Shijing Si
FFN: a Fine-grained Chinese-English Financial Domain Parallel Corpus
Jun 27, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have stunningly advanced the field of machine translation, though their effectiveness within the financial domain remains largely underexplored. To probe this issue, we constructed a fine-grained Chinese-English parallel corpus of financial news called FFN. We acquired financial news articles spanning between January 1st, 2014, to December 31, 2023, from mainstream media websites such as CNN, FOX, and China Daily. The dataset consists of 1,013 main text and 809 titles, all of which have been manually corrected. We measured the translation quality of two LLMs -- ChatGPT and ERNIE-bot, utilizing BLEU, TER and chrF scores as the evaluation metrics. For comparison, we also trained an OpenNMT model based on our dataset. We detail problems of LLMs and provide in-depth analysis, intending to stimulate further research and solutions in this largely uncharted territory. Our research underlines the need to optimize LLMs within the specific field of financial translation to ensure accuracy and quality.
Predicting Rental Price of Lane Houses in Shanghai with Machine Learning Methods and Large Language Models
May 26, 2024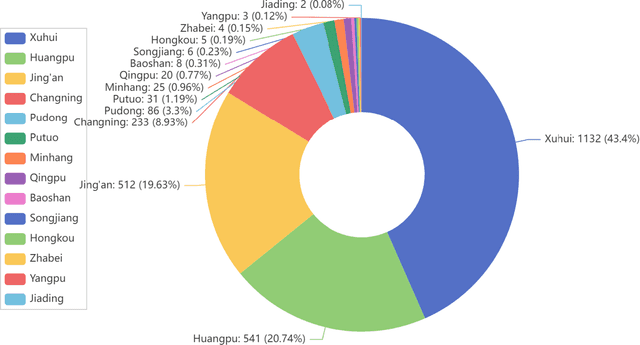
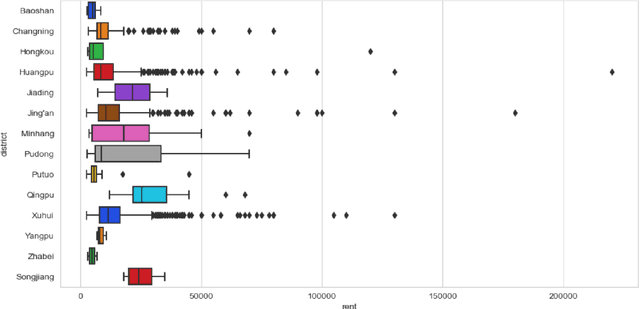
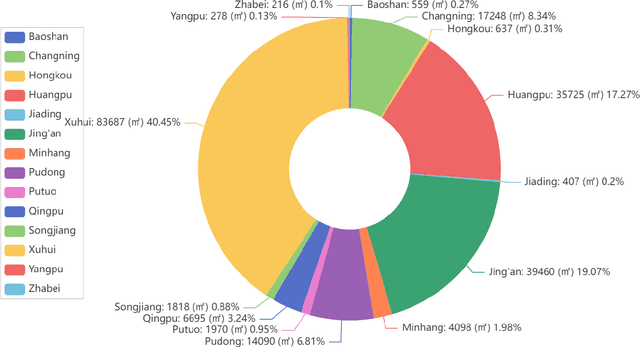
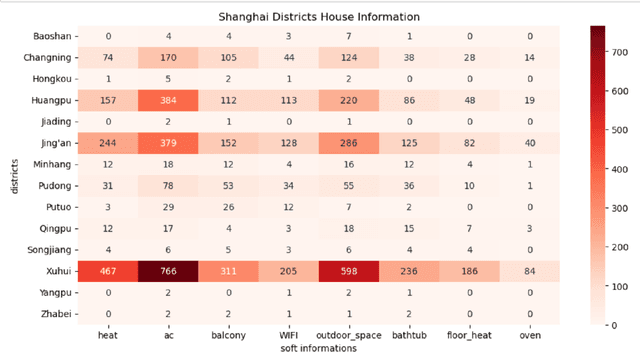
Abstract:Housing has emerged as a crucial concern among young individuals residing in major cities, including Shanghai. Given the unprecedented surge in property prices in this metropolis, young people have increasingly resorted to the rental market to address their housing needs. This study utilizes five traditional machine learning methods: multiple linear regression (MLR), ridge regression (RR), lasso regression (LR), decision tree (DT), and random forest (RF), along with a Large Language Model (LLM) approach using ChatGPT, for predicting the rental prices of lane houses in Shanghai. It applies these methods to examine a public data sample of about 2,609 lane house rental transactions in 2021 in Shanghai, and then compares the results of these methods. In terms of predictive power, RF has achieved the best performance among the traditional methods. However, the LLM approach, particularly in the 10-shot scenario, shows promising results that surpass traditional methods in terms of R-Squared value. The three performance metrics: mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and R-Squared, are used to evaluate the models. Our conclusion is that while traditional machine learning models offer robust techniques for rental price prediction, the integration of LLM such as ChatGPT holds significant potential for enhancing predictive accuracy.
Evaluating the Performance of ChatGPT for Spam Email Detection
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:Email continues to be a pivotal and extensively utilized communication medium within professional and commercial domains. Nonetheless, the prevalence of spam emails poses a significant challenge for users, disrupting their daily routines and diminishing productivity. Consequently, accurately identifying and filtering spam based on content has become crucial for cybersecurity. Recent advancements in natural language processing, particularly with large language models like ChatGPT, have shown remarkable performance in tasks such as question answering and text generation. However, its potential in spam identification remains underexplored. To fill in the gap, this study attempts to evaluate ChatGPT's capabilities for spam identification in both English and Chinese email datasets. We employ ChatGPT for spam email detection using in-context learning, which requires a prompt instruction and a few demonstrations. We also investigate how the training example size affects the performance of ChatGPT. For comparison, we also implement five popular benchmark methods, including naive Bayes, support vector machines (SVM), logistic regression (LR), feedforward dense neural networks (DNN), and BERT classifiers. Though extensive experiments, the performance of ChatGPT is significantly worse than deep supervised learning methods in the large English dataset, while it presents superior performance on the low-resourced Chinese dataset, even outperforming BERT in this case.
Evaluating the Capability of ChatGPT on Ancient Chinese
Dec 23, 2023Abstract:ChatGPT's proficiency in handling modern standard languages suggests potential for its use in understanding ancient Chinese. This project explores ChatGPT's capabilities on ancient Chinese via two tasks: translating ancient Chinese to modern Chinese and recognizing ancient Chinese names. A comparison of ChatGPT's output with human translations serves to evaluate its comprehension of ancient Chinese. The findings indicate that: (1.)the proficiency of ancient Chinese by ChatGPT is yet to reach a satisfactory level; (2.) ChatGPT performs the best on ancient-to-modern translation when feeding with three context sentences. To help reproduce our work, we display the python code snippets used in this study.
Label Smoothing for Enhanced Text Sentiment Classification
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:Label smoothing is a widely used technique in various domains, such as image classification and speech recognition, known for effectively combating model overfitting. However, there is few research on its application to text sentiment classification. To fill in the gap, this study investigates the implementation of label smoothing for sentiment classification by utilizing different levels of smoothing. The primary objective is to enhance sentiment classification accuracy by transforming discrete labels into smoothed label distributions. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate the superior performance of label smoothing in text sentiment classification tasks across eight diverse datasets and deep learning architectures: TextCNN, BERT, and RoBERTa, under two learning schemes: training from scratch and fine-tuning.
On the Calibration and Uncertainty with Pólya-Gamma Augmentation for Dialog Retrieval Models
Mar 15, 2023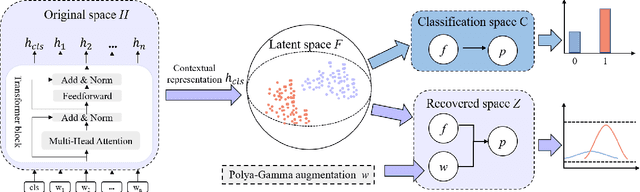
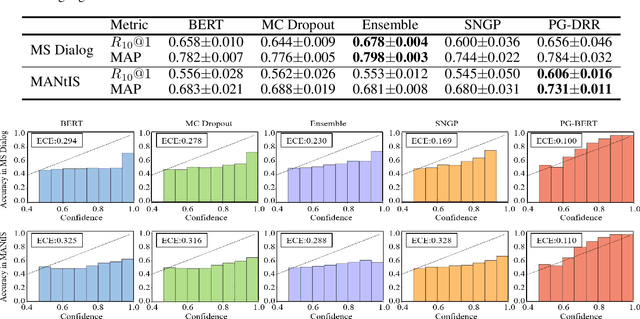

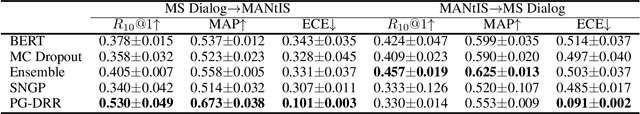
Abstract:Deep neural retrieval models have amply demonstrated their power but estimating the reliability of their predictions remains challenging. Most dialog response retrieval models output a single score for a response on how relevant it is to a given question. However, the bad calibration of deep neural network results in various uncertainty for the single score such that the unreliable predictions always misinform user decisions. To investigate these issues, we present an efficient calibration and uncertainty estimation framework PG-DRR for dialog response retrieval models which adds a Gaussian Process layer to a deterministic deep neural network and recovers conjugacy for tractable posterior inference by P\'{o}lya-Gamma augmentation. Finally, PG-DRR achieves the lowest empirical calibration error (ECE) in the in-domain datasets and the distributional shift task while keeping $R_{10}@1$ and MAP performance.
Efficient Document Retrieval by End-to-End Refining and Quantizing BERT Embedding with Contrastive Product Quantization
Oct 31, 2022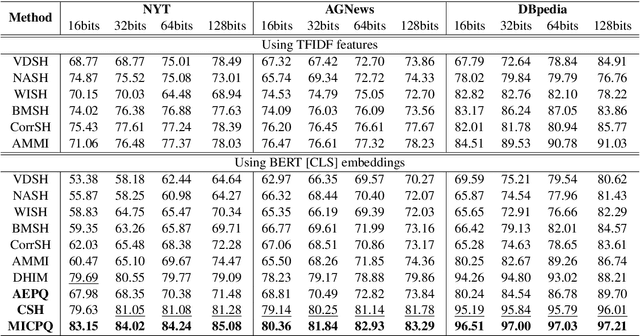
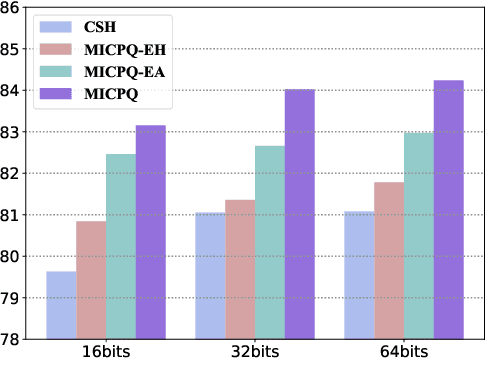
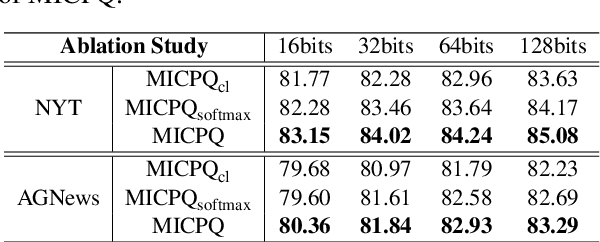
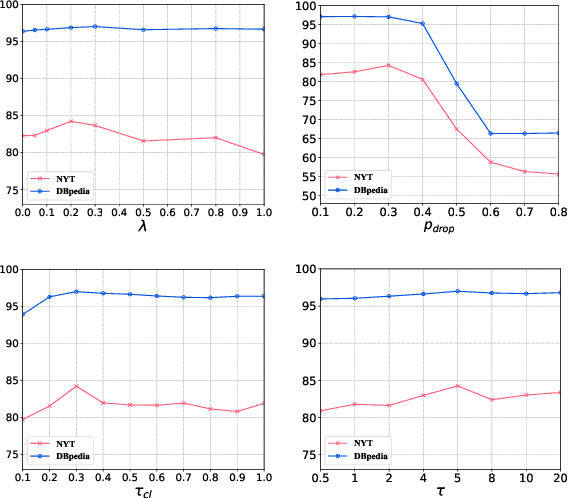
Abstract:Efficient document retrieval heavily relies on the technique of semantic hashing, which learns a binary code for every document and employs Hamming distance to evaluate document distances. However, existing semantic hashing methods are mostly established on outdated TFIDF features, which obviously do not contain lots of important semantic information about documents. Furthermore, the Hamming distance can only be equal to one of several integer values, significantly limiting its representational ability for document distances. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose to leverage BERT embeddings to perform efficient retrieval based on the product quantization technique, which will assign for every document a real-valued codeword from the codebook, instead of a binary code as in semantic hashing. Specifically, we first transform the original BERT embeddings via a learnable mapping and feed the transformed embedding into a probabilistic product quantization module to output the assigned codeword. The refining and quantizing modules can be optimized in an end-to-end manner by minimizing the probabilistic contrastive loss. A mutual information maximization based method is further proposed to improve the representativeness of codewords, so that documents can be quantized more accurately. Extensive experiments conducted on three benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art baselines.
Pushing the Efficiency Limit Using Structured Sparse Convolutions
Oct 23, 2022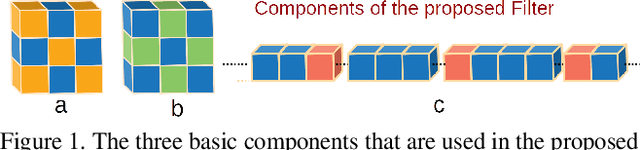
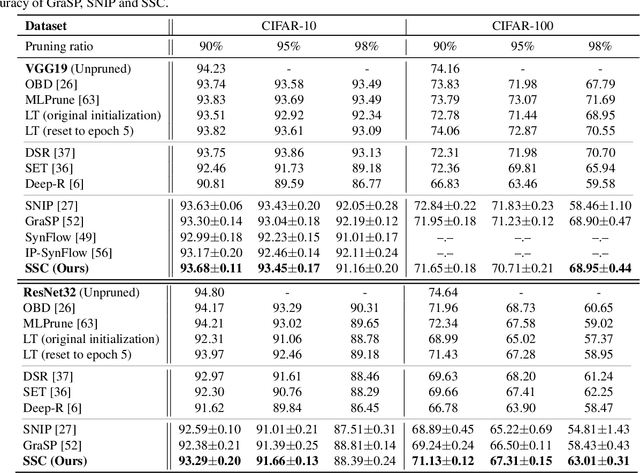
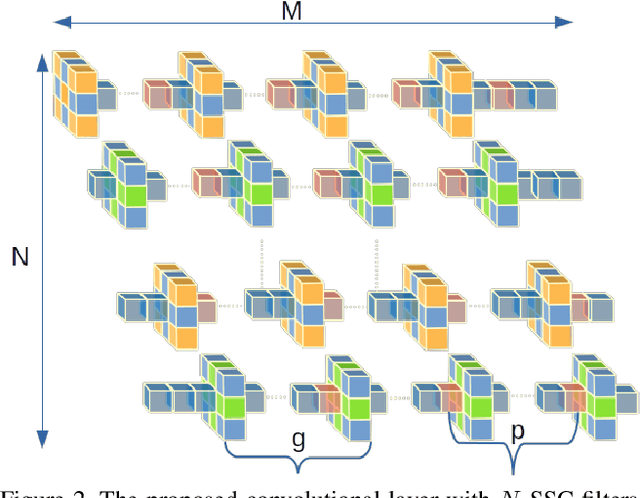
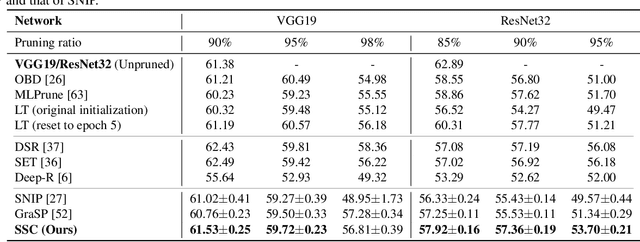
Abstract:Weight pruning is among the most popular approaches for compressing deep convolutional neural networks. Recent work suggests that in a randomly initialized deep neural network, there exist sparse subnetworks that achieve performance comparable to the original network. Unfortunately, finding these subnetworks involves iterative stages of training and pruning, which can be computationally expensive. We propose Structured Sparse Convolution (SSC), which leverages the inherent structure in images to reduce the parameters in the convolutional filter. This leads to improved efficiency of convolutional architectures compared to existing methods that perform pruning at initialization. We show that SSC is a generalization of commonly used layers (depthwise, groupwise and pointwise convolution) in ``efficient architectures.'' Extensive experiments on well-known CNN models and datasets show the effectiveness of the proposed method. Architectures based on SSC achieve state-of-the-art performance compared to baselines on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, Tiny-ImageNet, and ImageNet classification benchmarks.
Pose Guided Human Image Synthesis with Partially Decoupled GAN
Oct 07, 2022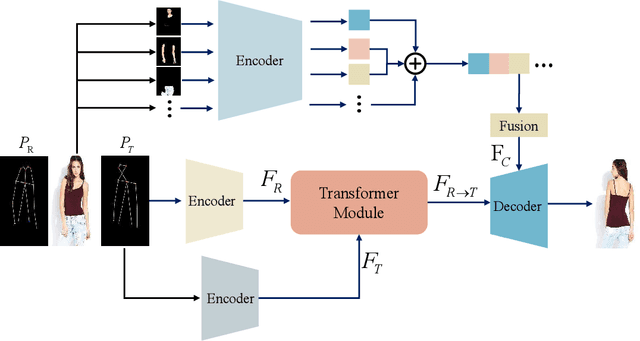
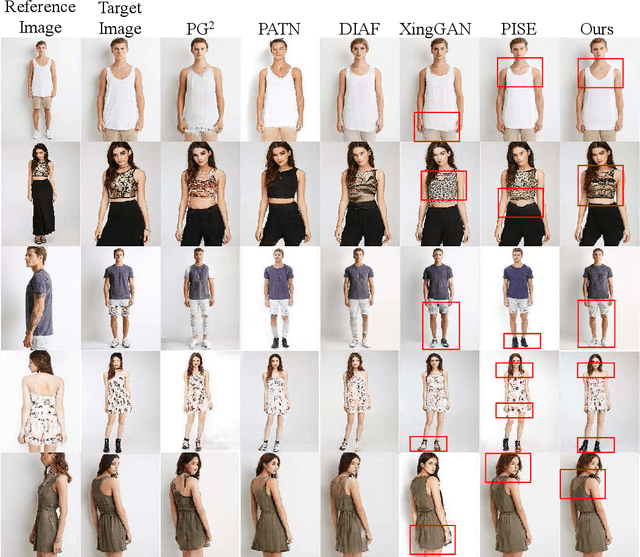
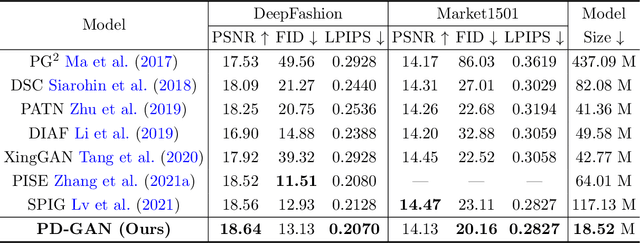
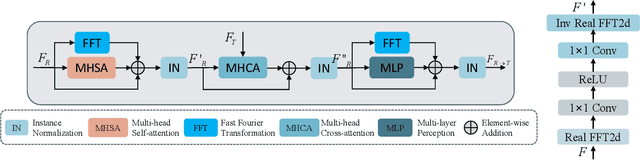

Abstract:Pose Guided Human Image Synthesis (PGHIS) is a challenging task of transforming a human image from the reference pose to a target pose while preserving its style. Most existing methods encode the texture of the whole reference human image into a latent space, and then utilize a decoder to synthesize the image texture of the target pose. However, it is difficult to recover the detailed texture of the whole human image. To alleviate this problem, we propose a method by decoupling the human body into several parts (\eg, hair, face, hands, feet, \etc) and then using each of these parts to guide the synthesis of a realistic image of the person, which preserves the detailed information of the generated images. In addition, we design a multi-head attention-based module for PGHIS. Because most convolutional neural network-based methods have difficulty in modeling long-range dependency due to the convolutional operation, the long-range modeling capability of attention mechanism is more suitable than convolutional neural networks for pose transfer task, especially for sharp pose deformation. Extensive experiments on Market-1501 and DeepFashion datasets reveal that our method almost outperforms other existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of both qualitative and quantitative metrics.
RL-MD: A Novel Reinforcement Learning Approach for DNA Motif Discovery
Sep 30, 2022



Abstract:The extraction of sequence patterns from a collection of functionally linked unlabeled DNA sequences is known as DNA motif discovery, and it is a key task in computational biology. Several deep learning-based techniques have recently been introduced to address this issue. However, these algorithms can not be used in real-world situations because of the need for labeled data. Here, we presented RL-MD, a novel reinforcement learning based approach for DNA motif discovery task. RL-MD takes unlabelled data as input, employs a relative information-based method to evaluate each proposed motif, and utilizes these continuous evaluation results as the reward. The experiments show that RL-MD can identify high-quality motifs in real-world data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge