Paul Covington
EMMA: End-to-End Multimodal Model for Autonomous Driving
Oct 30, 2024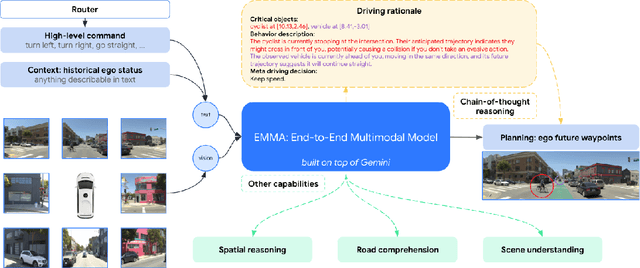
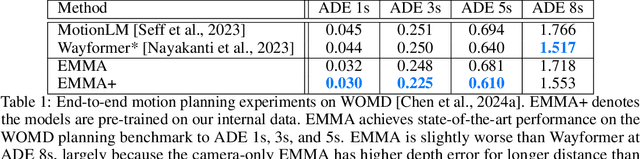
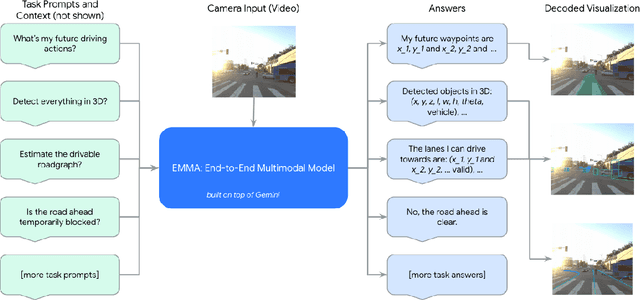
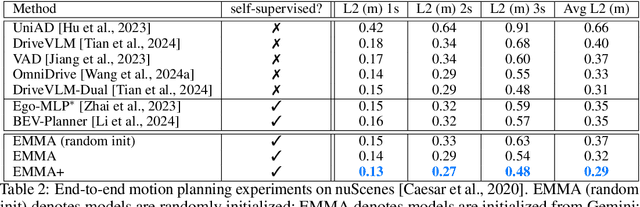
Abstract:We introduce EMMA, an End-to-end Multimodal Model for Autonomous driving. Built on a multi-modal large language model foundation, EMMA directly maps raw camera sensor data into various driving-specific outputs, including planner trajectories, perception objects, and road graph elements. EMMA maximizes the utility of world knowledge from the pre-trained large language models, by representing all non-sensor inputs (e.g. navigation instructions and ego vehicle status) and outputs (e.g. trajectories and 3D locations) as natural language text. This approach allows EMMA to jointly process various driving tasks in a unified language space, and generate the outputs for each task using task-specific prompts. Empirically, we demonstrate EMMA's effectiveness by achieving state-of-the-art performance in motion planning on nuScenes as well as competitive results on the Waymo Open Motion Dataset (WOMD). EMMA also yields competitive results for camera-primary 3D object detection on the Waymo Open Dataset (WOD). We show that co-training EMMA with planner trajectories, object detection, and road graph tasks yields improvements across all three domains, highlighting EMMA's potential as a generalist model for autonomous driving applications. However, EMMA also exhibits certain limitations: it can process only a small amount of image frames, does not incorporate accurate 3D sensing modalities like LiDAR or radar and is computationally expensive. We hope that our results will inspire further research to mitigate these issues and to further evolve the state of the art in autonomous driving model architectures.
KEMP: Keyframe-Based Hierarchical End-to-End Deep Model for Long-Term Trajectory Prediction
May 10, 2022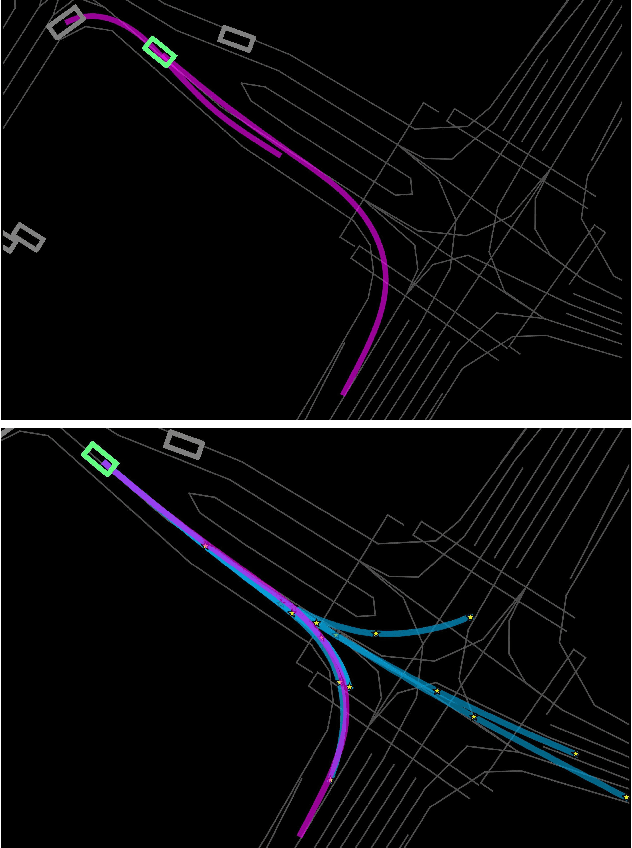
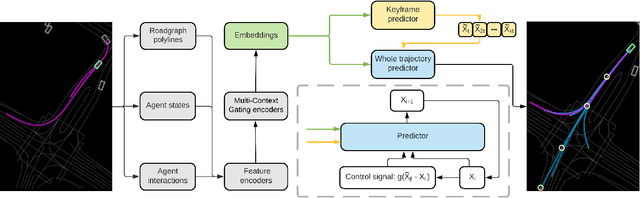
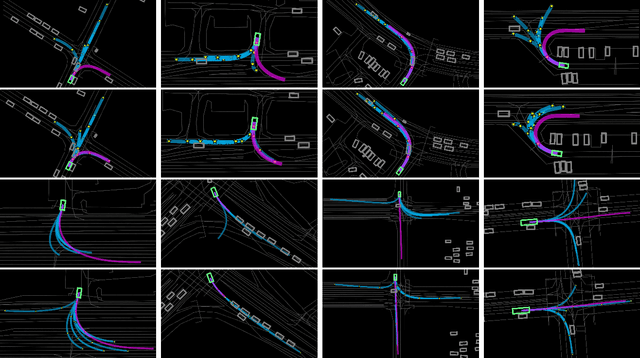
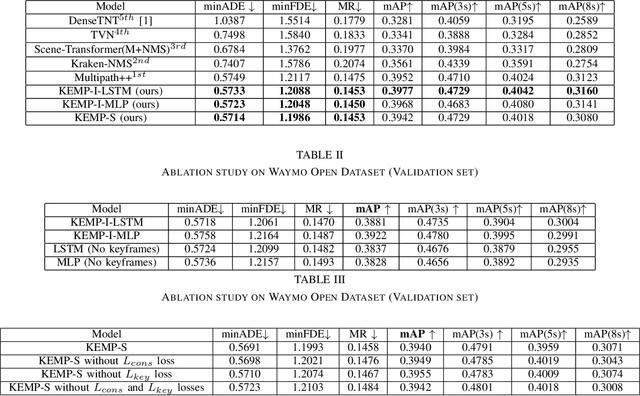
Abstract:Predicting future trajectories of road agents is a critical task for autonomous driving. Recent goal-based trajectory prediction methods, such as DenseTNT and PECNet, have shown good performance on prediction tasks on public datasets. However, they usually require complicated goal-selection algorithms and optimization. In this work, we propose KEMP, a hierarchical end-to-end deep learning framework for trajectory prediction. At the core of our framework is keyframe-based trajectory prediction, where keyframes are representative states that trace out the general direction of the trajectory. KEMP first predicts keyframes conditioned on the road context, and then fills in intermediate states conditioned on the keyframes and the road context. Under our general framework, goal-conditioned methods are special cases in which the number of keyframes equal to one. Unlike goal-conditioned methods, our keyframe predictor is learned automatically and does not require hand-crafted goal-selection algorithms. We evaluate our model on public benchmarks and our model ranked 1st on Waymo Open Motion Dataset Leaderboard (as of September 1, 2021).
Reinforcement Learning for Slate-based Recommender Systems: A Tractable Decomposition and Practical Methodology
May 31, 2019


Abstract:Most practical recommender systems focus on estimating immediate user engagement without considering the long-term effects of recommendations on user behavior. Reinforcement learning (RL) methods offer the potential to optimize recommendations for long-term user engagement. However, since users are often presented with slates of multiple items - which may have interacting effects on user choice - methods are required to deal with the combinatorics of the RL action space. In this work, we address the challenge of making slate-based recommendations to optimize long-term value using RL. Our contributions are three-fold. (i) We develop SLATEQ, a decomposition of value-based temporal-difference and Q-learning that renders RL tractable with slates. Under mild assumptions on user choice behavior, we show that the long-term value (LTV) of a slate can be decomposed into a tractable function of its component item-wise LTVs. (ii) We outline a methodology that leverages existing myopic learning-based recommenders to quickly develop a recommender that handles LTV. (iii) We demonstrate our methods in simulation, and validate the scalability of decomposed TD-learning using SLATEQ in live experiments on YouTube.
Top-K Off-Policy Correction for a REINFORCE Recommender System
Dec 06, 2018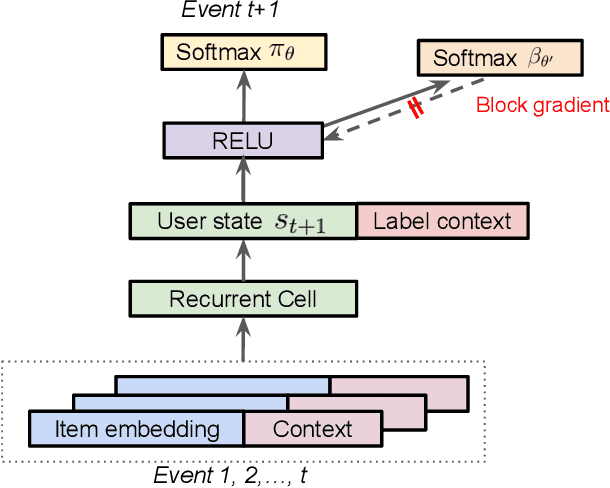
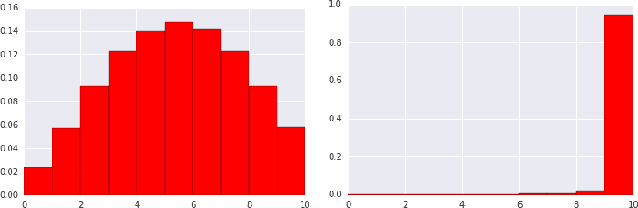
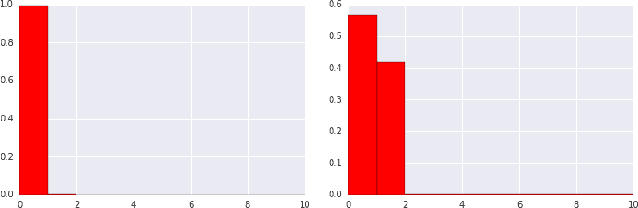
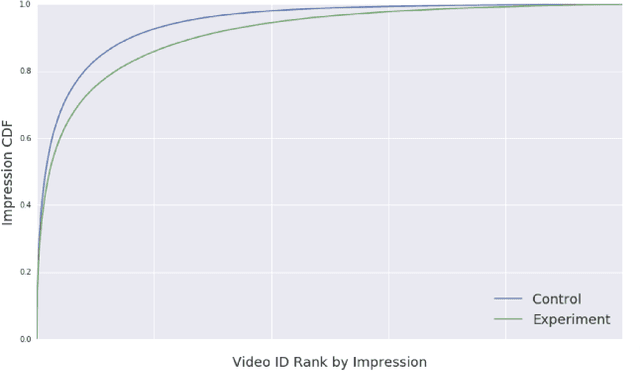
Abstract:Industrial recommender systems deal with extremely large action spaces -- many millions of items to recommend. Moreover, they need to serve billions of users, who are unique at any point in time, making a complex user state space. Luckily, huge quantities of logged implicit feedback (e.g., user clicks, dwell time) are available for learning. Learning from the logged feedback is however subject to biases caused by only observing feedback on recommendations selected by the previous versions of the recommender. In this work, we present a general recipe of addressing such biases in a production top-K recommender system at Youtube, built with a policy-gradient-based algorithm, i.e. REINFORCE. The contributions of the paper are: (1) scaling REINFORCE to a production recommender system with an action space on the orders of millions; (2) applying off-policy correction to address data biases in learning from logged feedback collected from multiple behavior policies; (3) proposing a novel top-K off-policy correction to account for our policy recommending multiple items at a time; (4) showcasing the value of exploration. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approaches through a series of simulations and multiple live experiments on Youtube.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge