Norman Sadeh
Large Language Models: A New Approach for Privacy Policy Analysis at Scale
May 31, 2024
Abstract:The number and dynamic nature of web and mobile applications presents significant challenges for assessing their compliance with data protection laws. In this context, symbolic and statistical Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques have been employed for the automated analysis of these systems' privacy policies. However, these techniques typically require labor-intensive and potentially error-prone manually annotated datasets for training and validation. This research proposes the application of Large Language Models (LLMs) as an alternative for effectively and efficiently extracting privacy practices from privacy policies at scale. Particularly, we leverage well-known LLMs such as ChatGPT and Llama 2, and offer guidance on the optimal design of prompts, parameters, and models, incorporating advanced strategies such as few-shot learning. We further illustrate its capability to detect detailed and varied privacy practices accurately. Using several renowned datasets in the domain as a benchmark, our evaluation validates its exceptional performance, achieving an F1 score exceeding 93%. Besides, it does so with reduced costs, faster processing times, and fewer technical knowledge requirements. Consequently, we advocate for LLM-based solutions as a sound alternative to traditional NLP techniques for the automated analysis of privacy policies at scale.
Purpose in the Machine: Do Traffic Simulators Produce Distributionally Equivalent Outcomes for Reinforcement Learning Applications?
Nov 14, 2023


Abstract:Traffic simulators are used to generate data for learning in intelligent transportation systems (ITSs). A key question is to what extent their modelling assumptions affect the capabilities of ITSs to adapt to various scenarios when deployed in the real world. This work focuses on two simulators commonly used to train reinforcement learning (RL) agents for traffic applications, CityFlow and SUMO. A controlled virtual experiment varying driver behavior and simulation scale finds evidence against distributional equivalence in RL-relevant measures from these simulators, with the root mean squared error and KL divergence being significantly greater than 0 for all assessed measures. While granular real-world validation generally remains infeasible, these findings suggest that traffic simulators are not a deus ex machina for RL training: understanding the impacts of inter-simulator differences is necessary to train and deploy RL-based ITSs.
Creation and Analysis of an International Corpus of Privacy Laws
Jun 28, 2022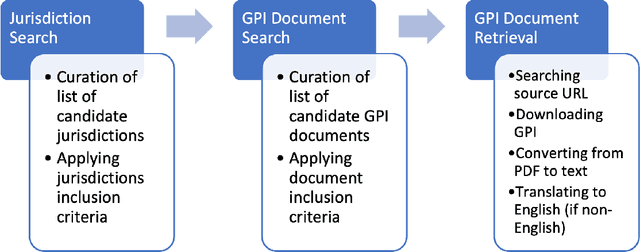
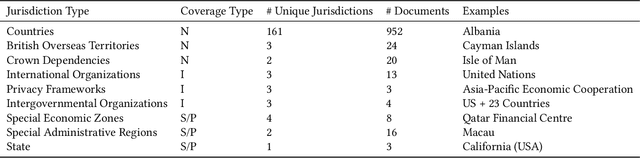
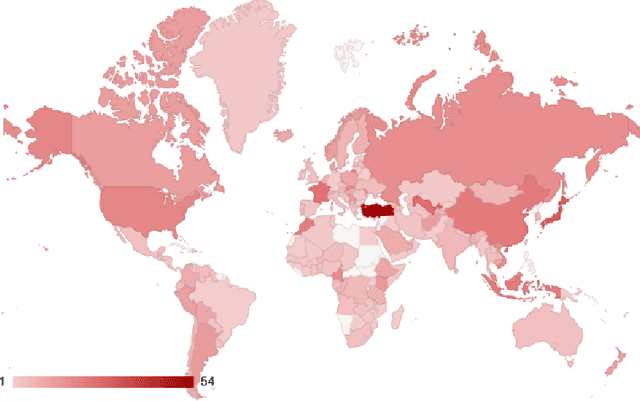
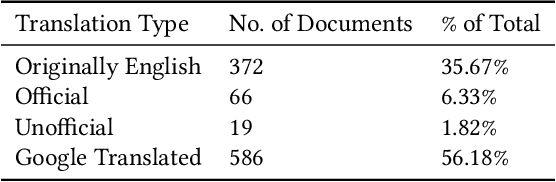
Abstract:The landscape of privacy laws and regulations around the world is complex and ever-changing. National and super-national laws, agreements, decrees, and other government-issued rules form a patchwork that companies must follow to operate internationally. To examine the status and evolution of this patchwork, we introduce the Government Privacy Instructions Corpus, or GPI Corpus, of 1,043 privacy laws, regulations, and guidelines, covering 182 jurisdictions. This corpus enables a large-scale quantitative and qualitative examination of legal foci on privacy. We examine the temporal distribution of when GPIs were created and illustrate the dramatic increase in privacy legislation over the past 50 years, although a finer-grained examination reveals that the rate of increase varies depending on the personal data types that GPIs address. Our exploration also demonstrates that most privacy laws respectively address relatively few personal data types, showing that comprehensive privacy legislation remains rare. Additionally, topic modeling results show the prevalence of common themes in GPIs, such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications. Finally, we release the corpus to the research community to promote further study.
The Real Deal: A Review of Challenges and Opportunities in Moving Reinforcement Learning-Based Traffic Signal Control Systems Towards Reality
Jun 23, 2022Abstract:Traffic signal control (TSC) is a high-stakes domain that is growing in importance as traffic volume grows globally. An increasing number of works are applying reinforcement learning (RL) to TSC; RL can draw on an abundance of traffic data to improve signalling efficiency. However, RL-based signal controllers have never been deployed. In this work, we provide the first review of challenges that must be addressed before RL can be deployed for TSC. We focus on four challenges involving (1) uncertainty in detection, (2) reliability of communications, (3) compliance and interpretability, and (4) heterogeneous road users. We show that the literature on RL-based TSC has made some progress towards addressing each challenge. However, more work should take a systems thinking approach that considers the impacts of other pipeline components on RL.
Explain, Edit, and Understand: Rethinking User Study Design for Evaluating Model Explanations
Dec 17, 2021



Abstract:In attempts to "explain" predictions of machine learning models, researchers have proposed hundreds of techniques for attributing predictions to features that are deemed important. While these attributions are often claimed to hold the potential to improve human "understanding" of the models, surprisingly little work explicitly evaluates progress towards this aspiration. In this paper, we conduct a crowdsourcing study, where participants interact with deception detection models that have been trained to distinguish between genuine and fake hotel reviews. They are challenged both to simulate the model on fresh reviews, and to edit reviews with the goal of lowering the probability of the originally predicted class. Successful manipulations would lead to an adversarial example. During the training (but not the test) phase, input spans are highlighted to communicate salience. Through our evaluation, we observe that for a linear bag-of-words model, participants with access to the feature coefficients during training are able to cause a larger reduction in model confidence in the testing phase when compared to the no-explanation control. For the BERT-based classifier, popular local explanations do not improve their ability to reduce the model confidence over the no-explanation case. Remarkably, when the explanation for the BERT model is given by the (global) attributions of a linear model trained to imitate the BERT model, people can effectively manipulate the model.
A Mixed Initiative Semantic Web Framework for Process Composition
Jun 03, 2020



Abstract:Semantic Web technologies offer the prospect of significantly reducing the amount of effort required to integrate existing enterprise functionality in support of new composite processes; whether within a given organization or across multiple ones. A significant body of work in this area has aimed to fully automate this process, while assuming that all functionality has already been encapsulated in the form of semantic web services with rich and accurate annotations. In this article, we argue that this assumption is often unrealistic. Instead, we describe a mixed initiative framework for semantic web service discovery and composition that aims at flexibly interleaving human decision making and automated functionality in environments where annotations may be incomplete and even inconsistent.
Question Answering for Privacy Policies: Combining Computational and Legal Perspectives
Nov 03, 2019
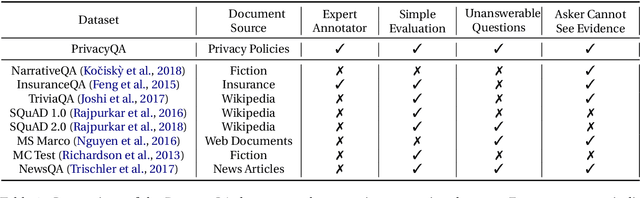

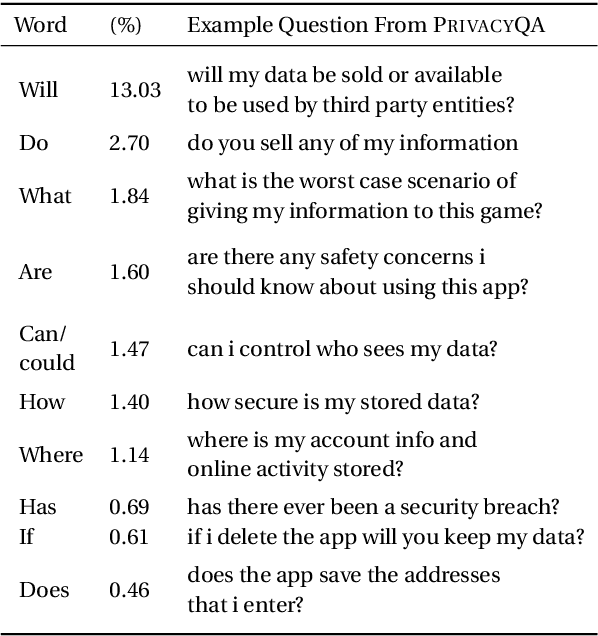
Abstract:Privacy policies are long and complex documents that are difficult for users to read and understand, and yet, they have legal effects on how user data is collected, managed and used. Ideally, we would like to empower users to inform themselves about issues that matter to them, and enable them to selectively explore those issues. We present PrivacyQA, a corpus consisting of 1750 questions about the privacy policies of mobile applications, and over 3500 expert annotations of relevant answers. We observe that a strong neural baseline underperforms human performance by almost 0.3 F1 on PrivacyQA, suggesting considerable room for improvement for future systems. Further, we use this dataset to shed light on challenges to question answerability, with domain-general implications for any question answering system. The PrivacyQA corpus offers a challenging corpus for question answering, with genuine real-world utility.
Stress Test Evaluation for Natural Language Inference
Jun 13, 2018



Abstract:Natural language inference (NLI) is the task of determining if a natural language hypothesis can be inferred from a given premise in a justifiable manner. NLI was proposed as a benchmark task for natural language understanding. Existing models perform well at standard datasets for NLI, achieving impressive results across different genres of text. However, the extent to which these models understand the semantic content of sentences is unclear. In this work, we propose an evaluation methodology consisting of automatically constructed "stress tests" that allow us to examine whether systems have the ability to make real inferential decisions. Our evaluation of six sentence-encoder models on these stress tests reveals strengths and weaknesses of these models with respect to challenging linguistic phenomena, and suggests important directions for future work in this area.
Toward Abstractive Summarization Using Semantic Representations
May 25, 2018



Abstract:We present a novel abstractive summarization framework that draws on the recent development of a treebank for the Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR). In this framework, the source text is parsed to a set of AMR graphs, the graphs are transformed into a summary graph, and then text is generated from the summary graph. We focus on the graph-to-graph transformation that reduces the source semantic graph into a summary graph, making use of an existing AMR parser and assuming the eventual availability of an AMR-to-text generator. The framework is data-driven, trainable, and not specifically designed for a particular domain. Experiments on gold-standard AMR annotations and system parses show promising results. Code is available at: https://github.com/summarization
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge