Shangxuan Tian
CPN: Complementary Proposal Network for Unconstrained Text Detection
Feb 18, 2024Abstract:Existing methods for scene text detection can be divided into two paradigms: segmentation-based and anchor-based. While Segmentation-based methods are well-suited for irregular shapes, they struggle with compact or overlapping layouts. Conversely, anchor-based approaches excel for complex layouts but suffer from irregular shapes. To strengthen their merits and overcome their respective demerits, we propose a Complementary Proposal Network (CPN) that seamlessly and parallelly integrates semantic and geometric information for superior performance. The CPN comprises two efficient networks for proposal generation: the Deformable Morphology Semantic Network, which generates semantic proposals employing an innovative deformable morphological operator, and the Balanced Region Proposal Network, which produces geometric proposals with pre-defined anchors. To further enhance the complementarity, we introduce an Interleaved Feature Attention module that enables semantic and geometric features to interact deeply before proposal generation. By leveraging both complementary proposals and features, CPN outperforms state-of-the-art approaches with significant margins under comparable computation cost. Specifically, our approach achieves improvements of 3.6%, 1.3% and 1.0% on challenging benchmarks ICDAR19-ArT, IC15, and MSRA-TD500, respectively. Code for our method will be released.
Center Contrastive Loss for Metric Learning
Aug 01, 2023Abstract:Contrastive learning is a major studied topic in metric learning. However, sampling effective contrastive pairs remains a challenge due to factors such as limited batch size, imbalanced data distribution, and the risk of overfitting. In this paper, we propose a novel metric learning function called Center Contrastive Loss, which maintains a class-wise center bank and compares the category centers with the query data points using a contrastive loss. The center bank is updated in real-time to boost model convergence without the need for well-designed sample mining. The category centers are well-optimized classification proxies to re-balance the supervisory signal of each class. Furthermore, the proposed loss combines the advantages of both contrastive and classification methods by reducing intra-class variations and enhancing inter-class differences to improve the discriminative power of embeddings. Our experimental results, as shown in Figure 1, demonstrate that a standard network (ResNet50) trained with our loss achieves state-of-the-art performance and faster convergence.
Video-Text as Game Players: Hierarchical Banzhaf Interaction for Cross-Modal Representation Learning
Mar 25, 2023



Abstract:Contrastive learning-based video-language representation learning approaches, e.g., CLIP, have achieved outstanding performance, which pursue semantic interaction upon pre-defined video-text pairs. To clarify this coarse-grained global interaction and move a step further, we have to encounter challenging shell-breaking interactions for fine-grained cross-modal learning. In this paper, we creatively model video-text as game players with multivariate cooperative game theory to wisely handle the uncertainty during fine-grained semantic interaction with diverse granularity, flexible combination, and vague intensity. Concretely, we propose Hierarchical Banzhaf Interaction (HBI) to value possible correspondence between video frames and text words for sensitive and explainable cross-modal contrast. To efficiently realize the cooperative game of multiple video frames and multiple text words, the proposed method clusters the original video frames (text words) and computes the Banzhaf Interaction between the merged tokens. By stacking token merge modules, we achieve cooperative games at different semantic levels. Extensive experiments on commonly used text-video retrieval and video-question answering benchmarks with superior performances justify the efficacy of our HBI. More encouragingly, it can also serve as a visualization tool to promote the understanding of cross-modal interaction, which have a far-reaching impact on the community. Project page is available at https://jpthu17.github.io/HBI/.
Deep Self-Adaptive Hashing for Image Retrieval
Aug 21, 2021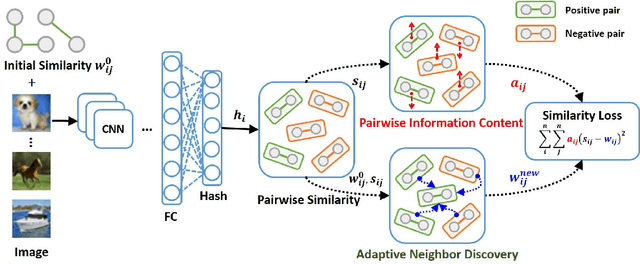
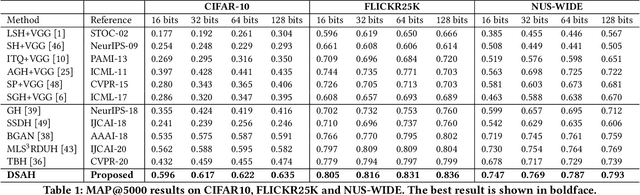
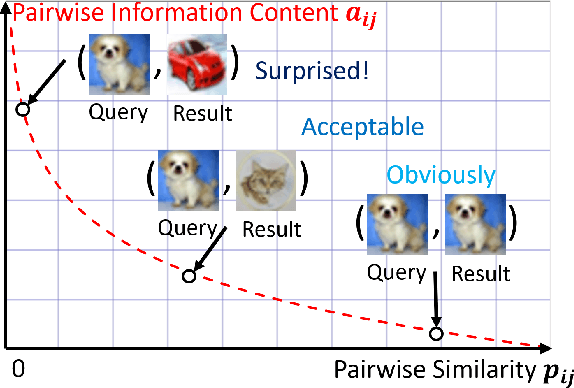
Abstract:Hashing technology has been widely used in image retrieval due to its computational and storage efficiency. Recently, deep unsupervised hashing methods have attracted increasing attention due to the high cost of human annotations in the real world and the superiority of deep learning technology. However, most deep unsupervised hashing methods usually pre-compute a similarity matrix to model the pairwise relationship in the pre-trained feature space. Then this similarity matrix would be used to guide hash learning, in which most of the data pairs are treated equivalently. The above process is confronted with the following defects: 1) The pre-computed similarity matrix is inalterable and disconnected from the hash learning process, which cannot explore the underlying semantic information. 2) The informative data pairs may be buried by the large number of less-informative data pairs. To solve the aforementioned problems, we propose a Deep Self-Adaptive Hashing (DSAH) model to adaptively capture the semantic information with two special designs: Adaptive Neighbor Discovery (AND) and Pairwise Information Content (PIC). Firstly, we adopt the AND to initially construct a neighborhood-based similarity matrix, and then refine this initial similarity matrix with a novel update strategy to further investigate the semantic structure behind the learned representation. Secondly, we measure the priorities of data pairs with PIC and assign adaptive weights to them, which is relies on the assumption that more dissimilar data pairs contain more discriminative information for hash learning. Extensive experiments on several datasets demonstrate that the above two technologies facilitate the deep hashing model to achieve superior performance.
A pooling based scene text proposal technique for scene text reading in the wild
Nov 25, 2018



Abstract:Automatic reading texts in scenes has attracted increasing interest in recent years as texts often carry rich semantic information that is useful for scene understanding. In this paper, we propose a novel scene text proposal technique aiming for accurate reading texts in scenes. Inspired by the pooling layer in the deep neural network architecture, a pooling based scene text proposal technique is developed. A novel score function is designed which exploits the histogram of oriented gradients and is capable of ranking the proposals according to their probabilities of being text. An end-to-end scene text reading system has also been developed by incorporating the proposed scene text proposal technique where false alarms elimination and words recognition are performed simultaneously. Extensive experiments over several public datasets show that the proposed technique can handle multi-orientation and multi-language scene texts and obtains outstanding proposal performance. The developed end-to-end systems also achieve very competitive scene text spotting and reading performance.
* The article has 34 pages with nine figures, six tables. It has been accepted to publish in Journal of Pattern Recognition
WeText: Scene Text Detection under Weak Supervision
Oct 13, 2017



Abstract:The requiring of large amounts of annotated training data has become a common constraint on various deep learning systems. In this paper, we propose a weakly supervised scene text detection method (WeText) that trains robust and accurate scene text detection models by learning from unannotated or weakly annotated data. With a "light" supervised model trained on a small fully annotated dataset, we explore semi-supervised and weakly supervised learning on a large unannotated dataset and a large weakly annotated dataset, respectively. For the unsupervised learning, the light supervised model is applied to the unannotated dataset to search for more character training samples, which are further combined with the small annotated dataset to retrain a superior character detection model. For the weakly supervised learning, the character searching is guided by high-level annotations of words/text lines that are widely available and also much easier to prepare. In addition, we design an unified scene character detector by adapting regression based deep networks, which greatly relieves the error accumulation issue that widely exists in most traditional approaches. Extensive experiments across different unannotated and weakly annotated datasets show that the scene text detection performance can be clearly boosted under both scenarios, where the weakly supervised learning can achieve the state-of-the-art performance by using only 229 fully annotated scene text images.
Text Flow: A Unified Text Detection System in Natural Scene Images
Apr 23, 2016



Abstract:The prevalent scene text detection approach follows four sequential steps comprising character candidate detection, false character candidate removal, text line extraction, and text line verification. However, errors occur and accumulate throughout each of these sequential steps which often lead to low detection performance. To address these issues, we propose a unified scene text detection system, namely Text Flow, by utilizing the minimum cost (min-cost) flow network model. With character candidates detected by cascade boosting, the min-cost flow network model integrates the last three sequential steps into a single process which solves the error accumulation problem at both character level and text line level effectively. The proposed technique has been tested on three public datasets, i.e, ICDAR2011 dataset, ICDAR2013 dataset and a multilingual dataset and it outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on all three datasets with much higher recall and F-score. The good performance on the multilingual dataset shows that the proposed technique can be used for the detection of texts in different languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge