Spatio-Temporal U-Net for Cerebral Artery and Vein Segmentation in Digital Subtraction Angiography
Paper and Code
Aug 03, 2022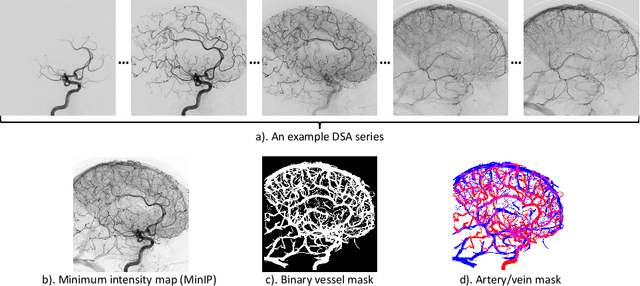
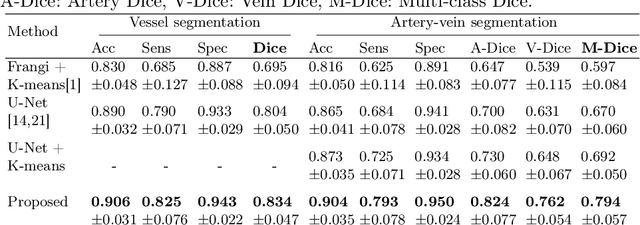
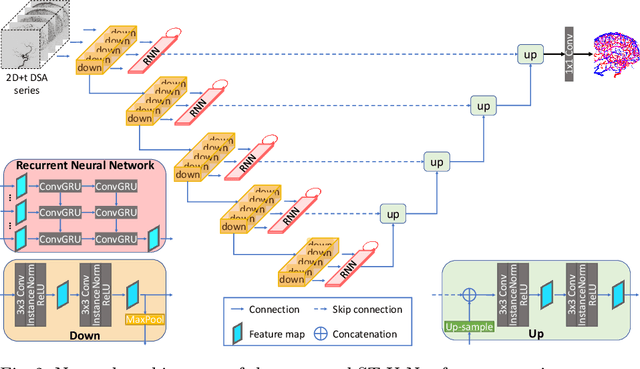
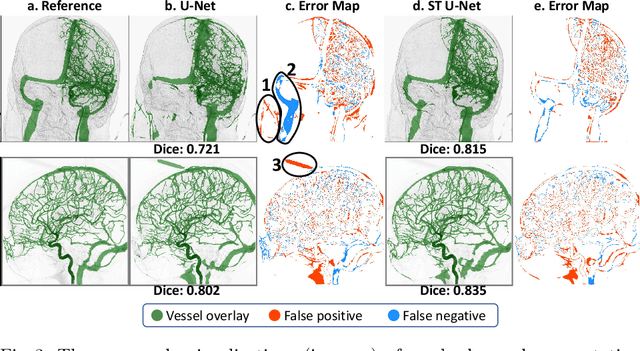
X-ray digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is widely used for vessel and/or flow visualization and interventional guidance during endovascular treatment of patients with a stroke or aneurysm. To assist in peri-operative decision making as well as post-operative prognosis, automatic DSA analysis algorithms are being developed to obtain relevant image-based information. Such analyses include detection of vascular disease, evaluation of perfusion based on time intensity curves (TIC), and quantitative biomarker extraction for automated treatment evaluation in endovascular thrombectomy. Methodologically, such vessel-based analysis tasks may be facilitated by automatic and accurate artery-vein segmentation algorithms. The present work describes to the best of our knowledge the first study that addresses automatic artery-vein segmentation in DSA using deep learning. We propose a novel spatio-temporal U-Net (ST U-Net) architecture which integrates convolutional gated recurrent units (ConvGRU) in the contracting branch of U-Net. The network encodes a 2D+t DSA series of variable length and decodes it into a 2D segmentation image. On a multi-center routinely acquired dataset, the proposed method significantly outperformed U-Net (P<0.001) and traditional Frangi-based K-means clustering (P$<$0.001). Particularly in artery-vein segmentation, ST U-Net achieved a Dice coefficient of 0.794, surpassing the existing state-of-the-art methods by a margin of 12\%-20\%. Code will be made publicly available upon acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge