Takayuki Okatani
CoReTab: Improving Multimodal Table Understanding with Code-driven Reasoning
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Existing datasets for multimodal table understanding, such as MMTab, primarily provide short factual answers without explicit multi-step reasoning supervision. Models trained on these datasets often generate brief responses that offers insufficient accuracy and limited interpretability into how these models arrive at the final answer. We introduce CoReTab, a code-driven reasoning framework that produces scalable, interpretable, and automatically verifiable annotations by coupling multi-step reasoning with executable Python code. Using the CoReTab framework, we curate a dataset of 115K verified samples averaging 529 tokens per response and fine-tune open-source MLLMs through a three-stage pipeline. We evaluate the resulting model trained on CoReTab across 17 MMTab benchmarks spanning table question answering, fact verification, and table structure understanding. Our model achieves significant gains of +6.2%, +5.7%, and +25.6%, respectively, over MMTab-trained baselines, while producing transparent and verifiable reasoning traces. These results establish CoReTab as a robust and generalizable supervision framework for improving multi-step reasoning in multimodal table understanding.
LAMS-Edit: Latent and Attention Mixing with Schedulers for Improved Content Preservation in Diffusion-Based Image and Style Editing
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Text-to-Image editing using diffusion models faces challenges in balancing content preservation with edit application and handling real-image editing. To address these, we propose LAMS-Edit, leveraging intermediate states from the inversion process--an essential step in real-image editing--during edited image generation. Specifically, latent representations and attention maps from both processes are combined at each step using weighted interpolation, controlled by a scheduler. This technique, Latent and Attention Mixing with Schedulers (LAMS), integrates with Prompt-to-Prompt (P2P) to form LAMS-Edit--an extensible framework that supports precise editing with region masks and enables style transfer via LoRA. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LAMS-Edit effectively balances content preservation and edit application.
MS-DPPs: Multi-Source Determinantal Point Processes for Contextual Diversity Refinement of Composite Attributes in Text to Image Retrieval
Jul 09, 2025
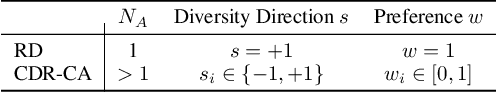
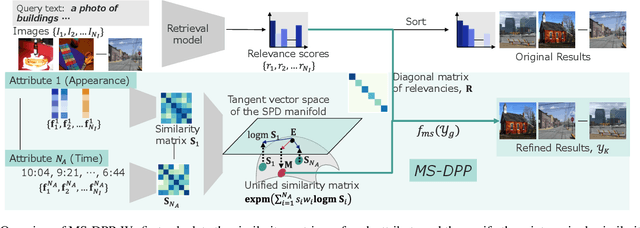
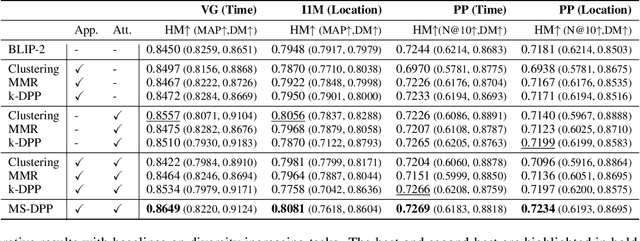
Abstract:Result diversification (RD) is a crucial technique in Text-to-Image Retrieval for enhancing the efficiency of a practical application. Conventional methods focus solely on increasing the diversity metric of image appearances. However, the diversity metric and its desired value vary depending on the application, which limits the applications of RD. This paper proposes a novel task called CDR-CA (Contextual Diversity Refinement of Composite Attributes). CDR-CA aims to refine the diversities of multiple attributes, according to the application's context. To address this task, we propose Multi-Source DPPs, a simple yet strong baseline that extends the Determinantal Point Process (DPP) to multi-sources. We model MS-DPP as a single DPP model with a unified similarity matrix based on a manifold representation. We also introduce Tangent Normalization to reflect contexts. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/NEC-N-SOGI/msdpp.
TB-Bench: Training and Testing Multi-Modal AI for Understanding Spatio-Temporal Traffic Behaviors from Dashcam Images/Videos
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:The application of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in Autonomous Driving (AD) faces significant challenges due to their limited training on traffic-specific data and the absence of dedicated benchmarks for spatiotemporal understanding. This study addresses these issues by proposing TB-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate MLLMs on understanding traffic behaviors across eight perception tasks from ego-centric views. We also introduce vision-language instruction tuning datasets, TB-100k and TB-250k, along with simple yet effective baselines for the tasks. Through extensive experiments, we show that existing MLLMs underperform in these tasks, with even a powerful model like GPT-4o achieving less than 35% accuracy on average. In contrast, when fine-tuned with TB-100k or TB-250k, our baseline models achieve average accuracy up to 85%, significantly enhancing performance on the tasks. Additionally, we demonstrate performance transfer by co-training TB-100k with another traffic dataset, leading to improved performance on the latter. Overall, this study represents a step forward by introducing a comprehensive benchmark, high-quality datasets, and baselines, thus supporting the gradual integration of MLLMs into the perception, prediction, and planning stages of AD.
Action-Agnostic Point-Level Supervision for Temporal Action Detection
Dec 30, 2024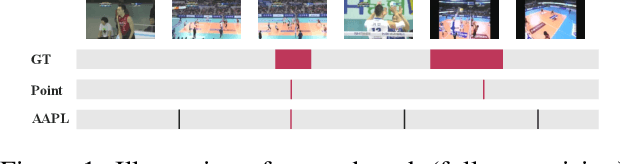
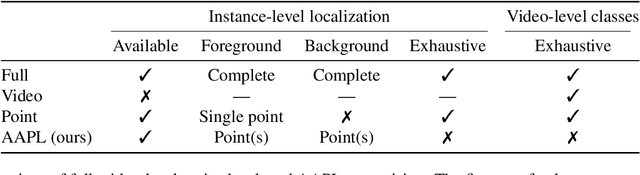
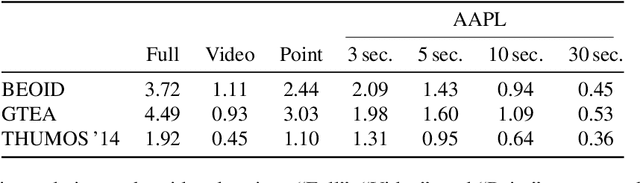
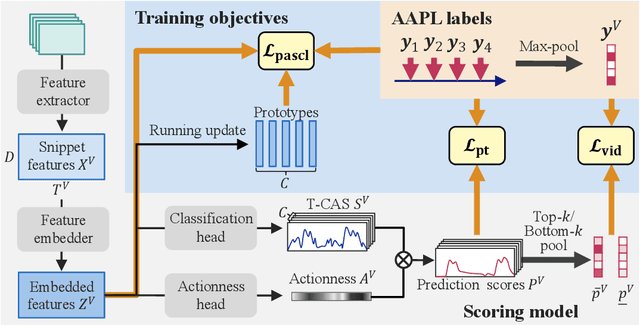
Abstract:We propose action-agnostic point-level (AAPL) supervision for temporal action detection to achieve accurate action instance detection with a lightly annotated dataset. In the proposed scheme, a small portion of video frames is sampled in an unsupervised manner and presented to human annotators, who then label the frames with action categories. Unlike point-level supervision, which requires annotators to search for every action instance in an untrimmed video, frames to annotate are selected without human intervention in AAPL supervision. We also propose a detection model and learning method to effectively utilize the AAPL labels. Extensive experiments on the variety of datasets (THUMOS '14, FineAction, GTEA, BEOID, and ActivityNet 1.3) demonstrate that the proposed approach is competitive with or outperforms prior methods for video-level and point-level supervision in terms of the trade-off between the annotation cost and detection performance.
RP-SLAM: Real-time Photorealistic SLAM with Efficient 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 13, 2024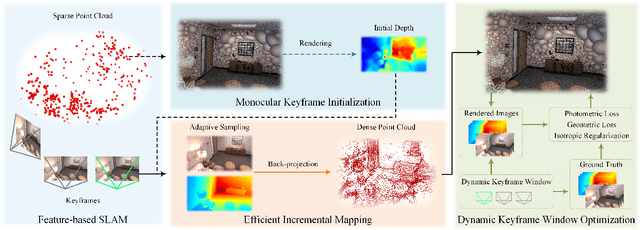

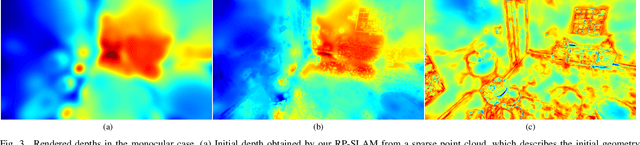

Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting has emerged as a promising technique for high-quality 3D rendering, leading to increasing interest in integrating 3DGS into realism SLAM systems. However, existing methods face challenges such as Gaussian primitives redundancy, forgetting problem during continuous optimization, and difficulty in initializing primitives in monocular case due to lack of depth information. In order to achieve efficient and photorealistic mapping, we propose RP-SLAM, a 3D Gaussian splatting-based vision SLAM method for monocular and RGB-D cameras. RP-SLAM decouples camera poses estimation from Gaussian primitives optimization and consists of three key components. Firstly, we propose an efficient incremental mapping approach to achieve a compact and accurate representation of the scene through adaptive sampling and Gaussian primitives filtering. Secondly, a dynamic window optimization method is proposed to mitigate the forgetting problem and improve map consistency. Finally, for the monocular case, a monocular keyframe initialization method based on sparse point cloud is proposed to improve the initialization accuracy of Gaussian primitives, which provides a geometric basis for subsequent optimization. The results of numerous experiments demonstrate that RP-SLAM achieves state-of-the-art map rendering accuracy while ensuring real-time performance and model compactness.
Rethinking Annotation for Object Detection: Is Annotating Small-size Instances Worth Its Cost?
Dec 07, 2024Abstract:Detecting objects occupying only small areas in an image is difficult, even for humans. Therefore, annotating small-size object instances is hard and thus costly. This study questions common sense by asking the following: is annotating small-size instances worth its cost? We restate it as the following verifiable question: can we detect small-size instances with a detector trained using training data free of small-size instances? We evaluate a method that upscales input images at test time and a method that downscales images at training time. The experiments conducted using the COCO dataset show the following. The first method, together with a remedy to narrow the domain gap between training and test inputs, achieves at least comparable performance to the baseline detector trained using complete training data. Although the method needs to apply the same detector twice to an input image with different scaling, we show that its distillation yields a single-path detector that performs equally well to the same baseline detector. These results point to the necessity of rethinking the annotation of training data for object detection.
Cascaded Multi-Scale Attention for Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Extraction and Interaction with Low-Resolution Images
Dec 03, 2024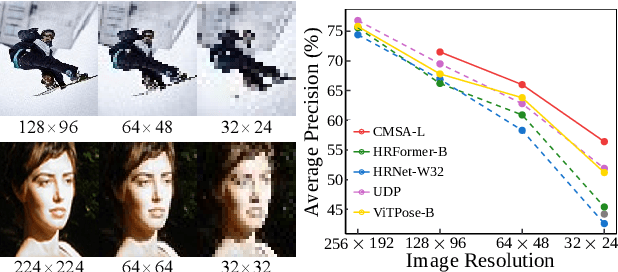
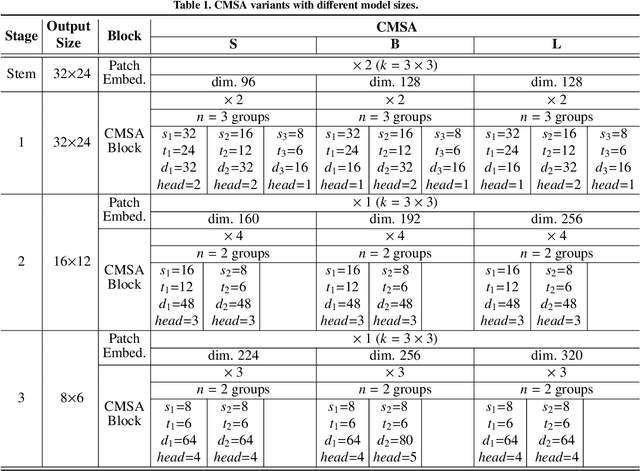
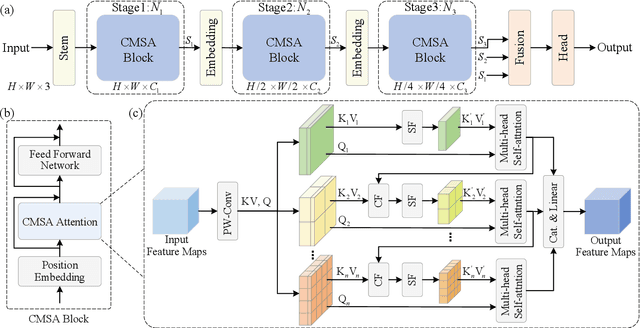
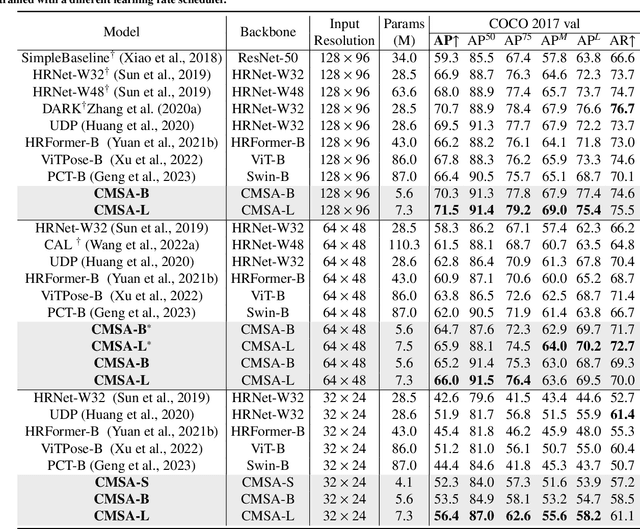
Abstract:In real-world applications of image recognition tasks, such as human pose estimation, cameras often capture objects, like human bodies, at low resolutions. This scenario poses a challenge in extracting and leveraging multi-scale features, which is often essential for precise inference. To address this challenge, we propose a new attention mechanism, named cascaded multi-scale attention (CMSA), tailored for use in CNN-ViT hybrid architectures, to handle low-resolution inputs effectively. The design of CMSA enables the extraction and seamless integration of features across various scales without necessitating the downsampling of the input image or feature maps. This is achieved through a novel combination of grouped multi-head self-attention mechanisms with window-based local attention and cascaded fusion of multi-scale features over different scales. This architecture allows for the effective handling of features across different scales, enhancing the model's ability to perform tasks such as human pose estimation, head pose estimation, and more with low-resolution images. Our experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in these areas with fewer parameters, showcasing its potential for broad application in real-world scenarios where capturing high-resolution images is not feasible. Code is available at https://github.com/xyongLu/CMSA.
Bi-Band ECoGNet for ECoG Decoding on Classification Task
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:In the application of brain-computer interface (BCI), being able to accurately decode brain signals is a critical task. For the multi-class classification task of brain signal ECoG, how to improve the classification accuracy is one of the current research hotspots. ECoG acquisition uses a high-density electrode array and a high sampling frequency, which makes ECoG data have a certain high similarity and data redundancy in the temporal domain, and also unique spatial pattern in spatial domain. How to effectively extract features is both exciting and challenging. Previous work found that visual-related ECoG can carry visual information via frequency and spatial domain. Based on this finding, we focused on using deep learning to design frequency and spatial feature extraction modules, and proposed a Bi-Band ECoGNet model based on deep learning. The main contributions of this paper are: 1) The Bi-BCWT (Bi-Band Channel-Wise Transform) neural network module is designed to replace the time-consume method MST, this module greatly improves the model calculation and data storage efficiency, and effectively increases the training speed; 2) The Bi-BCWT module can effectively take into account the information both in low-frequency and high-frequency domain, which is more conducive to ECoG multi-classification tasks; 3) ECoG is acquired using 2D electrode array, the newly designed 2D Spatial-Temporal feature encoder can extract the 2D spatial feature better. Experiments have shown that the unique 2D spatial data structure can effectively improve classification accuracy; 3) Compared with previous work, the Bi-Band ECoGNet model is smaller and has higher performance, with an accuracy increase of 1.24%, and the model training speed is increased by 6 times, which is more suitable for BCI applications.
Open-vocabulary vs. Closed-set: Best Practice for Few-shot Object Detection Considering Text Describability
Oct 20, 2024
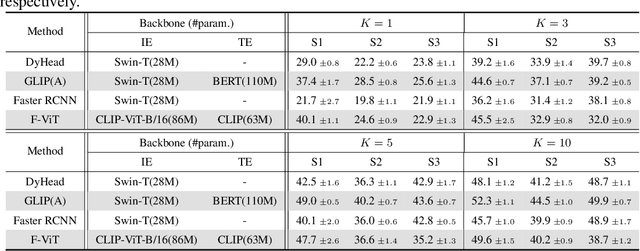
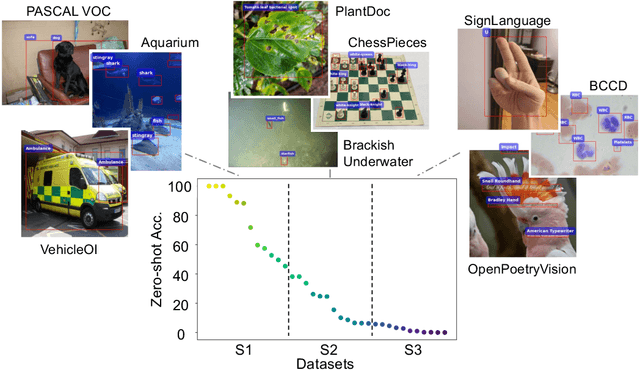
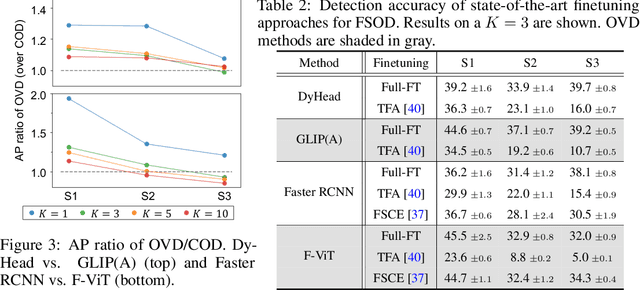
Abstract:Open-vocabulary object detection (OVD), detecting specific classes of objects using only their linguistic descriptions (e.g., class names) without any image samples, has garnered significant attention. However, in real-world applications, the target class concepts is often hard to describe in text and the only way to specify target objects is to provide their image examples, yet it is often challenging to obtain a good number of samples. Thus, there is a high demand from practitioners for few-shot object detection (FSOD). A natural question arises: Can the benefits of OVD extend to FSOD for object classes that are difficult to describe in text? Compared to traditional methods that learn only predefined classes (referred to in this paper as closed-set object detection, COD), can the extra cost of OVD be justified? To answer these questions, we propose a method to quantify the ``text-describability'' of object detection datasets using the zero-shot image classification accuracy with CLIP. This allows us to categorize various OD datasets with different text-describability and emprically evaluate the FSOD performance of OVD and COD methods within each category. Our findings reveal that: i) there is little difference between OVD and COD for object classes with low text-describability under equal conditions in OD pretraining; and ii) although OVD can learn from more diverse data than OD-specific data, thereby increasing the volume of training data, it can be counterproductive for classes with low-text-describability. These findings provide practitioners with valuable guidance amidst the recent advancements of OVD methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge