Sharon Fogel
Amazon Rekognition Israel
VisFocus: Prompt-Guided Vision Encoders for OCR-Free Dense Document Understanding
Jul 17, 2024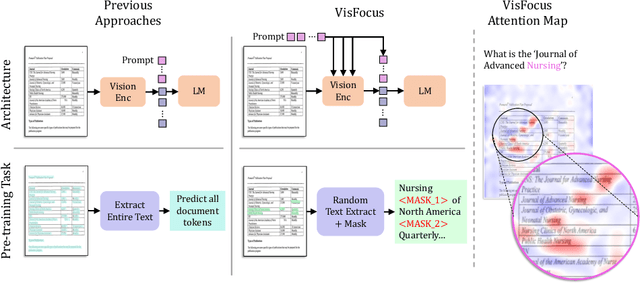
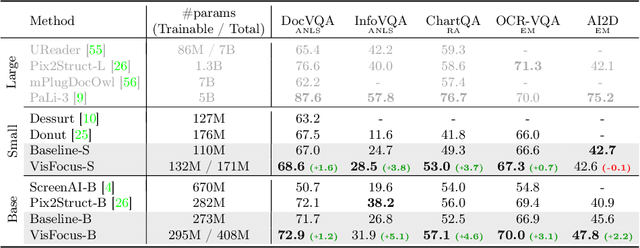
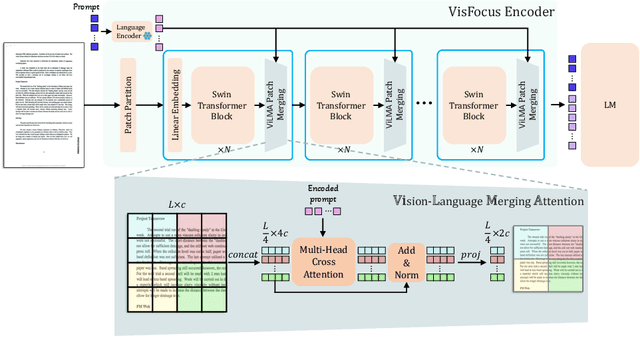

Abstract:In recent years, notable advancements have been made in the domain of visual document understanding, with the prevailing architecture comprising a cascade of vision and language models. The text component can either be extracted explicitly with the use of external OCR models in OCR-based approaches, or alternatively, the vision model can be endowed with reading capabilities in OCR-free approaches. Typically, the queries to the model are input exclusively to the language component, necessitating the visual features to encompass the entire document. In this paper, we present VisFocus, an OCR-free method designed to better exploit the vision encoder's capacity by coupling it directly with the language prompt. To do so, we replace the down-sampling layers with layers that receive the input prompt and allow highlighting relevant parts of the document, while disregarding others. We pair the architecture enhancements with a novel pre-training task, using language masking on a snippet of the document text fed to the visual encoder in place of the prompt, to empower the model with focusing capabilities. Consequently, VisFocus learns to allocate its attention to text patches pertinent to the provided prompt. Our experiments demonstrate that this prompt-guided visual encoding approach significantly improves performance, achieving state-of-the-art results on various benchmarks.
GRAM: Global Reasoning for Multi-Page VQA
Jan 07, 2024


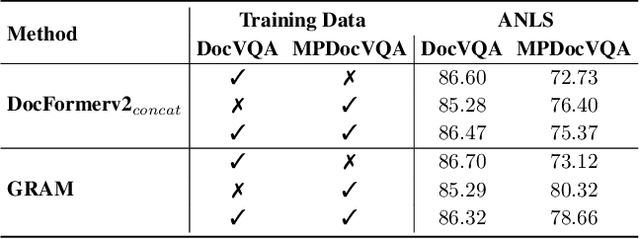
Abstract:The increasing use of transformer-based large language models brings forward the challenge of processing long sequences. In document visual question answering (DocVQA), leading methods focus on the single-page setting, while documents can span hundreds of pages. We present GRAM, a method that seamlessly extends pre-trained single-page models to the multi-page setting, without requiring computationally-heavy pretraining. To do so, we leverage a single-page encoder for local page-level understanding, and enhance it with document-level designated layers and learnable tokens, facilitating the flow of information across pages for global reasoning. To enforce our model to utilize the newly introduced document-level tokens, we propose a tailored bias adaptation method. For additional computational savings during decoding, we introduce an optional compression stage using our C-Former model, which reduces the encoded sequence length, thereby allowing a tradeoff between quality and latency. Extensive experiments showcase GRAM's state-of-the-art performance on the benchmarks for multi-page DocVQA, demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach.
Towards Weakly-Supervised Text Spotting using a Multi-Task Transformer
Feb 14, 2022



Abstract:Text spotting end-to-end methods have recently gained attention in the literature due to the benefits of jointly optimizing the text detection and recognition components. Existing methods usually have a distinct separation between the detection and recognition branches, requiring exact annotations for the two tasks. We introduce TextTranSpotter (TTS), a transformer-based approach for text spotting and the first text spotting framework which may be trained with both fully- and weakly-supervised settings. By learning a single latent representation per word detection, and using a novel loss function based on the Hungarian loss, our method alleviates the need for expensive localization annotations. Trained with only text transcription annotations on real data, our weakly-supervised method achieves competitive performance with previous state-of-the-art fully-supervised methods. When trained in a fully-supervised manner, TextTranSpotter shows state-of-the-art results on multiple benchmarks.
TextAdaIN: Fine-Grained AdaIN for Robust Text Recognition
May 09, 2021



Abstract:Leveraging the characteristics of convolutional layers, image classifiers are extremely effective. However, recent works have exposed that in many cases they immoderately rely on global image statistics that are easy to manipulate while preserving image semantics. In text recognition, we reveal that it is rather the local image statistics which the networks overly depend on. Motivated by this, we suggest an approach to regulate the reliance on local statistics that improves overall text recognition performance. Our method, termed TextAdaIN, creates local distortions in the feature map which prevent the network from overfitting to the local statistics. It does so by deliberately mismatching fine-grained feature statistics between samples in a mini-batch. Despite TextAdaIN's simplicity, extensive experiments show its effectiveness compared to other, more complicated methods. TextAdaIN achieves state-of-the-art results on standard handwritten text recognition benchmarks. Additionally, it generalizes to multiple architectures and to the domain of scene text recognition. Furthermore, we demonstrate that integrating TextAdaIN improves robustness towards image corruptions.
Weakly Aligned Joint Cross-Modality Super Resolution
Apr 21, 2020



Abstract:Non-visual imaging sensors are widely used in the industry for different purposes. Those sensors are more expensive than visual (RGB) sensors, and usually produce images with lower resolution. To this end, Cross-Modality Super-Resolution methods were introduced, where an RGB image of a high-resolution assists in increasing the resolution of the low-resolution modality. However, fusing images from different modalities is not a trivial task; the output must be artifact-free and remain loyal to the characteristics of the target modality. Moreover, the input images are never perfectly aligned, which results in further artifacts during the fusion process. We present CMSR, a deep network for Cross-Modality Super-Resolution, which unlike previous methods, is designed to deal with weakly aligned images. The network is trained on the two input images only, learns their internal statistics and correlations, and applies them to up-sample the target modality. CMSR contains an internal transformer that is trained on-the-fly together with the up-sampling process itself, without explicit supervision. We show that CMSR succeeds to increase the resolution of the input image, gaining valuable information from its RGB counterpart, yet in a conservative way, without introducing artifacts or irrelevant details.
ScrabbleGAN: Semi-Supervised Varying Length Handwritten Text Generation
Mar 23, 2020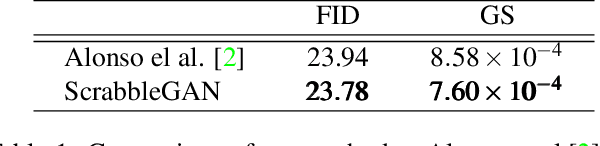
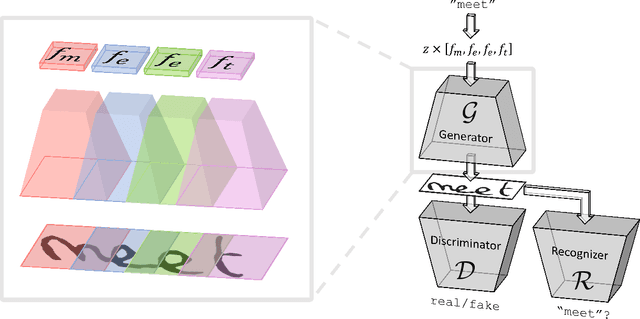
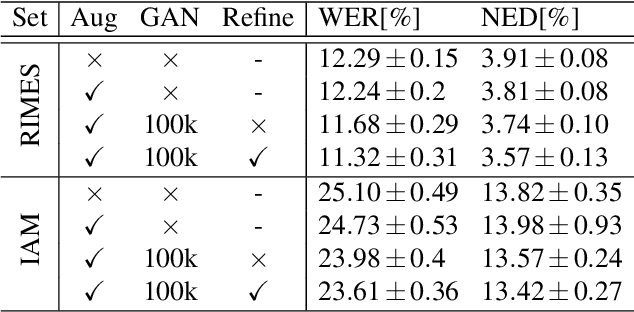

Abstract:Optical character recognition (OCR) systems performance have improved significantly in the deep learning era. This is especially true for handwritten text recognition (HTR), where each author has a unique style, unlike printed text, where the variation is smaller by design. That said, deep learning based HTR is limited, as in every other task, by the number of training examples. Gathering data is a challenging and costly task, and even more so, the labeling task that follows, of which we focus here. One possible approach to reduce the burden of data annotation is semi-supervised learning. Semi supervised methods use, in addition to labeled data, some unlabeled samples to improve performance, compared to fully supervised ones. Consequently, such methods may adapt to unseen images during test time. We present ScrabbleGAN, a semi-supervised approach to synthesize handwritten text images that are versatile both in style and lexicon. ScrabbleGAN relies on a novel generative model which can generate images of words with an arbitrary length. We show how to operate our approach in a semi-supervised manner, enjoying the aforementioned benefits such as performance boost over state of the art supervised HTR. Furthermore, our generator can manipulate the resulting text style. This allows us to change, for instance, whether the text is cursive, or how thin is the pen stroke.
Blind Visual Motif Removal from a Single Image
Apr 04, 2019



Abstract:Many images shared over the web include overlaid objects, or visual motifs, such as text, symbols or drawings, which add a description or decoration to the image. For example, decorative text that specifies where the image was taken, repeatedly appears across a variety of different images. Often, the reoccurring visual motif, is semantically similar, yet, differs in location, style and content (e.g. text placement, font and letters). This work proposes a deep learning based technique for blind removal of such objects. In the blind setting, the location and exact geometry of the motif are unknown. Our approach simultaneously estimates which pixels contain the visual motif, and synthesizes the underlying latent image. It is applied to a single input image, without any user assistance in specifying the location of the motif, achieving state-of-the-art results for blind removal of both opaque and semi-transparent visual motifs.
Clustering-driven Deep Embedding with Pairwise Constraints
Oct 19, 2018



Abstract:Recently, there has been increasing interest to leverage the competence of neural networks to analyze data. In particular, new clustering methods that employ deep embeddings have been presented. In this paper, we depart from centroid-based models and suggest a new framework, called Clustering-driven deep embedding with PAirwise Constraints (CPAC), for non-parametric clustering using a neural network. We present a clustering-driven embedding based on a Siamese network that encourages pairs of data points to output similar representations in the latent space. Our pair-based model allows augmenting the information with labeled pairs to constitute a semi-supervised framework. Our approach is based on analyzing the losses associated with each pair to refine the set of constraints. We show that clustering performance increases when using this scheme, even with a limited amount of user queries. We demonstrate how our architecture is adapted for various types of data and present the first deep framework to cluster 3D shapes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge