Ivaxi Sheth
PersistBench: When Should Long-Term Memories Be Forgotten by LLMs?
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Conversational assistants are increasingly integrating long-term memory with large language models (LLMs). This persistence of memories, e.g., the user is vegetarian, can enhance personalization in future conversations. However, the same persistence can also introduce safety risks that have been largely overlooked. Hence, we introduce PersistBench to measure the extent of these safety risks. We identify two long-term memory-specific risks: cross-domain leakage, where LLMs inappropriately inject context from the long-term memories; and memory-induced sycophancy, where stored long-term memories insidiously reinforce user biases. We evaluate 18 frontier and open-source LLMs on our benchmark. Our results reveal a surprisingly high failure rate across these LLMs - a median failure rate of 53% on cross-domain samples and 97% on sycophancy samples. To address this, our benchmark encourages the development of more robust and safer long-term memory usage in frontier conversational systems.
Funny or Persuasive, but Not Both: Evaluating Fine-Grained Multi-Concept Control in LLMs
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) offer strong generative capabilities, but many applications require explicit and \textit{fine-grained} control over specific textual concepts, such as humor, persuasiveness, or formality. Prior approaches in prompting and representation engineering can provide coarse or single-attribute control, but systematic evaluation of multi-attribute settings remains limited. We introduce an evaluation framework for fine-grained controllability for both single- and dual-concept scenarios, focusing on linguistically distinct concept pairs (e.g., persuasiveness vs.~humor). Surprisingly, across multiple LLMs and generative tasks, we find that performance often drops in the dual-concept setting, even though the chosen concepts should in principle be separable. This reveals a fundamental limitation of naive prompting-based control: models struggle with compositionality even when concepts are intuitively independent. Our framework provides systematic evidence of this gap and offers a principled approach for measuring the ability of future methods for multi-concept control.
ProtocolLLM: RTL Benchmark for SystemVerilog Generation of Communication Protocols
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promising capabilities in generating code for general-purpose programming languages. In contrast, their applicability for hardware description languages, particularly for generating synthesizable and functionally correct designs, remains significantly underexplored. HDLs such as SystemVerilog are logic-oriented and demand strict adherence to timing semantics, concurrency, and synthesizability constraints. Moreover, HDL-based design flows encompass a broad set of tasks beyond structural code generation, including testbench development, assertion-based verification, timing closure, and protocol-level integration for on-chip communication. The objective of our paper is to analyze the capabilities of state-of-the-art LLMs in generating SystemVerilog implementations of standard communication protocols, a core component of embedded and System-on-Chip (SoC) architectures. This paper introduces the first benchmark suite targeting four widely used protocols: SPI, I2C, UART, and AXI. We define code generation tasks that capture varying levels of design abstraction and prompt specificity. The generated designs are assessed for syntactic correctness, synthesizability, and functional fidelity via waveform simulation and test benches.
Causality Is Key to Understand and Balance Multiple Goals in Trustworthy ML and Foundation Models
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Ensuring trustworthiness in machine learning (ML) systems is crucial as they become increasingly embedded in high-stakes domains. This paper advocates for the integration of causal methods into machine learning to navigate the trade-offs among key principles of trustworthy ML, including fairness, privacy, robustness, accuracy, and explainability. While these objectives should ideally be satisfied simultaneously, they are often addressed in isolation, leading to conflicts and suboptimal solutions. Drawing on existing applications of causality in ML that successfully align goals such as fairness and accuracy or privacy and robustness, this paper argues that a causal approach is essential for balancing multiple competing objectives in both trustworthy ML and foundation models. Beyond highlighting these trade-offs, we examine how causality can be practically integrated into ML and foundation models, offering solutions to enhance their reliability and interpretability. Finally, we discuss the challenges, limitations, and opportunities in adopting causal frameworks, paving the way for more accountable and ethically sound AI systems.
Safety is Essential for Responsible Open-Ended Systems
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:AI advancements have been significantly driven by a combination of foundation models and curiosity-driven learning aimed at increasing capability and adaptability. A growing area of interest within this field is Open-Endedness - the ability of AI systems to continuously and autonomously generate novel and diverse artifacts or solutions. This has become relevant for accelerating scientific discovery and enabling continual adaptation in AI agents. This position paper argues that the inherently dynamic and self-propagating nature of Open-Ended AI introduces significant, underexplored risks, including challenges in maintaining alignment, predictability, and control. This paper systematically examines these challenges, proposes mitigation strategies, and calls for action for different stakeholders to support the safe, responsible and successful development of Open-Ended AI.
MedG-KRP: Medical Graph Knowledge Representation Probing
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently emerged as powerful tools, finding many medical applications. LLMs' ability to coalesce vast amounts of information from many sources to generate a response-a process similar to that of a human expert-has led many to see potential in deploying LLMs for clinical use. However, medicine is a setting where accurate reasoning is paramount. Many researchers are questioning the effectiveness of multiple choice question answering (MCQA) benchmarks, frequently used to test LLMs. Researchers and clinicians alike must have complete confidence in LLMs' abilities for them to be deployed in a medical setting. To address this need for understanding, we introduce a knowledge graph (KG)-based method to evaluate the biomedical reasoning abilities of LLMs. Essentially, we map how LLMs link medical concepts in order to better understand how they reason. We test GPT-4, Llama3-70b, and PalmyraMed-70b, a specialized medical model. We enlist a panel of medical students to review a total of 60 LLM-generated graphs and compare these graphs to BIOS, a large biomedical KG. We observe GPT-4 to perform best in our human review but worst in our ground truth comparison; vice-versa with PalmyraMed, the medical model. Our work provides a means of visualizing the medical reasoning pathways of LLMs so they can be implemented in clinical settings safely and effectively.
CausalGraph2LLM: Evaluating LLMs for Causal Queries
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Causality is essential in scientific research, enabling researchers to interpret true relationships between variables. These causal relationships are often represented by causal graphs, which are directed acyclic graphs. With the recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), there is an increasing interest in exploring their capabilities in causal reasoning and their potential use to hypothesize causal graphs. These tasks necessitate the LLMs to encode the causal graph effectively for subsequent downstream tasks. In this paper, we propose a comprehensive benchmark, \emph{CausalGraph2LLM}, encompassing a variety of causal graph settings to assess the causal graph understanding capability of LLMs. We categorize the causal queries into two types: graph-level and node-level queries. We benchmark both open-sourced and closed models for our study. Our findings reveal that while LLMs show promise in this domain, they are highly sensitive to the encoding used. Even capable models like GPT-4 and Gemini-1.5 exhibit sensitivity to encoding, with deviations of about $60\%$. We further demonstrate this sensitivity for downstream causal intervention tasks. Moreover, we observe that LLMs can often display biases when presented with contextual information about a causal graph, potentially stemming from their parametric memory.
LLM4GRN: Discovering Causal Gene Regulatory Networks with LLMs -- Evaluation through Synthetic Data Generation
Oct 21, 2024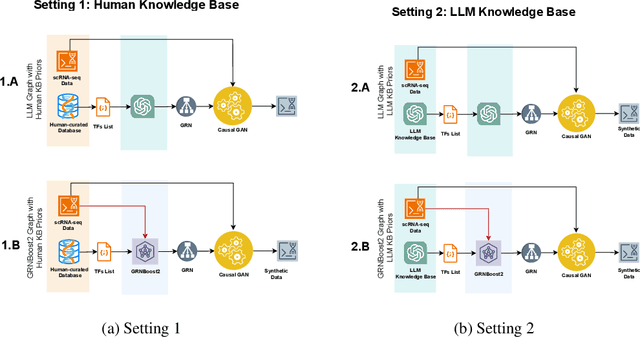



Abstract:Gene regulatory networks (GRNs) represent the causal relationships between transcription factors (TFs) and target genes in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data. Understanding these networks is crucial for uncovering disease mechanisms and identifying therapeutic targets. In this work, we investigate the potential of large language models (LLMs) for GRN discovery, leveraging their learned biological knowledge alone or in combination with traditional statistical methods. We develop a task-based evaluation strategy to address the challenge of unavailable ground truth causal graphs. Specifically, we use the GRNs suggested by LLMs to guide causal synthetic data generation and compare the resulting data against the original dataset. Our statistical and biological assessments show that LLMs can support statistical modeling and data synthesis for biological research.
Hypothesizing Missing Causal Variables with LLMs
Sep 04, 2024Abstract:Scientific discovery is a catalyst for human intellectual advances, driven by the cycle of hypothesis generation, experimental design, data evaluation, and iterative assumption refinement. This process, while crucial, is expensive and heavily dependent on the domain knowledge of scientists to generate hypotheses and navigate the scientific cycle. Central to this is causality, the ability to establish the relationship between the cause and the effect. Motivated by the scientific discovery process, in this work, we formulate a novel task where the input is a partial causal graph with missing variables, and the output is a hypothesis about the missing variables to complete the partial graph. We design a benchmark with varying difficulty levels and knowledge assumptions about the causal graph. With the growing interest in using Large Language Models (LLMs) to assist in scientific discovery, we benchmark open-source and closed models on our testbed. We show the strong ability of LLMs to hypothesize the mediation variables between a cause and its effect. In contrast, they underperform in hypothesizing the cause and effect variables themselves. We also observe surprising results where some of the open-source models outperform the closed GPT-4 model.
LLM Task Interference: An Initial Study on the Impact of Task-Switch in Conversational History
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:With the recent emergence of powerful instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs), various helpful conversational Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems have been deployed across many applications. When prompted by users, these AI systems successfully perform a wide range of tasks as part of a conversation. To provide some sort of memory and context, such approaches typically condition their output on the entire conversational history. Although this sensitivity to the conversational history can often lead to improved performance on subsequent tasks, we find that performance can in fact also be negatively impacted, if there is a task-switch. To the best of our knowledge, our work makes the first attempt to formalize the study of such vulnerabilities and interference of tasks in conversational LLMs caused by task-switches in the conversational history. Our experiments across 5 datasets with 15 task switches using popular LLMs reveal that many of the task-switches can lead to significant performance degradation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge