Raphael Köster
Language Agents as Digital Representatives in Collective Decision-Making
Feb 13, 2025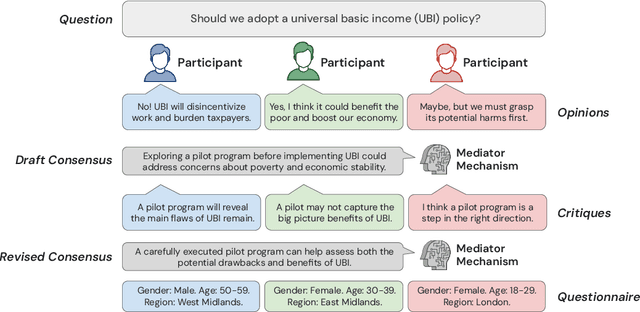

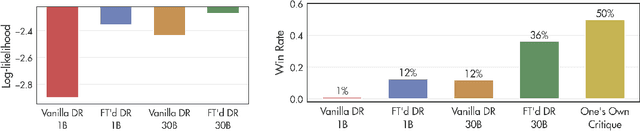
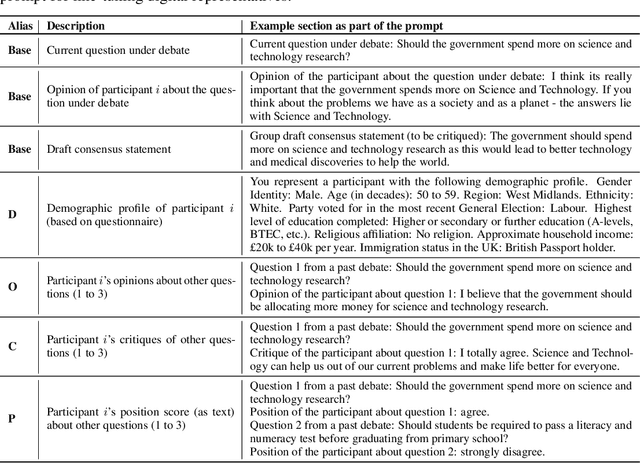
Abstract:Consider the process of collective decision-making, in which a group of individuals interactively select a preferred outcome from among a universe of alternatives. In this context, "representation" is the activity of making an individual's preferences present in the process via participation by a proxy agent -- i.e. their "representative". To this end, learned models of human behavior have the potential to fill this role, with practical implications for multi-agent scenario studies and mechanism design. In this work, we investigate the possibility of training \textit{language agents} to behave in the capacity of representatives of human agents, appropriately expressing the preferences of those individuals whom they stand for. First, we formalize the setting of \textit{collective decision-making} -- as the episodic process of interaction between a group of agents and a decision mechanism. On this basis, we then formalize the problem of \textit{digital representation} -- as the simulation of an agent's behavior to yield equivalent outcomes from the mechanism. Finally, we conduct an empirical case study in the setting of \textit{consensus-finding} among diverse humans, and demonstrate the feasibility of fine-tuning large language models to act as digital representatives.
Melting Pot 2.0
Dec 13, 2022Abstract:Multi-agent artificial intelligence research promises a path to develop intelligent technologies that are more human-like and more human-compatible than those produced by "solipsistic" approaches, which do not consider interactions between agents. Melting Pot is a research tool developed to facilitate work on multi-agent artificial intelligence, and provides an evaluation protocol that measures generalization to novel social partners in a set of canonical test scenarios. Each scenario pairs a physical environment (a "substrate") with a reference set of co-players (a "background population"), to create a social situation with substantial interdependence between the individuals involved. For instance, some scenarios were inspired by institutional-economics-based accounts of natural resource management and public-good-provision dilemmas. Others were inspired by considerations from evolutionary biology, game theory, and artificial life. Melting Pot aims to cover a maximally diverse set of interdependencies and incentives. It includes the commonly-studied extreme cases of perfectly-competitive (zero-sum) motivations and perfectly-cooperative (shared-reward) motivations, but does not stop with them. As in real-life, a clear majority of scenarios in Melting Pot have mixed incentives. They are neither purely competitive nor purely cooperative and thus demand successful agents be able to navigate the resulting ambiguity. Here we describe Melting Pot 2.0, which revises and expands on Melting Pot. We also introduce support for scenarios with asymmetric roles, and explain how to integrate them into the evaluation protocol. This report also contains: (1) details of all substrates and scenarios; (2) a complete description of all baseline algorithms and results. Our intention is for it to serve as a reference for researchers using Melting Pot 2.0.
MEMO: A Deep Network for Flexible Combination of Episodic Memories
Jan 29, 2020



Abstract:Recent research developing neural network architectures with external memory have often used the benchmark bAbI question and answering dataset which provides a challenging number of tasks requiring reasoning. Here we employed a classic associative inference task from the memory-based reasoning neuroscience literature in order to more carefully probe the reasoning capacity of existing memory-augmented architectures. This task is thought to capture the essence of reasoning -- the appreciation of distant relationships among elements distributed across multiple facts or memories. Surprisingly, we found that current architectures struggle to reason over long distance associations. Similar results were obtained on a more complex task involving finding the shortest path between nodes in a path. We therefore developed MEMO, an architecture endowed with the capacity to reason over longer distances. This was accomplished with the addition of two novel components. First, it introduces a separation between memories (facts) stored in external memory and the items that comprise these facts in external memory. Second, it makes use of an adaptive retrieval mechanism, allowing a variable number of "memory hops" before the answer is produced. MEMO is capable of solving our novel reasoning tasks, as well as match state of the art results in bAbI.
Silly rules improve the capacity of agents to learn stable enforcement and compliance behaviors
Jan 25, 2020



Abstract:How can societies learn to enforce and comply with social norms? Here we investigate the learning dynamics and emergence of compliance and enforcement of social norms in a foraging game, implemented in a multi-agent reinforcement learning setting. In this spatiotemporally extended game, individuals are incentivized to implement complex berry-foraging policies and punish transgressions against social taboos covering specific berry types. We show that agents benefit when eating poisonous berries is taboo, meaning the behavior is punished by other agents, as this helps overcome a credit-assignment problem in discovering delayed health effects. Critically, however, we also show that introducing an additional taboo, which results in punishment for eating a harmless berry, improves the rate and stability with which agents learn to punish taboo violations and comply with taboos. Counterintuitively, our results show that an arbitrary taboo (a "silly rule") can enhance social learning dynamics and achieve better outcomes in the middle stages of learning. We discuss the results in the context of studying normativity as a group-level emergent phenomenon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge