Zhangcheng Huang
Personalized Federated Learning via Gradient Modulation for Heterogeneous Text Summarization
Apr 23, 2023Abstract:Text summarization is essential for information aggregation and demands large amounts of training data. However, concerns about data privacy and security limit data collection and model training. To eliminate this concern, we propose a federated learning text summarization scheme, which allows users to share the global model in a cooperative learning manner without sharing raw data. Personalized federated learning (PFL) balances personalization and generalization in the process of optimizing the global model, to guide the training of local models. However, multiple local data have different distributions of semantics and context, which may cause the local model to learn deviated semantic and context information. In this paper, we propose FedSUMM, a dynamic gradient adapter to provide more appropriate local parameters for local model. Simultaneously, FedSUMM uses differential privacy to prevent parameter leakage during distributed training. Experimental evidence verifies FedSUMM can achieve faster model convergence on PFL algorithm for task-specific text summarization, and the method achieves superior performance for different optimization metrics for text summarization.
Blur the Linguistic Boundary: Interpreting Chinese Buddhist Sutra in English via Neural Machine Translation
Sep 30, 2022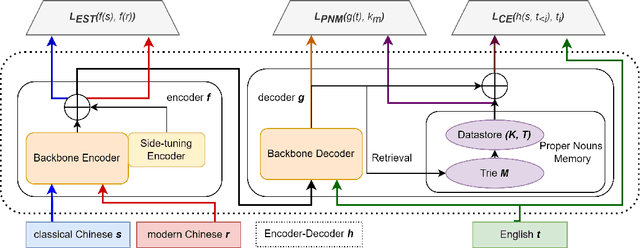
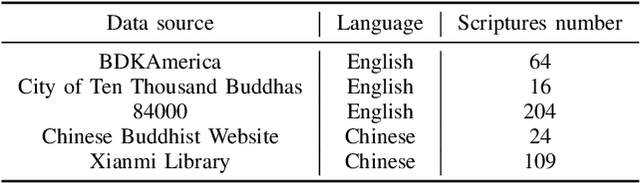
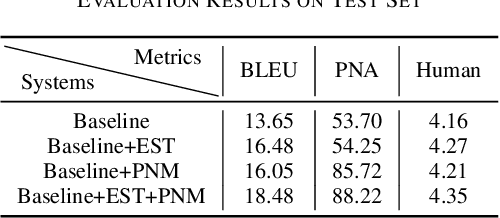
Abstract:Buddhism is an influential religion with a long-standing history and profound philosophy. Nowadays, more and more people worldwide aspire to learn the essence of Buddhism, attaching importance to Buddhism dissemination. However, Buddhist scriptures written in classical Chinese are obscure to most people and machine translation applications. For instance, general Chinese-English neural machine translation (NMT) fails in this domain. In this paper, we proposed a novel approach to building a practical NMT model for Buddhist scriptures. The performance of our translation pipeline acquired highly promising results in ablation experiments under three criteria.
RL-MD: A Novel Reinforcement Learning Approach for DNA Motif Discovery
Sep 30, 2022



Abstract:The extraction of sequence patterns from a collection of functionally linked unlabeled DNA sequences is known as DNA motif discovery, and it is a key task in computational biology. Several deep learning-based techniques have recently been introduced to address this issue. However, these algorithms can not be used in real-world situations because of the need for labeled data. Here, we presented RL-MD, a novel reinforcement learning based approach for DNA motif discovery task. RL-MD takes unlabelled data as input, employs a relative information-based method to evaluate each proposed motif, and utilizes these continuous evaluation results as the reward. The experiments show that RL-MD can identify high-quality motifs in real-world data.
Machine Unlearning Method Based On Projection Residual
Sep 30, 2022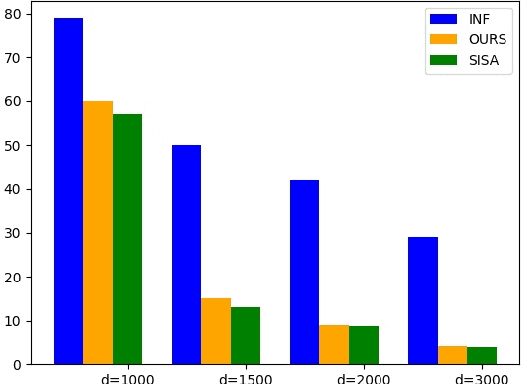
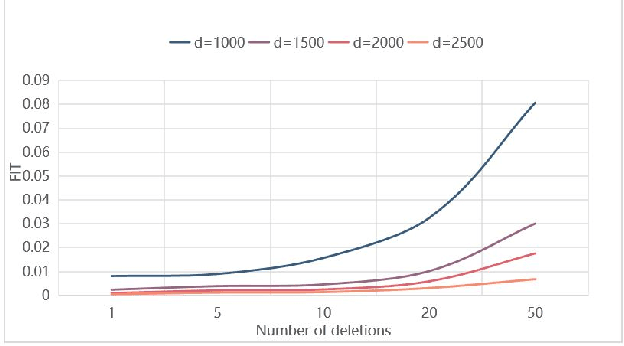
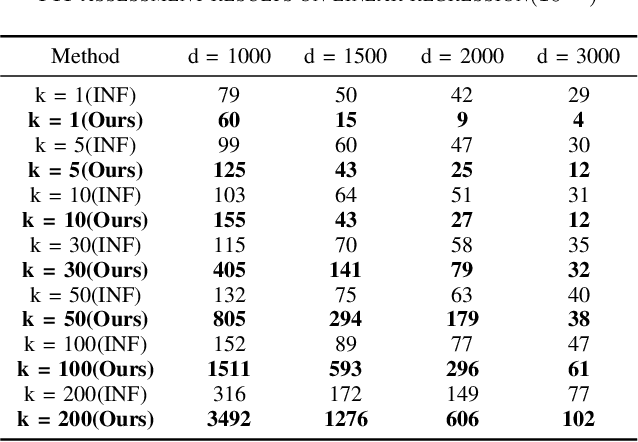
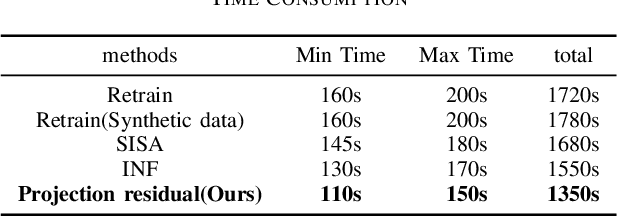
Abstract:Machine learning models (mainly neural networks) are used more and more in real life. Users feed their data to the model for training. But these processes are often one-way. Once trained, the model remembers the data. Even when data is removed from the dataset, the effects of these data persist in the model. With more and more laws and regulations around the world protecting data privacy, it becomes even more important to make models forget this data completely through machine unlearning. This paper adopts the projection residual method based on Newton iteration method. The main purpose is to implement machine unlearning tasks in the context of linear regression models and neural network models. This method mainly uses the iterative weighting method to completely forget the data and its corresponding influence, and its computational cost is linear in the feature dimension of the data. This method can improve the current machine learning method. At the same time, it is independent of the size of the training set. Results were evaluated by feature injection testing (FIT). Experiments show that this method is more thorough in deleting data, which is close to model retraining.
A Privacy-Preserving Subgraph-Level Federated Graph Neural Network via Differential Privacy
Jun 07, 2022



Abstract:Currently, the federated graph neural network (GNN) has attracted a lot of attention due to its wide applications in reality without violating the privacy regulations. Among all the privacy-preserving technologies, the differential privacy (DP) is the most promising one due to its effectiveness and light computational overhead. However, the DP-based federated GNN has not been well investigated, especially in the sub-graph-level setting, such as the scenario of recommendation system. The biggest challenge is how to guarantee the privacy and solve the non independent and identically distributed (non-IID) data in federated GNN simultaneously. In this paper, we propose DP-FedRec, a DP-based federated GNN to fill the gap. Private Set Intersection (PSI) is leveraged to extend the local graph for each client, and thus solve the non-IID problem. Most importantly, DP is applied not only on the weights but also on the edges of the intersection graph from PSI to fully protect the privacy of clients. The evaluation demonstrates DP-FedRec achieves better performance with the graph extension and DP only introduces little computations overhead.
Micro-Expression Recognition Based on Attribute Information Embedding and Cross-modal Contrastive Learning
May 29, 2022



Abstract:Facial micro-expressions recognition has attracted much attention recently. Micro-expressions have the characteristics of short duration and low intensity, and it is difficult to train a high-performance classifier with the limited number of existing micro-expressions. Therefore, recognizing micro-expressions is a challenge task. In this paper, we propose a micro-expression recognition method based on attribute information embedding and cross-modal contrastive learning. We use 3D CNN to extract RGB features and FLOW features of micro-expression sequences and fuse them, and use BERT network to extract text information in Facial Action Coding System. Through cross-modal contrastive loss, we embed attribute information in the visual network, thereby improving the representation ability of micro-expression recognition in the case of limited samples. We conduct extensive experiments in CASME II and MMEW databases, and the accuracy is 77.82% and 71.04%, respectively. The comparative experiments show that this method has better recognition effect than other methods for micro-expression recognition.
FedSmart: An Auto Updating Federated Learning Optimization Mechanism
Sep 16, 2020



Abstract:Federated learning has made an important contribution to data privacy-preserving. Many previous works are based on the assumption that the data are independently identically distributed (IID). As a result, the model performance on non-identically independently distributed (non-IID) data is beyond expectation, which is the concrete situation. Some existing methods of ensuring the model robustness on non-IID data, like the data-sharing strategy or pretraining, may lead to privacy leaking. In addition, there exist some participants who try to poison the model with low-quality data. In this paper, a performance-based parameter return method for optimization is introduced, we term it FederatedSmart (FedSmart). It optimizes different model for each client through sharing global gradients, and it extracts the data from each client as a local validation set, and the accuracy that model achieves in round t determines the weights of the next round. The experiment results show that FedSmart enables the participants to allocate a greater weight to the ones with similar data distribution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge