Simon Clematide
Information Representation Fairness in Long-Document Embeddings: The Peculiar Interaction of Positional and Language Bias
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:To be discoverable in an embedding-based search process, each part of a document should be reflected in its embedding representation. To quantify any potential reflection biases, we introduce a permutation-based evaluation framework. With this, we observe that state-of-the-art embedding models exhibit systematic positional and language biases when documents are longer and consist of multiple segments. Specifically, early segments and segments in higher-resource languages like English are over-represented, while later segments and segments in lower-resource languages are marginalized. In our further analysis, we find that the positional bias stems from front-loaded attention distributions in pooling-token embeddings, where early tokens receive more attention. To mitigate this issue, we introduce an inference-time attention calibration method that redistributes attention more evenly across document positions, increasing discoverabiltiy of later segments. Our evaluation framework and attention calibration is available at https://github.com/impresso/fair-sentence-transformers
Interpretable Text Embeddings and Text Similarity Explanation: A Primer
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Text embeddings and text embedding models are a backbone of many AI and NLP systems, particularly those involving search. However, interpretability challenges persist, especially in explaining obtained similarity scores, which is crucial for applications requiring transparency. In this paper, we give a structured overview of interpretability methods specializing in explaining those similarity scores, an emerging research area. We study the methods' individual ideas and techniques, evaluating their potential for improving interpretability of text embeddings and explaining predicted similarities.
Sentence Smith: Formally Controllable Text Transformation and its Application to Evaluation of Text Embedding Models
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:We propose the Sentence Smith framework that enables controlled and specified manipulation of text meaning. It consists of three main steps: 1. Parsing a sentence into a semantic graph, 2. Applying human-designed semantic manipulation rules, and 3. Generating text from the manipulated graph. A final filtering step (4.) ensures the validity of the applied transformation. To demonstrate the utility of Sentence Smith in an application study, we use it to generate hard negative pairs that challenge text embedding models. Since the controllable generation makes it possible to clearly isolate different types of semantic shifts, we can gain deeper insights into the specific strengths and weaknesses of widely used text embedding models, also addressing an issue in current benchmarking where linguistic phenomena remain opaque. Human validation confirms that the generations produced by Sentence Smith are highly accurate.
MMTEB: Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Text embeddings are typically evaluated on a limited set of tasks, which are constrained by language, domain, and task diversity. To address these limitations and provide a more comprehensive evaluation, we introduce the Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark (MMTEB) - a large-scale, community-driven expansion of MTEB, covering over 500 quality-controlled evaluation tasks across 250+ languages. MMTEB includes a diverse set of challenging, novel tasks such as instruction following, long-document retrieval, and code retrieval, representing the largest multilingual collection of evaluation tasks for embedding models to date. Using this collection, we develop several highly multilingual benchmarks, which we use to evaluate a representative set of models. We find that while large language models (LLMs) with billions of parameters can achieve state-of-the-art performance on certain language subsets and task categories, the best-performing publicly available model is multilingual-e5-large-instruct with only 560 million parameters. To facilitate accessibility and reduce computational cost, we introduce a novel downsampling method based on inter-task correlation, ensuring a diverse selection while preserving relative model rankings. Furthermore, we optimize tasks such as retrieval by sampling hard negatives, creating smaller but effective splits. These optimizations allow us to introduce benchmarks that drastically reduce computational demands. For instance, our newly introduced zero-shot English benchmark maintains a ranking order similar to the full-scale version but at a fraction of the computational cost.
Examining Multilingual Embedding Models Cross-Lingually Through LLM-Generated Adversarial Examples
Feb 12, 2025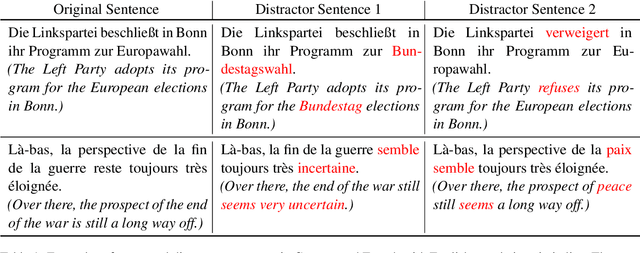
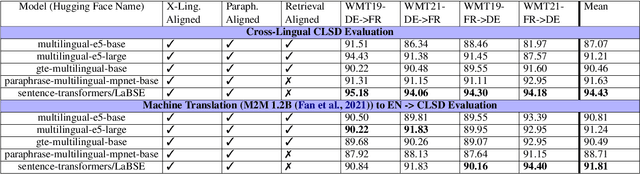
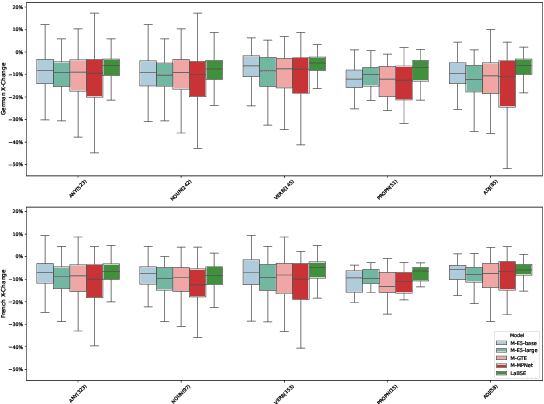

Abstract:The evaluation of cross-lingual semantic search capabilities of models is often limited to existing datasets from tasks such as information retrieval and semantic textual similarity. To allow for domain-specific evaluation, we introduce Cross Lingual Semantic Discrimination (CLSD), a novel cross-lingual semantic search task that requires only a set of parallel sentence pairs of the language pair of interest within the target domain. This task focuses on the ability of a model to cross-lingually rank the true parallel sentence higher than hard negatives generated by a large language model. We create four instances of our introduced CLSD task for the language pair German-French within the domain of news. Within this case study, we find that models that are also fine-tuned for retrieval tasks (e.g., multilingual E5) benefit from using English as the pivot language, while bitext mining models such as LaBSE perform best directly cross-lingually. We also show a fine-grained similarity analysis enabled by our distractor generation strategy, indicating that different embedding models are sensitive to different types of perturbations.
Adapting Multilingual Embedding Models to Historical Luxembourgish
Feb 11, 2025


Abstract:The growing volume of digitized historical texts requires effective semantic search using text embeddings. However, pre-trained multilingual models, typically evaluated on contemporary texts, face challenges with historical digitized content due to OCR noise and outdated spellings. We explore the use of multilingual embeddings for cross-lingual semantic search on historical Luxembourgish, a low-resource language. We collect historical Luxembourgish news articles spanning various time periods and use GPT-4o to segment and translate them into closely related languages, creating 20,000 parallel training sentences per language pair. We further create a historical bitext mining evaluation set and find that these models struggle to perform cross-lingual search on historical Luxembourgish. To address this, we propose a simple adaptation method using in-domain training data, achieving up to 98\% accuracy in cross-lingual evaluations. We release our adapted models and historical Luxembourgish-German/French bitexts to support further research.
PARAPHRASUS : A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Paraphrase Detection Models
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:The task of determining whether two texts are paraphrases has long been a challenge in NLP. However, the prevailing notion of paraphrase is often quite simplistic, offering only a limited view of the vast spectrum of paraphrase phenomena. Indeed, we find that evaluating models in a paraphrase dataset can leave uncertainty about their true semantic understanding. To alleviate this, we release paraphrasus, a benchmark designed for multi-dimensional assessment of paraphrase detection models and finer model selection. We find that paraphrase detection models under a fine-grained evaluation lens exhibit trade-offs that cannot be captured through a single classification dataset.
Automatic Generation and Evaluation of Reading Comprehension Test Items with Large Language Models
Apr 11, 2024


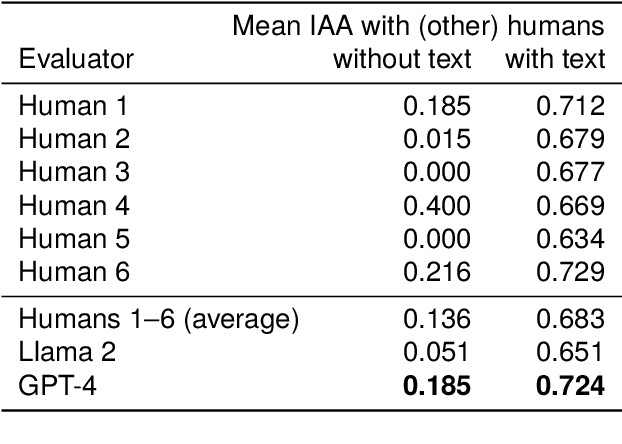
Abstract:Reading comprehension tests are used in a variety of applications, reaching from education to assessing the comprehensibility of simplified texts. However, creating such tests manually and ensuring their quality is difficult and time-consuming. In this paper, we explore how large language models (LLMs) can be used to generate and evaluate multiple-choice reading comprehension items. To this end, we compiled a dataset of German reading comprehension items and developed a new protocol for human and automatic evaluation, including a metric we call text informativity, which is based on guessability and answerability. We then used this protocol and the dataset to evaluate the quality of items generated by Llama 2 and GPT-4. Our results suggest that both models are capable of generating items of acceptable quality in a zero-shot setting, but GPT-4 clearly outperforms Llama 2. We also show that LLMs can be used for automatic evaluation by eliciting item reponses from them. In this scenario, evaluation results with GPT-4 were the most similar to human annotators. Overall, zero-shot generation with LLMs is a promising approach for generating and evaluating reading comprehension test items, in particular for languages without large amounts of available data.
UZH_CLyp at SemEval-2023 Task 9: Head-First Fine-Tuning and ChatGPT Data Generation for Cross-Lingual Learning in Tweet Intimacy Prediction
Mar 02, 2023



Abstract:This paper describes the submission of UZH_CLyp for the SemEval 2023 Task 9 "Multilingual Tweet Intimacy Analysis". We achieved second-best results in all 10 languages according to the official Pearson's correlation regression evaluation measure. Our cross-lingual transfer learning approach explores the benefits of using a Head-First Fine-Tuning method (HeFiT) that first updates only the regression head parameters and then also updates the pre-trained transformer encoder parameters at a reduced learning rate. Additionally, we study the impact of using a small set of automatically generated examples (in our case, from ChatGPT) for low-resource settings where no human-labeled data is available. Our study shows that HeFiT stabilizes training and consistently improves results for pre-trained models that lack domain adaptation to tweets. Our study also shows a noticeable performance increase in cross-lingual learning when synthetic data is used, confirming the usefulness of current text generation systems to improve zero-shot baseline results. Finally, we examine how possible inconsistencies in the annotated data contribute to cross-lingual interference issues.
Transformer-based HTR for Historical Documents
Mar 21, 2022
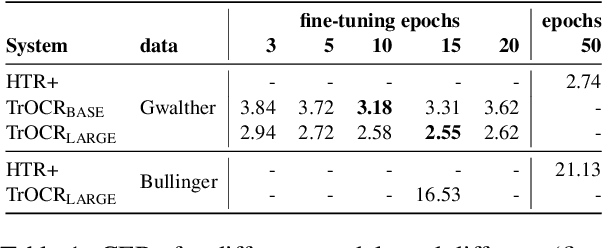
Abstract:We apply the TrOCR framework to real-world, historical manuscripts and show that TrOCR per se is a strong model, ideal for transfer learning. TrOCR has been trained on English only, but it can adapt to other languages that use the Latin alphabet fairly easily and with little training material. We compare TrOCR against a SOTA HTR framework (Transkribus) and show that it can beat such systems. This finding is essential since Transkribus performs best when it has access to baseline information, which is not needed at all to fine-tune TrOCR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge