Predicting Rental Price of Lane Houses in Shanghai with Machine Learning Methods and Large Language Models
Paper and Code
May 26, 2024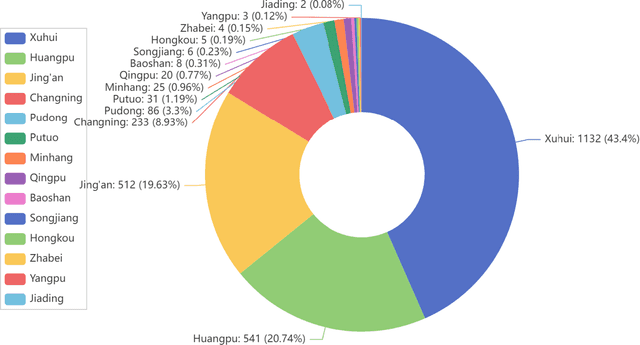
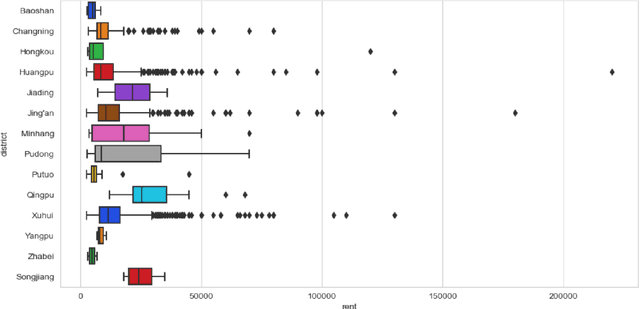
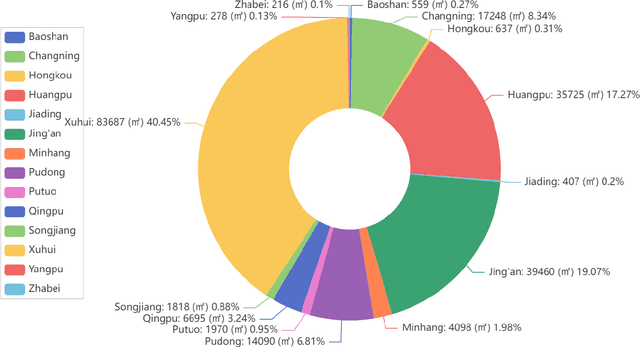
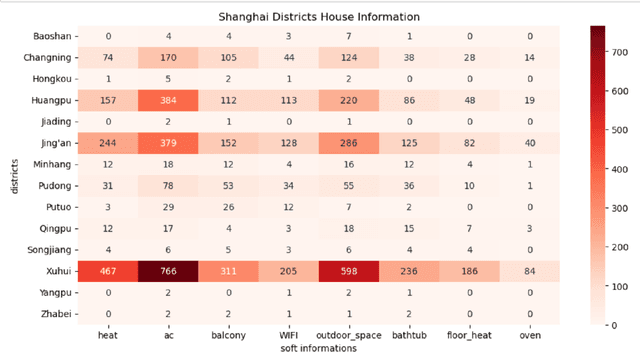
Housing has emerged as a crucial concern among young individuals residing in major cities, including Shanghai. Given the unprecedented surge in property prices in this metropolis, young people have increasingly resorted to the rental market to address their housing needs. This study utilizes five traditional machine learning methods: multiple linear regression (MLR), ridge regression (RR), lasso regression (LR), decision tree (DT), and random forest (RF), along with a Large Language Model (LLM) approach using ChatGPT, for predicting the rental prices of lane houses in Shanghai. It applies these methods to examine a public data sample of about 2,609 lane house rental transactions in 2021 in Shanghai, and then compares the results of these methods. In terms of predictive power, RF has achieved the best performance among the traditional methods. However, the LLM approach, particularly in the 10-shot scenario, shows promising results that surpass traditional methods in terms of R-Squared value. The three performance metrics: mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and R-Squared, are used to evaluate the models. Our conclusion is that while traditional machine learning models offer robust techniques for rental price prediction, the integration of LLM such as ChatGPT holds significant potential for enhancing predictive accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge