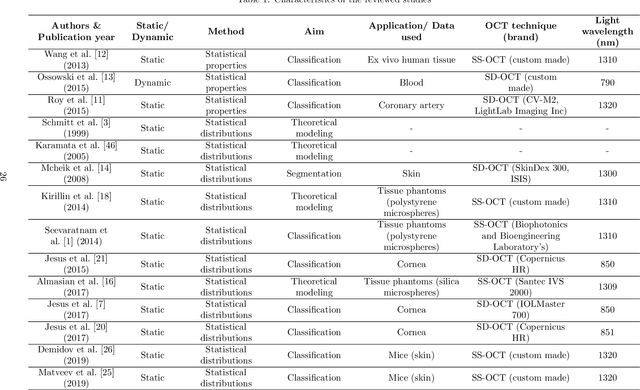
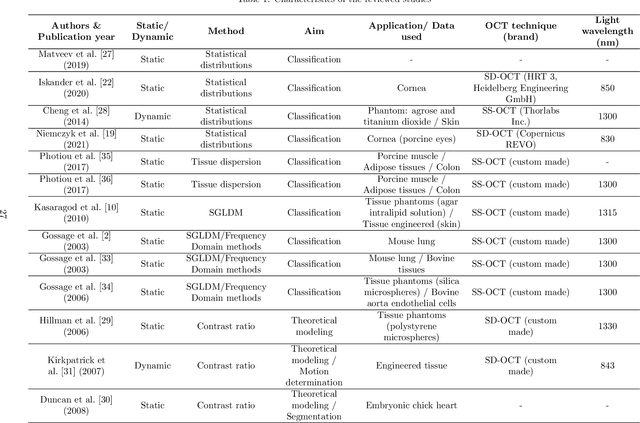
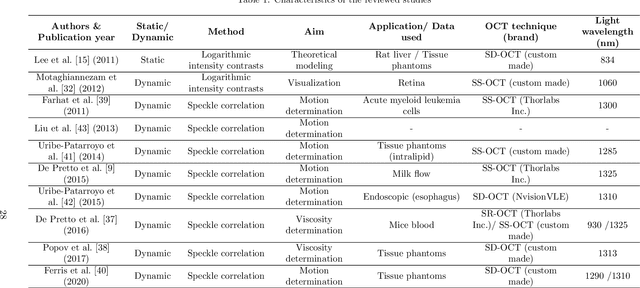
Abstract:Significance: Speckle has historically been considered a source of noise in coherent light imaging. However, a number of works in optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging have shown that speckle patterns may contain relevant information regarding sub-resolution and structural properties of the tissues from which it is originated. Aim: The objective of this work is to provide a comprehensive overview of the methods developed for retrieving speckle information in biomedical OCT applications. Approach: PubMed and Scopus databases were used to perform a systematic review on studies published until April 2021. From 134-screened studies, 37 were eligible for this review. Results: The studies have been clustered according to the nature of their analysis, namely static or dynamic, and all features were described and analysed. The results show that features retrieved from speckle can be used successfully in different applications, such as classification and segmentation. However, the results also show that speckle analysis is highly application-dependant, and the best approach varies between applications. Conclusions: Several of the reviewed analysis were only performed in a theoretical context or using phantoms, showing that signal-carrying speckle analysis in OCT imaging is still in its early stage, and further work is needed to validate its applicability and reproducibility in a clinical context.
autoTICI: Automatic Brain Tissue Reperfusion Scoring on 2D DSA Images of Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients
Oct 06, 2020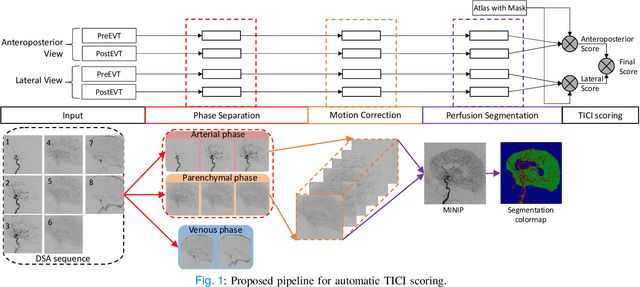
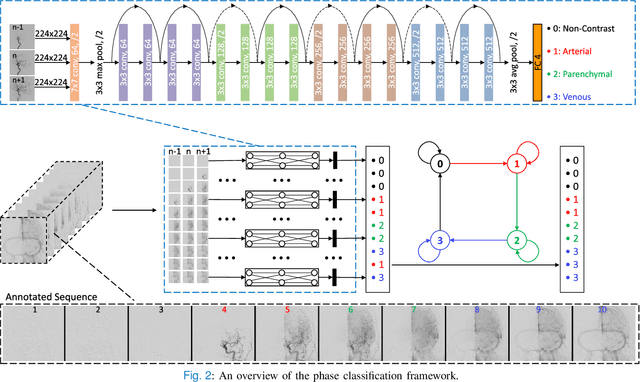
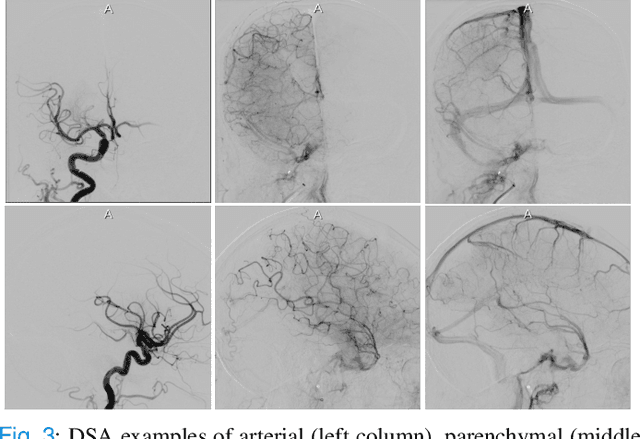
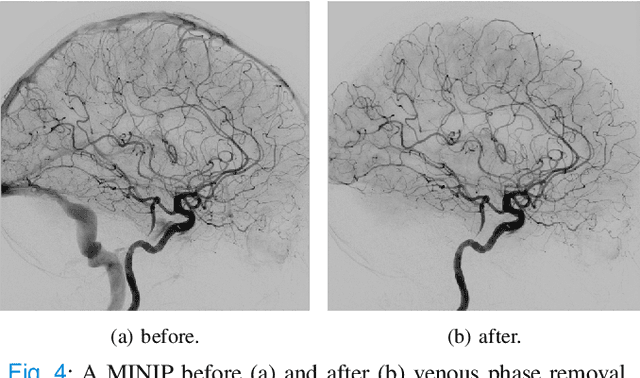
Abstract:The Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction (TICI) score is an important metric for reperfusion therapy assessment in acute ischemic stroke. It is commonly used as a technical outcome measure after endovascular treatment (EVT). Existing TICI scores are defined in coarse ordinal grades based on visual inspection, leading to inter- and intra-observer variation. In this work, we present autoTICI, an automatic and quantitative TICI scoring method. First, each digital subtraction angiography (DSA) sequence is separated into four phases (non-contrast, arterial, parenchymal and venous phase) using a multi-path convolutional neural network (CNN), which exploits spatio-temporal features. The network also incorporates sequence level label dependencies in the form of a state-transition matrix. Next, a minimum intensity map (MINIP) is computed using the motion corrected arterial and parenchymal frames. On the MINIP image, vessel, perfusion and background pixels are segmented. Finally, we quantify the autoTICI score as the ratio of reperfused pixels after EVT. On a routinely acquired multi-center dataset, the proposed autoTICI shows good correlation with the extended TICI (eTICI) reference with an average area under the curve (AUC) score of 0.81. The AUC score is 0.90 with respect to the dichotomized eTICI. In terms of clinical outcome prediction, we demonstrate that autoTICI is overall comparable to eTICI.
Dynamic Coronary Roadmapping via Catheter Tip Tracking in X-ray Fluoroscopy with Deep Learning Based Bayesian Filtering
Jan 11, 2020



Abstract:Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is typically performed with image guidance using X-ray angiograms in which coronary arteries are opacified with X-ray opaque contrast agents. Interventional cardiologists typically navigate instruments using non-contrast-enhanced fluoroscopic images, since higher use of contrast agents increases the risk of kidney failure. When using fluoroscopic images, the interventional cardiologist needs to rely on a mental anatomical reconstruction. This paper reports on the development of a novel dynamic coronary roadmapping approach for improving visual feedback and reducing contrast use during PCI. The approach compensates cardiac and respiratory induced vessel motion by ECG alignment and catheter tip tracking in X-ray fluoroscopy, respectively. In particular, for accurate and robust tracking of the catheter tip, we proposed a new deep learning based Bayesian filtering method that integrates the detection outcome of a convolutional neural network and the motion estimation between frames using a particle filtering framework. The proposed roadmapping and tracking approaches were validated on clinical X-ray images, achieving accurate performance on both catheter tip tracking and dynamic coronary roadmapping experiments. In addition, our approach runs in real-time on a computer with a single GPU and has the potential to be integrated into the clinical workflow of PCI procedures, providing cardiologists with visual guidance during interventions without the need of extra use of contrast agent.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge