Ju Zhang
Interpretable deep learning illuminates multiple structures fluorescence imaging: a path toward trustworthy artificial intelligence in microscopy
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:Live-cell imaging of multiple subcellular structures is essential for understanding subcellular dynamics. However, the conventional multi-color sequential fluorescence microscopy suffers from significant imaging delays and limited number of subcellular structure separate labeling, resulting in substantial limitations for real-time live-cell research applications. Here, we present the Adaptive Explainable Multi-Structure Network (AEMS-Net), a deep-learning framework that enables simultaneous prediction of two subcellular structures from a single image. The model normalizes staining intensity and prioritizes critical image features by integrating attention mechanisms and brightness adaptation layers. Leveraging the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem, our model decomposes learned features into interpretable univariate functions, enhancing the explainability of complex subcellular morphologies. We demonstrate that AEMS-Net allows real-time recording of interactions between mitochondria and microtubules, requiring only half the conventional sequential-channel imaging procedures. Notably, this approach achieves over 30% improvement in imaging quality compared to traditional deep learning methods, establishing a new paradigm for long-term, interpretable live-cell imaging that advances the ability to explore subcellular dynamics.
Using multiple reference audios and style embedding constraints for speech synthesis
Oct 09, 2021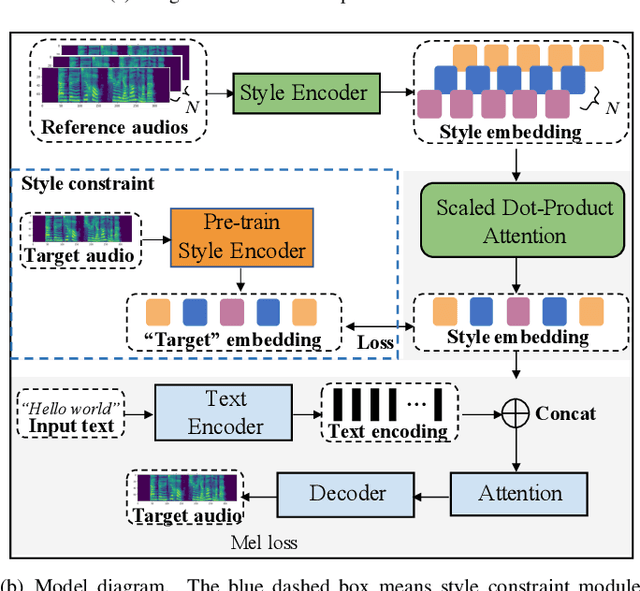
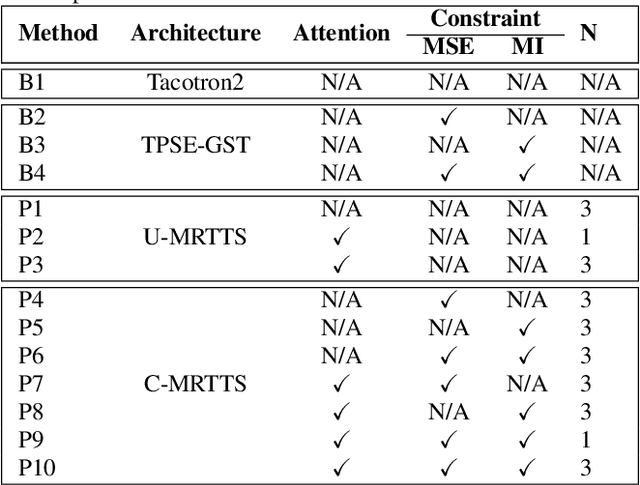
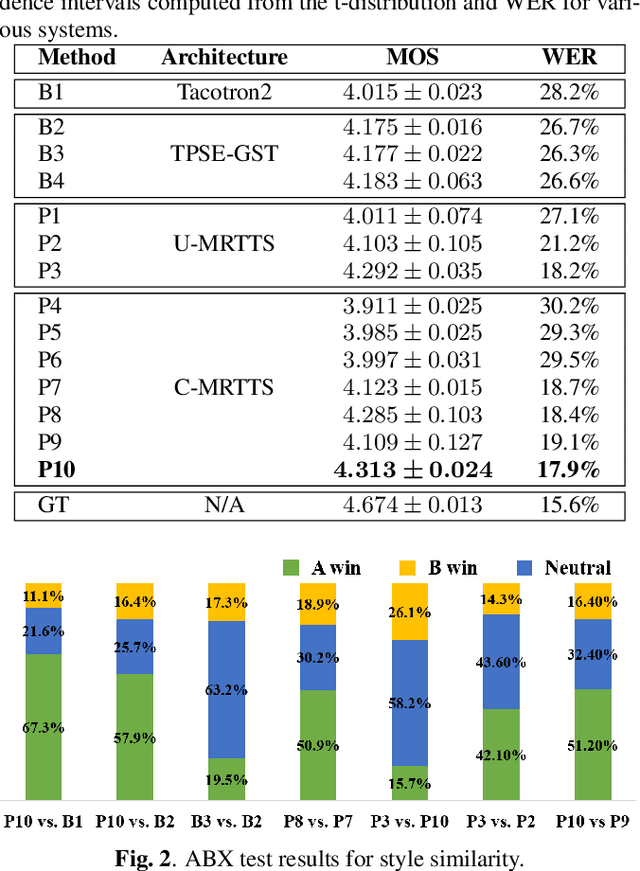
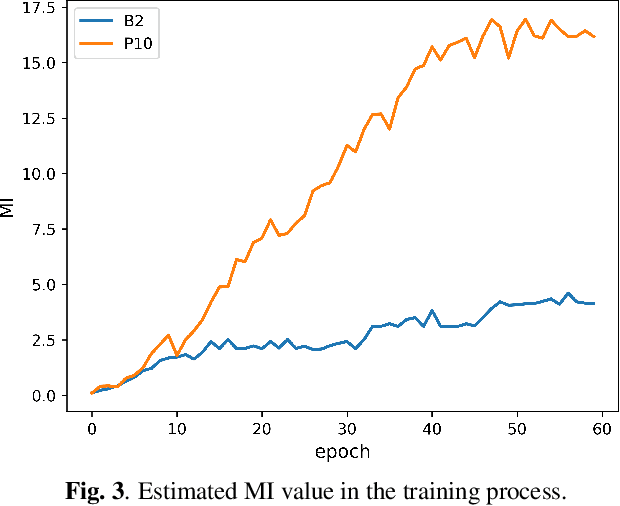
Abstract:The end-to-end speech synthesis model can directly take an utterance as reference audio, and generate speech from the text with prosody and speaker characteristics similar to the reference audio. However, an appropriate acoustic embedding must be manually selected during inference. Due to the fact that only the matched text and speech are used in the training process, using unmatched text and speech for inference would cause the model to synthesize speech with low content quality. In this study, we propose to mitigate these two problems by using multiple reference audios and style embedding constraints rather than using only the target audio. Multiple reference audios are automatically selected using the sentence similarity determined by Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT). In addition, we use ''target'' style embedding from a Pre-trained encoder as a constraint by considering the mutual information between the predicted and ''target'' style embedding. The experimental results show that the proposed model can improve the speech naturalness and content quality with multiple reference audios and can also outperform the baseline model in ABX preference tests of style similarity.
Three-Dimensional Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent Speaker Recognition
Oct 13, 2020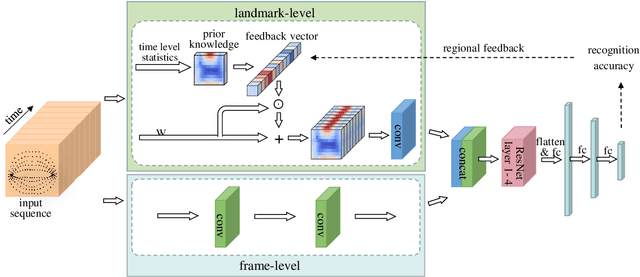
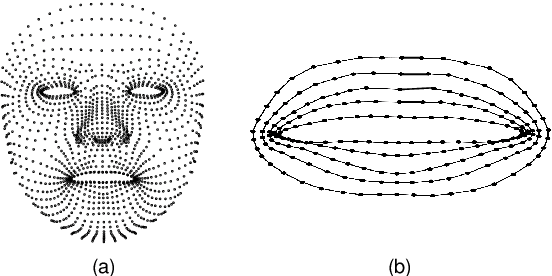
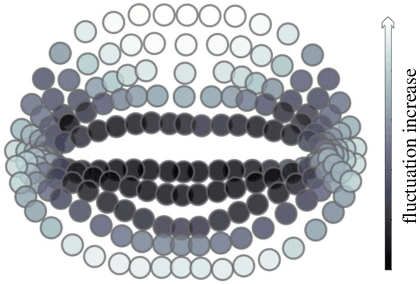
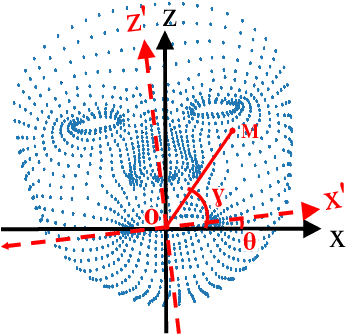
Abstract:Lip motion reflects behavior characteristics of speakers, and thus can be used as a new kind of biometrics in speaker recognition. In the literature, lots of works used two-dimensional (2D) lip images to recognize speaker in a textdependent context. However, 2D lip easily suffers from various face orientations. To this end, in this work, we present a novel end-to-end 3D lip motion Network (3LMNet) by utilizing the sentence-level 3D lip motion (S3DLM) to recognize speakers in both the text-independent and text-dependent contexts. A new regional feedback module (RFM) is proposed to obtain attentions in different lip regions. Besides, prior knowledge of lip motion is investigated to complement RFM, where landmark-level and frame-level features are merged to form a better feature representation. Moreover, we present two methods, i.e., coordinate transformation and face posture correction to pre-process the LSD-AV dataset, which contains 68 speakers and 146 sentences per speaker. The evaluation results on this dataset demonstrate that our proposed 3LMNet is superior to the baseline models, i.e., LSTM, VGG-16 and ResNet-34, and outperforms the state-of-the-art using 2D lip image as well as the 3D face. The code of this work is released at https://github.com/wutong18/Three-Dimensional-Lip- Motion-Network-for-Text-Independent-Speaker-Recognition.
Hybrid Adaptive Fuzzy Extreme Learning Machine for text classification
May 10, 2018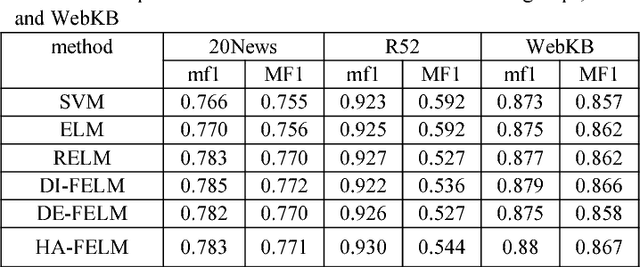
Abstract:In traditional ELM and its improved versions suffer from the problems of outliers or noises due to overfitting and imbalance due to distribution. We propose a novel hybrid adaptive fuzzy ELM(HA-FELM), which introduces a fuzzy membership function to the traditional ELM method to deal with the above problems. We define the fuzzy membership function not only basing on the distance between each sample and the center of the class but also the density among samples which based on the quantum harmonic oscillator model. The proposed fuzzy membership function overcomes the shortcoming of the traditional fuzzy membership function and could make itself adjusted according to the specific distribution of different samples adaptively. Experiments show the proposed HA-FELM can produce better performance than SVM, ELM, and RELM in text classification.
Text classification based on ensemble extreme learning machine
May 10, 2018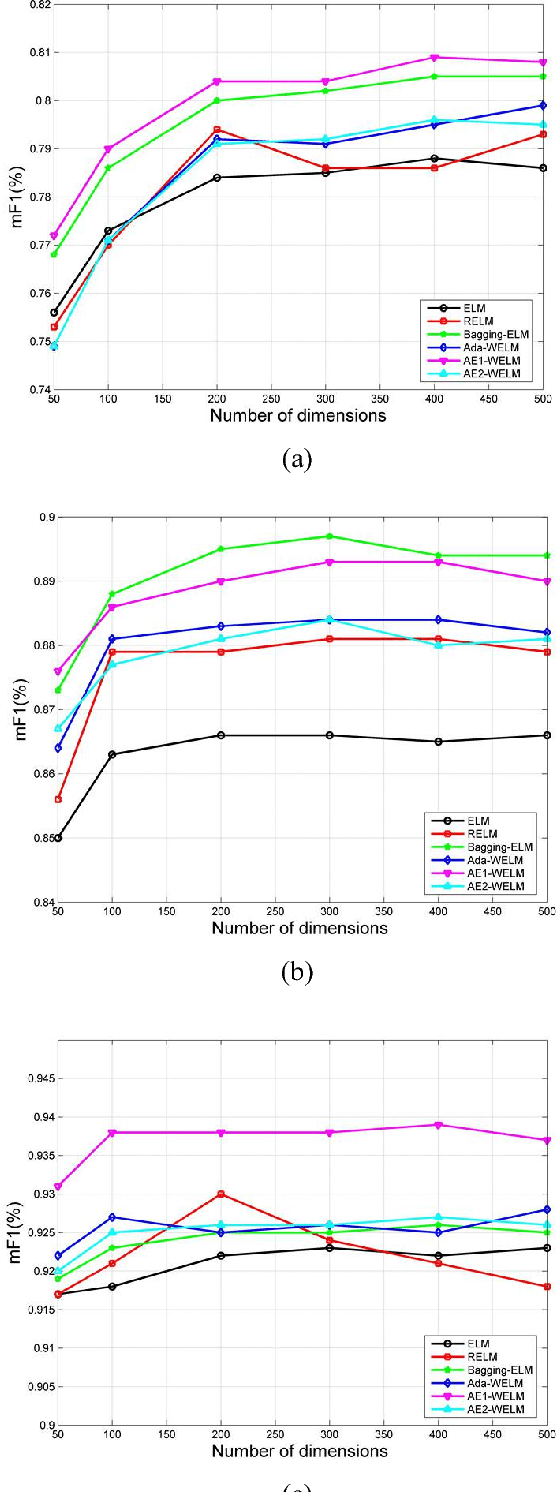
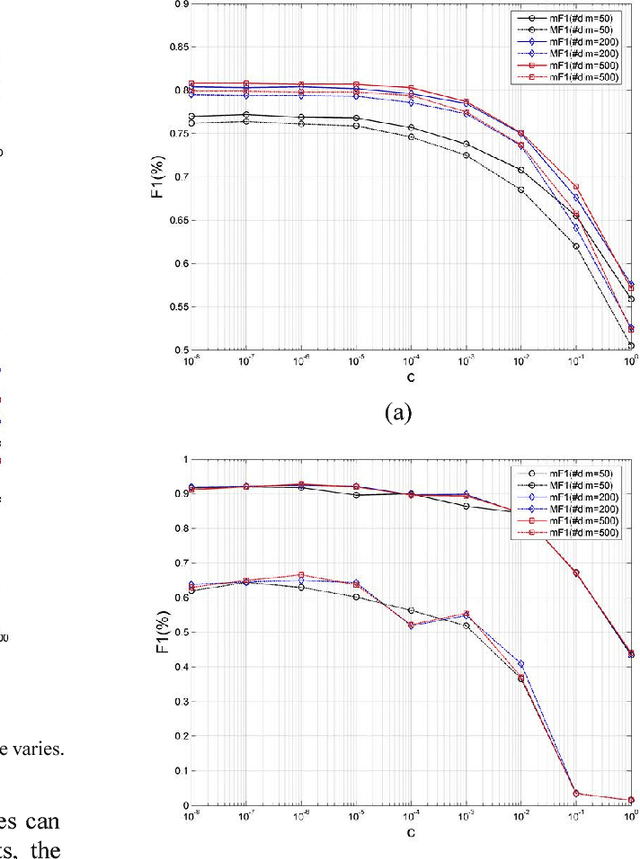
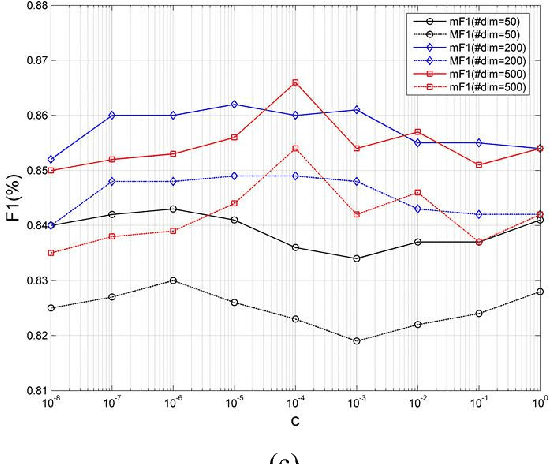
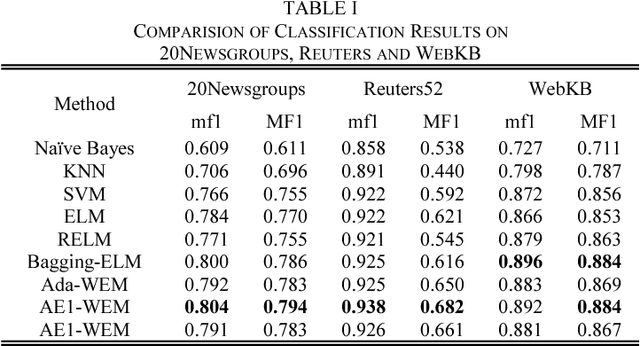
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel approach based on cost-sensitive ensemble weighted extreme learning machine; we call this approach AE1-WELM. We apply this approach to text classification. AE1-WELM is an algorithm including balanced and imbalanced multiclassification for text classification. Weighted ELM assigning the different weights to the different samples improves the classification accuracy to a certain extent, but weighted ELM considers the differences between samples in the different categories only and ignores the differences between samples within the same categories. We measure the importance of the documents by the sample information entropy, and generate cost-sensitive matrix and factor based on the document importance, then embed the cost-sensitive weighted ELM into the AdaBoost.M1 framework seamlessly. Vector space model(VSM) text representation produces the high dimensions and sparse features which increase the burden of ELM. To overcome this problem, we develop a text classification framework combining the word vector and AE1-WELM. The experimental results show that our method provides an accurate, reliable and effective solution for text classification.
A WL-SPPIM Semantic Model for Document Classification
May 26, 2017
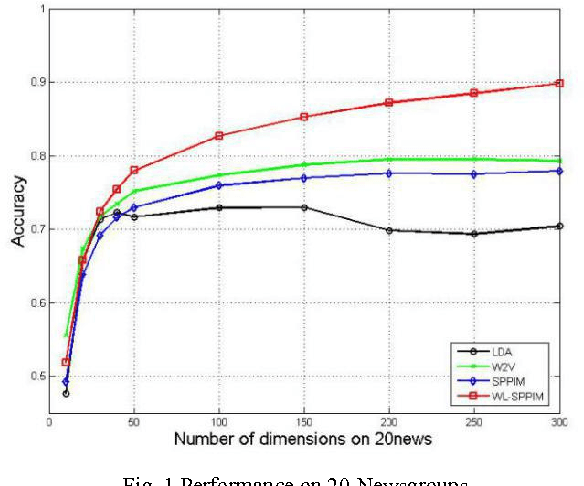
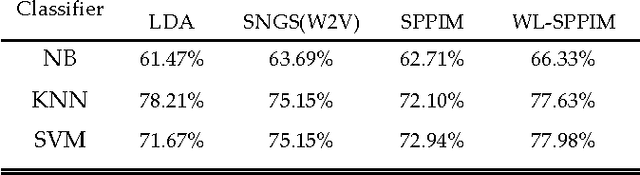
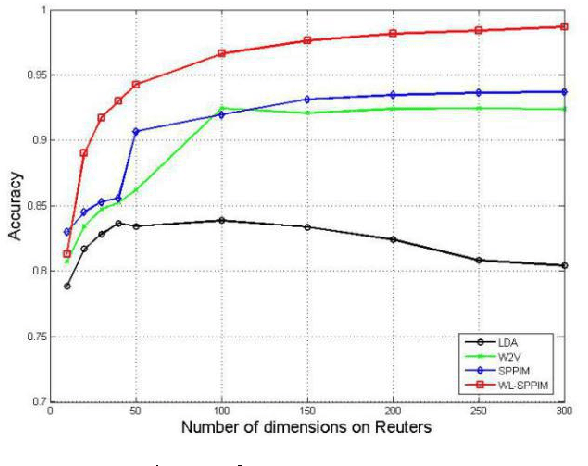
Abstract:In this paper, we explore SPPIM-based text classification method, and the experiment reveals that the SPPIM method is equal to or even superior than SGNS method in text classification task on three international and standard text datasets, namely 20newsgroups, Reuters52 and WebKB. Comparing to SGNS, although SPPMI provides a better solution, it is not necessarily better than SGNS in text classification tasks. Based on our analysis, SGNS takes into the consideration of weight calculation during decomposition process, so it has better performance than SPPIM in some standard datasets. Inspired by this, we propose a WL-SPPIM semantic model based on SPPIM model, and experiment shows that WL-SPPIM approach has better classification and higher scalability in the text classification task compared with LDA, SGNS and SPPIM approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge