Tejaswi Kasarla
Action100M: A Large-scale Video Action Dataset
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Inferring physical actions from visual observations is a fundamental capability for advancing machine intelligence in the physical world. Achieving this requires large-scale, open-vocabulary video action datasets that span broad domains. We introduce Action100M, a large-scale dataset constructed from 1.2M Internet instructional videos (14.6 years of duration), yielding O(100 million) temporally localized segments with open-vocabulary action supervision and rich captions. Action100M is generated by a fully automated pipeline that (i) performs hierarchical temporal segmentation using V-JEPA 2 embeddings, (ii) produces multi-level frame and segment captions organized as a Tree-of-Captions, and (iii) aggregates evidence with a reasoning model (GPT-OSS-120B) under a multi-round Self-Refine procedure to output structured annotations (brief/detailed action, actor, brief/detailed caption). Training VL-JEPA on Action100M demonstrates consistent data-scaling improvements and strong zero-shot performance across diverse action recognition benchmarks, establishing Action100M as a new foundation for scalable research in video understanding and world modeling.
VL-JEPA: Joint Embedding Predictive Architecture for Vision-language
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:We introduce VL-JEPA, a vision-language model built on a Joint Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA). Instead of autoregressively generating tokens as in classical VLMs, VL-JEPA predicts continuous embeddings of the target texts. By learning in an abstract representation space, the model focuses on task-relevant semantics while abstracting away surface-level linguistic variability. In a strictly controlled comparison against standard token-space VLM training with the same vision encoder and training data, VL-JEPA achieves stronger performance while having 50% fewer trainable parameters. At inference time, a lightweight text decoder is invoked only when needed to translate VL-JEPA predicted embeddings into text. We show that VL-JEPA natively supports selective decoding that reduces the number of decoding operations by 2.85x while maintaining similar performance compared to non-adaptive uniform decoding. Beyond generation, the VL-JEPA's embedding space naturally supports open-vocabulary classification, text-to-video retrieval, and discriminative VQA without any architecture modification. On eight video classification and eight video retrieval datasets, the average performance VL-JEPA surpasses that of CLIP, SigLIP2, and Perception Encoder. At the same time, the model achieves comparable performance as classical VLMs (InstructBLIP, QwenVL) on four VQA datasets: GQA, TallyQA, POPE and POPEv2, despite only having 1.6B parameters.
Balanced Hyperbolic Embeddings Are Natural Out-of-Distribution Detectors
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Out-of-distribution recognition forms an important and well-studied problem in deep learning, with the goal to filter out samples that do not belong to the distribution on which a network has been trained. The conclusion of this paper is simple: a good hierarchical hyperbolic embedding is preferred for discriminating in- and out-of-distribution samples. We introduce Balanced Hyperbolic Learning. We outline a hyperbolic class embedding algorithm that jointly optimizes for hierarchical distortion and balancing between shallow and wide subhierarchies. We then use the class embeddings as hyperbolic prototypes for classification on in-distribution data. We outline how to generalize existing out-of-distribution scoring functions to operate with hyperbolic prototypes. Empirical evaluations across 13 datasets and 13 scoring functions show that our hyperbolic embeddings outperform existing out-of-distribution approaches when trained on the same data with the same backbones. We also show that our hyperbolic embeddings outperform other hyperbolic approaches, beat state-of-the-art contrastive methods, and natively enable hierarchical out-of-distribution generalization.
Hyperbolic Safety-Aware Vision-Language Models
Mar 15, 2025



Abstract:Addressing the retrieval of unsafe content from vision-language models such as CLIP is an important step towards real-world integration. Current efforts have relied on unlearning techniques that try to erase the model's knowledge of unsafe concepts. While effective in reducing unwanted outputs, unlearning limits the model's capacity to discern between safe and unsafe content. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that shifts from unlearning to an awareness paradigm by leveraging the inherent hierarchical properties of the hyperbolic space. We propose to encode safe and unsafe content as an entailment hierarchy, where both are placed in different regions of hyperbolic space. Our HySAC, Hyperbolic Safety-Aware CLIP, employs entailment loss functions to model the hierarchical and asymmetrical relations between safe and unsafe image-text pairs. This modelling, ineffective in standard vision-language models due to their reliance on Euclidean embeddings, endows the model with awareness of unsafe content, enabling it to serve as both a multimodal unsafe classifier and a flexible content retriever, with the option to dynamically redirect unsafe queries toward safer alternatives or retain the original output. Extensive experiments show that our approach not only enhances safety recognition but also establishes a more adaptable and interpretable framework for content moderation in vision-language models. Our source code is available at https://github.com/aimagelab/HySAC.
Maximally Separated Active Learning
Nov 26, 2024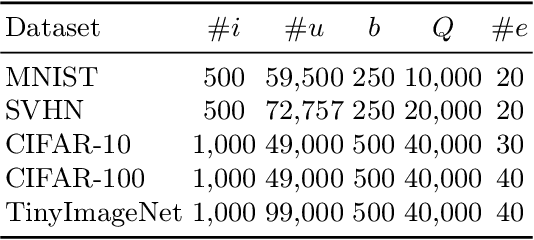
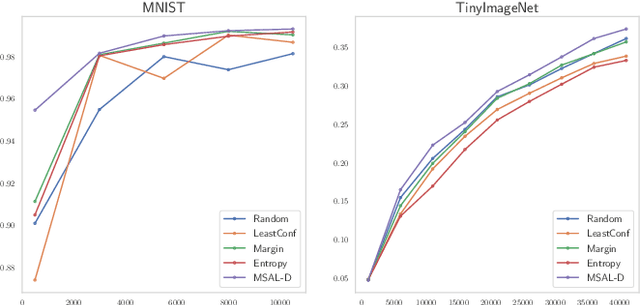
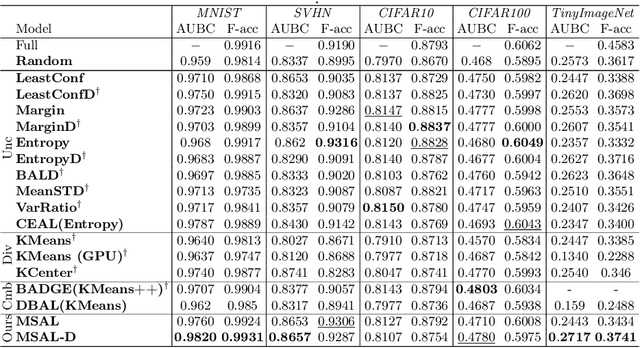
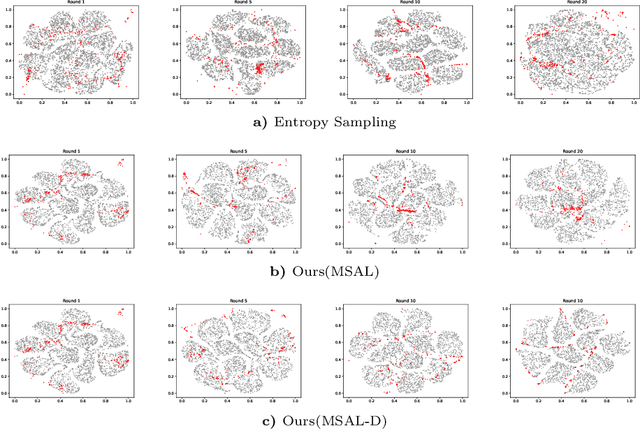
Abstract:Active Learning aims to optimize performance while minimizing annotation costs by selecting the most informative samples from an unlabelled pool. Traditional uncertainty sampling often leads to sampling bias by choosing similar uncertain samples. We propose an active learning method that utilizes fixed equiangular hyperspherical points as class prototypes, ensuring consistent inter-class separation and robust feature representations. Our approach introduces Maximally Separated Active Learning (MSAL) for uncertainty sampling and a combined strategy (MSAL-D) for incorporating diversity. This method eliminates the need for costly clustering steps, while maintaining diversity through hyperspherical uniformity. We demonstrate strong performance over existing active learning techniques across five benchmark datasets, highlighting the method's effectiveness and integration ease. The code is available on GitHub.
Lightweight Uncertainty Quantification with Simplex Semantic Segmentation for Terrain Traversability
Jul 18, 2024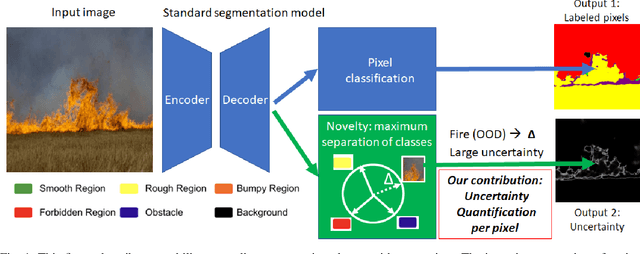
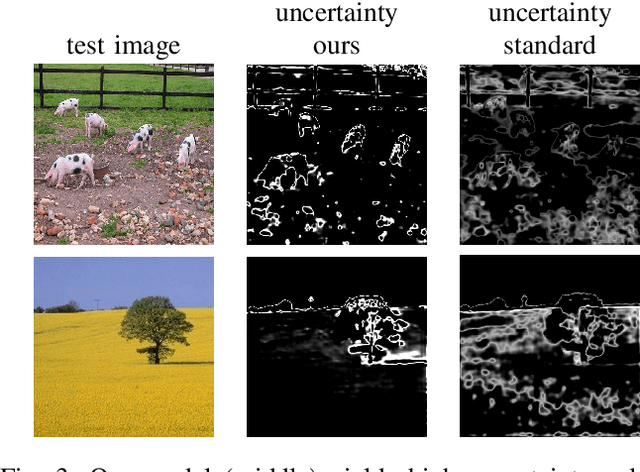
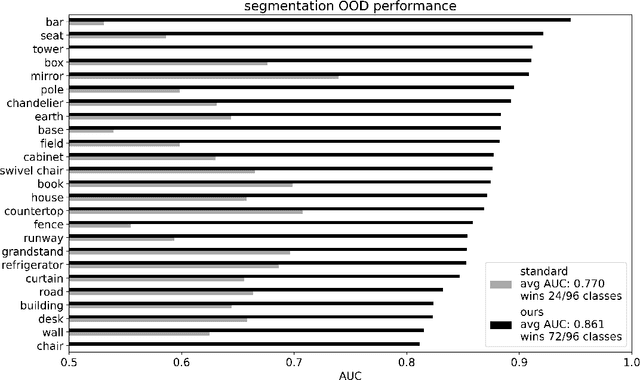

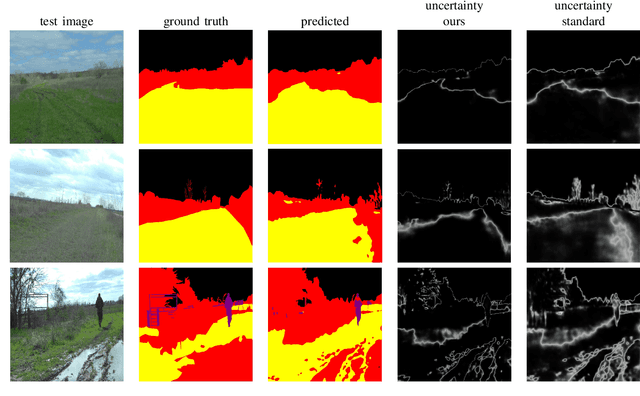
Abstract:For navigation of robots, image segmentation is an important component to determining a terrain's traversability. For safe and efficient navigation, it is key to assess the uncertainty of the predicted segments. Current uncertainty estimation methods are limited to a specific choice of model architecture, are costly in terms of training time, require large memory for inference (ensembles), or involve complex model architectures (energy-based, hyperbolic, masking). In this paper, we propose a simple, light-weight module that can be connected to any pretrained image segmentation model, regardless of its architecture, with marginal additional computation cost because it reuses the model's backbone. Our module is based on maximum separation of the segmentation classes by respective prototype vectors. This optimizes the probability that out-of-distribution segments are projected in between the prototype vectors. The uncertainty value in the classification label is obtained from the distance to the nearest prototype. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our module for terrain segmentation.
* 10 pages
WiCV 2022: The Tenth Women In Computer Vision Workshop
Aug 24, 2022

Abstract:In this paper, we present the details of Women in Computer Vision Workshop - WiCV 2022, organized alongside the hybrid CVPR 2022 in New Orleans, Louisiana. It provides a voice to a minority (female) group in the computer vision community and focuses on increasing the visibility of these researchers, both in academia and industry. WiCV believes that such an event can play an important role in lowering the gender imbalance in the field of computer vision. WiCV is organized each year where it provides a) opportunity for collaboration between researchers from minority groups, b) mentorship to female junior researchers, c) financial support to presenters to overcome monetary burden and d) large and diverse choice of role models, who can serve as examples to younger researchers at the beginning of their careers. In this paper, we present a report on the workshop program, trends over the past years, a summary of statistics regarding presenters, attendees, and sponsorship for the WiCV 2022 workshop.
Maximum Class Separation as Inductive Bias in One Matrix
Jun 17, 2022



Abstract:Maximizing the separation between classes constitutes a well-known inductive bias in machine learning and a pillar of many traditional algorithms. By default, deep networks are not equipped with this inductive bias and therefore many alternative solutions have been proposed through differential optimization. Current approaches tend to optimize classification and separation jointly: aligning inputs with class vectors and separating class vectors angularly. This paper proposes a simple alternative: encoding maximum separation as an inductive bias in the network by adding one fixed matrix multiplication before computing the softmax activations. The main observation behind our approach is that separation does not require optimization but can be solved in closed-form prior to training and plugged into a network. We outline a recursive approach to obtain the matrix consisting of maximally separable vectors for any number of classes, which can be added with negligible engineering effort and computational overhead. Despite its simple nature, this one matrix multiplication provides real impact. We show that our proposal directly boosts classification, long-tailed recognition, out-of-distribution detection, and open-set recognition, from CIFAR to ImageNet. We find empirically that maximum separation works best as a fixed bias; making the matrix learnable adds nothing to the performance. The closed-form implementation and code to reproduce the experiments are on github.
WiCV 2021: The Eighth Women In Computer Vision Workshop
Mar 11, 2022

Abstract:In this paper, we present the details of Women in Computer Vision Workshop - WiCV 2021, organized alongside the virtual CVPR 2021. It provides a voice to a minority (female) group in the computer vision community and focuses on increasing the visibility of these researchers, both in academia and industry. WiCV believes that such an event can play an important role in lowering the gender imbalance in the field of computer vision. WiCV is organized each year where it provides a)~opportunity for collaboration between researchers from minority groups, b)~mentorship to female junior researchers, c)~financial support to presenters to overcome monetary burden and d)~large and diverse choice of role models, who can serve as examples to younger researchers at the beginning of their careers. In this paper, we present a report on the workshop program, trends over the past years, a summary of statistics regarding presenters, attendees, and sponsorship for the WiCV 2021 workshop.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge