Shiv Gehlot
Parametric Shadow Control for Portrait Generationin Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models excel at generating diverse portraits, but lack intuitive shadow control. Existing editing approaches, as post-processing, struggle to offer effective manipulation across diverse styles. Additionally, these methods either rely on expensive real-world light-stage data collection or require extensive computational resources for training. To address these limitations, we introduce Shadow Director, a method that extracts and manipulates hidden shadow attributes within well-trained diffusion models. Our approach uses a small estimation network that requires only a few thousand synthetic images and hours of training-no costly real-world light-stage data needed. Shadow Director enables parametric and intuitive control over shadow shape, placement, and intensity during portrait generation while preserving artistic integrity and identity across diverse styles. Despite training only on synthetic data built on real-world identities, it generalizes effectively to generated portraits with diverse styles, making it a more accessible and resource-friendly solution.
Standardizing Generative Face Video Compression using Supplemental Enhancement Information
Oct 19, 2024Abstract:This paper proposes a Generative Face Video Compression (GFVC) approach using Supplemental Enhancement Information (SEI), where a series of compact spatial and temporal representations of a face video signal (i.e., 2D/3D key-points, facial semantics and compact features) can be coded using SEI message and inserted into the coded video bitstream. At the time of writing, the proposed GFVC approach is an official "technology under consideration" (TuC) for standardization by the Joint Video Experts Team (JVET) of ISO/IEC JVT 1/SC 29 and ITU-T SG16. To the best of the authors' knowledge, the JVET work on the proposed SEI-based GFVC approach is the first standardization activity for generative video compression. The proposed SEI approach has not only advanced the reconstruction quality of early-day Model-Based Coding (MBC) via the state-of-the-art generative technique, but also established a new SEI definition for future GFVC applications and deployment. Experimental results illustrate that the proposed SEI-based GFVC approach can achieve remarkable rate-distortion performance compared with the latest Versatile Video Coding (VVC) standard, whilst also potentially enabling a wide variety of functionalities including user-specified animation/filtering and metaverse-related applications.
FUSION: Fully Unsupervised Test-Time Stain Adaptation via Fused Normalization Statistics
Aug 30, 2022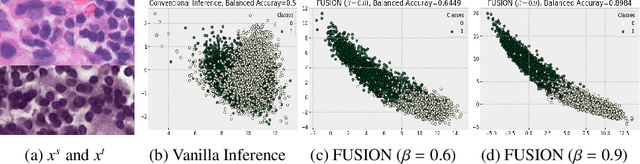
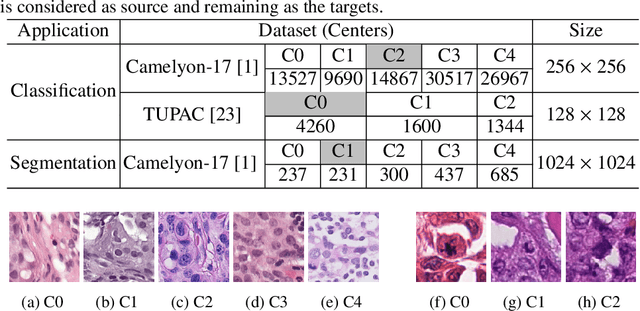
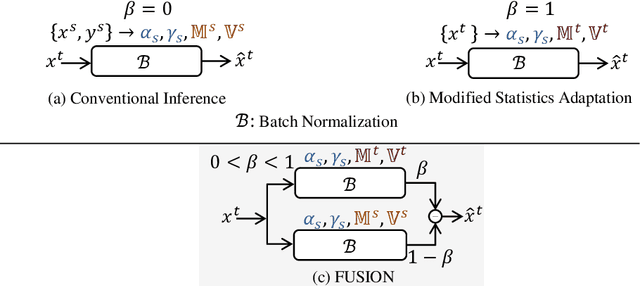
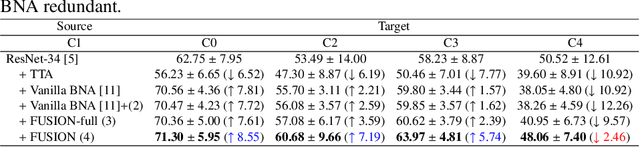
Abstract:Staining reveals the micro structure of the aspirate while creating histopathology slides. Stain variation, defined as a chromatic difference between the source and the target, is caused by varying characteristics during staining, resulting in a distribution shift and poor performance on the target. The goal of stain normalization is to match the target's chromatic distribution to that of the source. However, stain normalisation causes the underlying morphology to distort, resulting in an incorrect diagnosis. We propose FUSION, a new method for promoting stain-adaption by adjusting the model to the target in an unsupervised test-time scenario, eliminating the necessity for significant labelling at the target end. FUSION works by altering the target's batch normalization statistics and fusing them with source statistics using a weighting factor. The algorithm reduces to one of two extremes based on the weighting factor. Despite the lack of training or supervision, FUSION surpasses existing equivalent algorithms for classification and dense predictions (segmentation), as demonstrated by comprehensive experiments on two public datasets.
Seeking an Optimal Approach for Computer-Aided Pulmonary Embolism Detection
Sep 15, 2021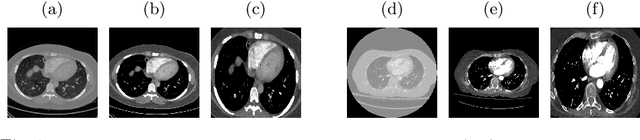
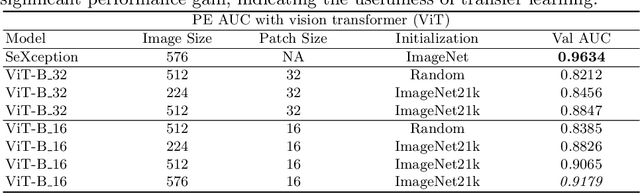
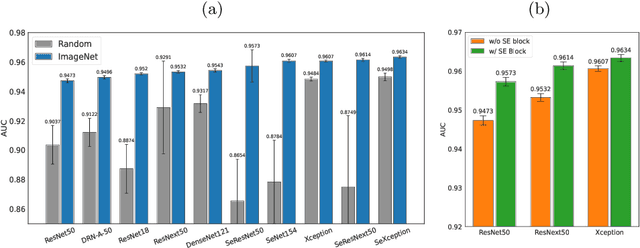

Abstract:Pulmonary embolism (PE) represents a thrombus ("blood clot"), usually originating from a lower extremity vein, that travels to the blood vessels in the lung, causing vascular obstruction and in some patients, death. This disorder is commonly diagnosed using CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA). Deep learning holds great promise for the computer-aided CTPA diagnosis (CAD) of PE. However, numerous competing methods for a given task in the deep learning literature exist, causing great confusion regarding the development of a CAD PE system. To address this confusion, we present a comprehensive analysis of competing deep learning methods applicable to PE diagnosis using CTPA at the both image and exam levels. At the image level, we compare convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with vision transformers, and contrast self-supervised learning (SSL) with supervised learning, followed by an evaluation of transfer learning compared with training from scratch. At the exam level, we focus on comparing conventional classification (CC) with multiple instance learning (MIL). Our extensive experiments consistently show: (1) transfer learning consistently boosts performance despite differences between natural images and CT scans, (2) transfer learning with SSL surpasses its supervised counterparts; (3) CNNs outperform vision transformers, which otherwise show satisfactory performance; and (4) CC is, surprisingly, superior to MIL. Compared with the state of the art, our optimal approach provides an AUC gain of 0.2\% and 1.05\% for image-level and exam-level, respectively.
SDCT-AuxNet$^θ$: DCT Augmented Stain Deconvolutional CNN with Auxiliary Classifier for Cancer Diagnosis
Jun 08, 2020
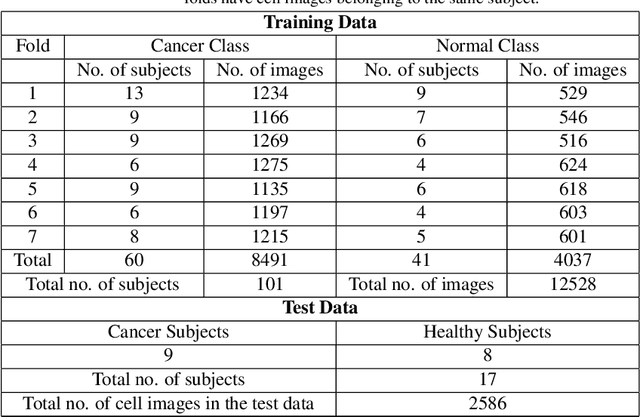

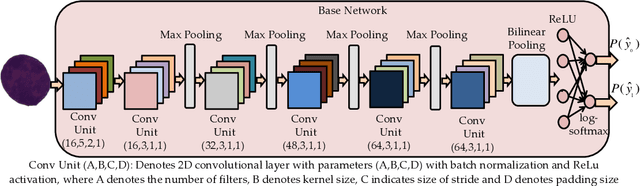
Abstract:Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a pervasive pediatric white blood cell cancer across the globe. With the popularity of convolutional neural networks (CNNs), computer-aided diagnosis of cancer has attracted considerable attention. Such tools are easily deployable and are cost-effective. Hence, these can enable extensive coverage of cancer diagnostic facilities. However, the development of such a tool for ALL cancer was challenging so far due to the non-availability of a large training dataset. The visual similarity between the malignant and normal cells adds to the complexity of the problem. This paper discusses the recent release of a large dataset and presents a novel deep learning architecture for the classification of cell images of ALL cancer. The proposed architecture, namely, SDCT-AuxNet$^{\theta}$ is a 2-module framework that utilizes a compact CNN as the main classifier in one module and a Kernel SVM as the auxiliary classifier in the other one. While CNN classifier uses features through bilinear-pooling, spectral-averaged features are used by the auxiliary classifier. Further, this CNN is trained on the stain deconvolved quantity images in the optical density domain instead of the conventional RGB images. A novel test strategy is proposed that exploits both the classifiers for decision making using the confidence scores of their predicted class labels. Elaborate experiments have been carried out on our recently released public dataset of 15114 images of ALL cancer and healthy cells to establish the validity of the proposed methodology that is also robust to subject-level variability. A weighted F1 score of 94.8$\%$ is obtained that is best so far on this challenging dataset.
* The final version of this preprint has been published in Medical Image Analysis
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge