Qiang Fang
SD2AIL: Adversarial Imitation Learning from Synthetic Demonstrations via Diffusion Models
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Adversarial Imitation Learning (AIL) is a dominant framework in imitation learning that infers rewards from expert demonstrations to guide policy optimization. Although providing more expert demonstrations typically leads to improved performance and greater stability, collecting such demonstrations can be challenging in certain scenarios. Inspired by the success of diffusion models in data generation, we propose SD2AIL, which utilizes synthetic demonstrations via diffusion models. We first employ a diffusion model in the discriminator to generate synthetic demonstrations as pseudo-expert data that augment the expert demonstrations. To selectively replay the most valuable demonstrations from the large pool of (pseudo-) expert demonstrations, we further introduce a prioritized expert demonstration replay strategy (PEDR). The experimental results on simulation tasks demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our method. In particular, in the Hopper task, our method achieves an average return of 3441, surpassing the state-of-the-art method by 89. Our code will be available at https://github.com/positron-lpc/SD2AIL.
Similarity Distance-Based Label Assignment for Tiny Object Detection
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:Tiny object detection is becoming one of the most challenging tasks in computer vision because of the limited object size and lack of information. The label assignment strategy is a key factor affecting the accuracy of object detection. Although there are some effective label assignment strategies for tiny objects, most of them focus on reducing the sensitivity to the bounding boxes to increase the number of positive samples and have some fixed hyperparameters need to set. However, more positive samples may not necessarily lead to better detection results, in fact, excessive positive samples may lead to more false positives. In this paper, we introduce a simple but effective strategy named the Similarity Distance (SimD) to evaluate the similarity between bounding boxes. This proposed strategy not only considers both location and shape similarity but also learns hyperparameters adaptively, ensuring that it can adapt to different datasets and various object sizes in a dataset. Our approach can be simply applied in common anchor-based detectors in place of the IoU for label assignment and Non Maximum Suppression (NMS). Extensive experiments on four mainstream tiny object detection datasets demonstrate superior performance of our method, especially, 1.8 AP points and 4.1 AP points of very tiny higher than the state-of-the-art competitors on AI-TOD. Code is available at: \url{https://github.com/cszzshi/SimD}.
Continual Learning through Networks Splitting and Merging with Dreaming-Meta-Weighted Model Fusion
Dec 12, 2023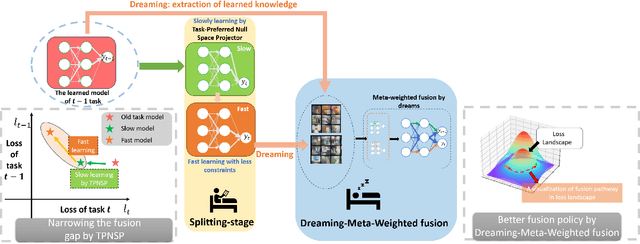
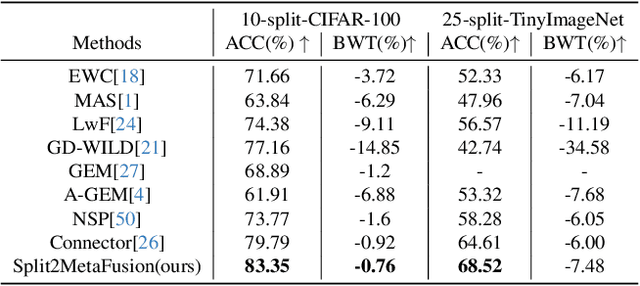
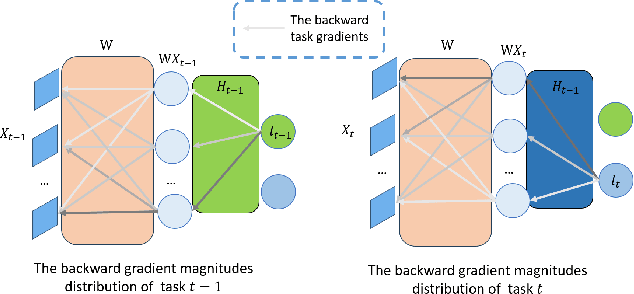
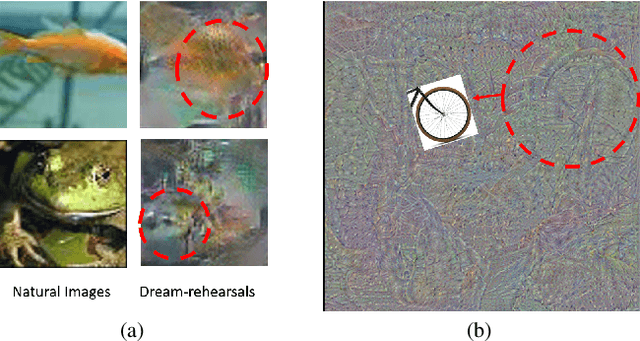
Abstract:It's challenging to balance the networks stability and plasticity in continual learning scenarios, considering stability suffers from the update of model and plasticity benefits from it. Existing works usually focus more on the stability and restrict the learning plasticity of later tasks to avoid catastrophic forgetting of learned knowledge. Differently, we propose a continual learning method named Split2MetaFusion which can achieve better trade-off by employing a two-stage strategy: splitting and meta-weighted fusion. In this strategy, a slow model with better stability, and a fast model with better plasticity are learned sequentially at the splitting stage. Then stability and plasticity are both kept by fusing the two models in an adaptive manner. Towards this end, we design an optimizer named Task-Preferred Null Space Projector(TPNSP) to the slow learning process for narrowing the fusion gap. To achieve better model fusion, we further design a Dreaming-Meta-Weighted fusion policy for better maintaining the old and new knowledge simultaneously, which doesn't require to use the previous datasets. Experimental results and analysis reported in this work demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method for maintaining networks stability and keeping its plasticity. Our code will be released.
Adaptive Dense Pseudo Label Selection for Semi-supervised Oriented Object Detection
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:Recently, dense pseudo-label, which directly selects pseudo labels from the original output of the teacher model without any complicated post-processing steps, has received considerable attention in semi-supervised object detection (SSOD). However, for the multi-oriented and dense objects that are common in aerial scenes, existing dense pseudo-label selection methods are inefficient and impede the performance in semi-supervised oriented object detection. Therefore, we propose Adaptive Dense Pseudo Label Selection (ADPLS) for semi-supervised oriented object detection. In ADPLS, we design a simple but effective adaptive mechanism to guide the selection of dense pseudo labels. Specifically, we propose the mean Feature-Richness Score (mFRS) to estimate the density of potential objects and use this score to adjust the number of dense pseudo labels. On the DOTA-v1.5 benchmark, the proposed method outperforms previous methods especially when labeled data are scarce. For example, it achieves 49.78 mAP given only 5% of annotated data, which surpasses previous state-of-the-art method given 10% of annotated data by 1.15 mAP. Our codes will be available soon.
Two-Stream Joint-Training for Speaker Independent Acoustic-to-Articulatory Inversion
Feb 26, 2023Abstract:Acoustic-to-articulatory inversion (AAI) aims to estimate the parameters of articulators from speech audio. There are two common challenges in AAI, which are the limited data and the unsatisfactory performance in speaker independent scenario. Most current works focus on extracting features directly from speech and ignoring the importance of phoneme information which may limit the performance of AAI. To this end, we propose a novel network called SPN that uses two different streams to carry out the AAI task. Firstly, to improve the performance of speaker-independent experiment, we propose a new phoneme stream network to estimate the articulatory parameters as the phoneme features. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that extracts the speaker-independent features from phonemes to improve the performance of AAI. Secondly, in order to better represent the speech information, we train a speech stream network to combine the local features and the global features. Compared with state-of-the-art (SOTA), the proposed method reduces 0.18mm on RMSE and increases 6.0% on Pearson correlation coefficient in the speaker-independent experiment. The code has been released at https://github.com/liujinyu123/AAINetwork-SPN.
MVNet: Memory Assistance and Vocal Reinforcement Network for Speech Enhancement
Sep 15, 2022



Abstract:Speech enhancement improves speech quality and promotes the performance of various downstream tasks. However, most current speech enhancement work was mainly devoted to improving the performance of downstream automatic speech recognition (ASR), only a relatively small amount of work focused on the automatic speaker verification (ASV) task. In this work, we propose a MVNet consisted of a memory assistance module which improves the performance of downstream ASR and a vocal reinforcement module which boosts the performance of ASV. In addition, we design a new loss function to improve speaker vocal similarity. Experimental results on the Libri2mix dataset show that our method outperforms baseline methods in several metrics, including speech quality, intelligibility, and speaker vocal similarity et al.
Residual-guided Personalized Speech Synthesis based on Face Image
Apr 01, 2022



Abstract:Previous works derive personalized speech features by training the model on a large dataset composed of his/her audio sounds. It was reported that face information has a strong link with the speech sound. Thus in this work, we innovatively extract personalized speech features from human faces to synthesize personalized speech using neural vocoder. A Face-based Residual Personalized Speech Synthesis Model (FR-PSS) containing a speech encoder, a speech synthesizer and a face encoder is designed for PSS. In this model, by designing two speech priors, a residual-guided strategy is introduced to guide the face feature to approach the true speech feature in the training. Moreover, considering the error of feature's absolute values and their directional bias, we formulate a novel tri-item loss function for face encoder. Experimental results show that the speech synthesized by our model is comparable to the personalized speech synthesized by training a large amount of audio data in previous works.
Solving ESL Sentence Completion Questions via Pre-trained Neural Language Models
Jul 15, 2021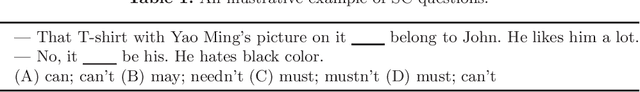
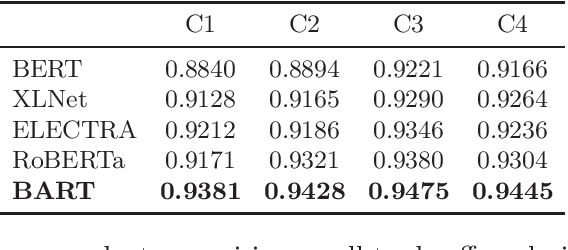
Abstract:Sentence completion (SC) questions present a sentence with one or more blanks that need to be filled in, three to five possible words or phrases as options. SC questions are widely used for students learning English as a Second Language (ESL) and building computational approaches to automatically solve such questions is beneficial to language learners. In this work, we propose a neural framework to solve SC questions in English examinations by utilizing pre-trained language models. We conduct extensive experiments on a real-world K-12 ESL SC question dataset and the results demonstrate the superiority of our model in terms of prediction accuracy. Furthermore, we run precision-recall trade-off analysis to discuss the practical issues when deploying it in real-life scenarios. To encourage reproducible results, we make our code publicly available at \url{https://github.com/AIED2021/ESL-SentenceCompletion}.
Cross-Modal Knowledge Distillation Method for Automatic Cued Speech Recognition
Jun 25, 2021



Abstract:Cued Speech (CS) is a visual communication system for the deaf or hearing impaired people. It combines lip movements with hand cues to obtain a complete phonetic repertoire. Current deep learning based methods on automatic CS recognition suffer from a common problem, which is the data scarcity. Until now, there are only two public single speaker datasets for French (238 sentences) and British English (97 sentences). In this work, we propose a cross-modal knowledge distillation method with teacher-student structure, which transfers audio speech information to CS to overcome the limited data problem. Firstly, we pretrain a teacher model for CS recognition with a large amount of open source audio speech data, and simultaneously pretrain the feature extractors for lips and hands using CS data. Then, we distill the knowledge from teacher model to the student model with frame-level and sequence-level distillation strategies. Importantly, for frame-level, we exploit multi-task learning to weigh losses automatically, to obtain the balance coefficient. Besides, we establish a five-speaker British English CS dataset for the first time. The proposed method is evaluated on French and British English CS datasets, showing superior CS recognition performance to the state-of-the-art (SOTA) by a large margin.
Three-Dimensional Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent Speaker Recognition
Oct 13, 2020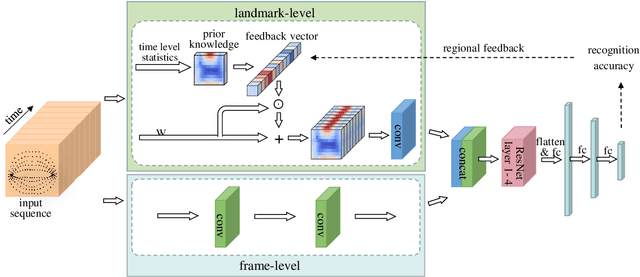
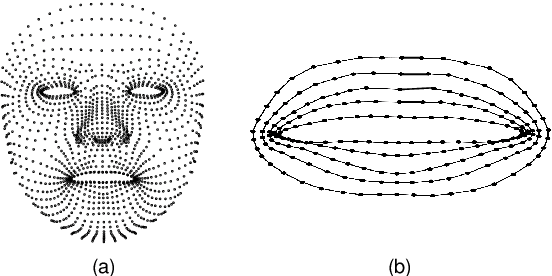
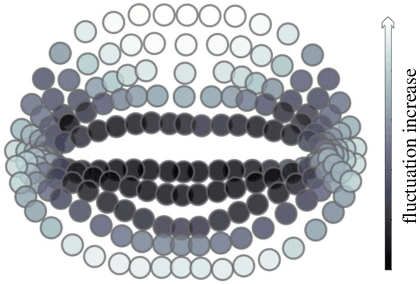
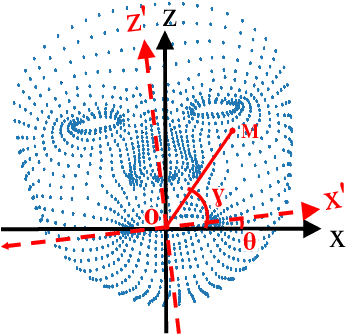
Abstract:Lip motion reflects behavior characteristics of speakers, and thus can be used as a new kind of biometrics in speaker recognition. In the literature, lots of works used two-dimensional (2D) lip images to recognize speaker in a textdependent context. However, 2D lip easily suffers from various face orientations. To this end, in this work, we present a novel end-to-end 3D lip motion Network (3LMNet) by utilizing the sentence-level 3D lip motion (S3DLM) to recognize speakers in both the text-independent and text-dependent contexts. A new regional feedback module (RFM) is proposed to obtain attentions in different lip regions. Besides, prior knowledge of lip motion is investigated to complement RFM, where landmark-level and frame-level features are merged to form a better feature representation. Moreover, we present two methods, i.e., coordinate transformation and face posture correction to pre-process the LSD-AV dataset, which contains 68 speakers and 146 sentences per speaker. The evaluation results on this dataset demonstrate that our proposed 3LMNet is superior to the baseline models, i.e., LSTM, VGG-16 and ResNet-34, and outperforms the state-of-the-art using 2D lip image as well as the 3D face. The code of this work is released at https://github.com/wutong18/Three-Dimensional-Lip- Motion-Network-for-Text-Independent-Speaker-Recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge