Kathleen M. Carley
Generative AI collective behavior needs an interactionist paradigm
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:In this article, we argue that understanding the collective behavior of agents based on large language models (LLMs) is an essential area of inquiry, with important implications in terms of risks and benefits, impacting us as a society at many levels. We claim that the distinctive nature of LLMs--namely, their initialization with extensive pre-trained knowledge and implicit social priors, together with their capability of adaptation through in-context learning--motivates the need for an interactionist paradigm consisting of alternative theoretical foundations, methodologies, and analytical tools, in order to systematically examine how prior knowledge and embedded values interact with social context to shape emergent phenomena in multi-agent generative AI systems. We propose and discuss four directions that we consider crucial for the development and deployment of LLM-based collectives, focusing on theory, methods, and trans-disciplinary dialogue.
Data Voids and Warning Banners on Google Search
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:The content moderation systems used by social media sites are a topic of widespread interest and research, but less is known about the use of similar systems by web search engines. For example, Google Search attempts to help its users navigate three distinct types of data voids--when the available search results are deemed low-quality, low-relevance, or rapidly-changing--by placing one of three corresponding warning banners at the top of the search page. Here we collected 1.4M unique search queries shared on social media to surface Google's warning banners, examine when and why those banners were applied, and train deep learning models to identify data voids beyond Google's classifications. Across three data collection waves (Oct 2023, Mar 2024, Sept 2024), we found that Google returned a warning banner for about 1% of our search queries, with substantial churn in the set of queries that received a banner across waves. The low-quality banners, which warn users that their results "may not have reliable information on this topic," were especially rare, and their presence was associated with low-quality domains in the search results and conspiracy-related keywords in the search query. Low-quality banner presence was also inconsistent over short time spans, even when returning highly similar search results. In August 2024, low-quality banners stopped appearing on the SERPs we collected, but average search result quality remained largely unchanged, suggesting they may have been discontinued by Google. Using our deep learning models to analyze both queries and search results in context, we identify 29 to 58 times more low-quality data voids than there were low-quality banners, and find a similar number after the banners had disappeared. Our findings point to the need for greater transparency on search engines' content moderation practices, especially around important events like elections.
Quantifying Memorization and Retriever Performance in Retrieval-Augmented Vision-Language Models
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities in question answering (QA), but metrics for assessing their reliance on memorization versus retrieval remain underdeveloped. Moreover, while finetuned models are state-of-the-art on closed-domain tasks, general-purpose models like GPT-4o exhibit strong zero-shot performance. This raises questions about the trade-offs between memorization, generalization, and retrieval. In this work, we analyze the extent to which multimodal retrieval-augmented VLMs memorize training data compared to baseline VLMs. Using the WebQA benchmark, we contrast finetuned models with baseline VLMs on multihop retrieval and question answering, examining the impact of finetuning on data memorization. To quantify memorization in end-to-end retrieval and QA systems, we propose several proxy metrics by investigating instances where QA succeeds despite retrieval failing. Our results reveal the extent to which finetuned models rely on memorization. In contrast, retrieval-augmented VLMs have lower memorization scores, at the cost of accuracy (72% vs 52% on WebQA test set). As such, our measures pose a challenge for future work to reconcile memorization and generalization in both Open-Domain QA and joint Retrieval-QA tasks.
KOALA: Knowledge Conflict Augmentations for Robustness in Vision Language Models
Feb 19, 2025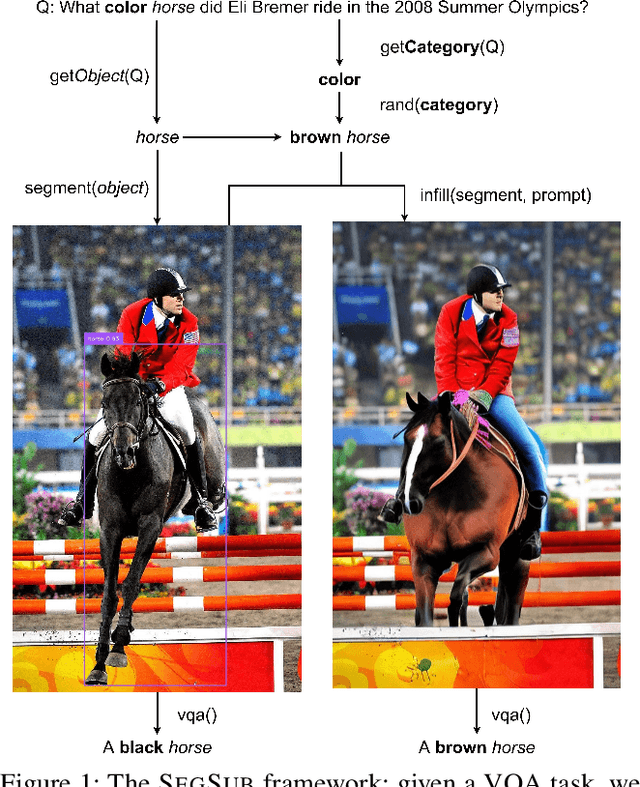
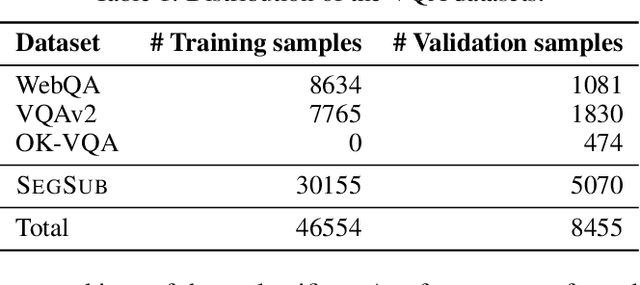


Abstract:The robustness of large language models (LLMs) against knowledge conflicts in unimodal question answering systems has been well studied. However, the effect of conflicts in information sources on vision language models (VLMs) in multimodal settings has not yet been explored. In this work, we propose \segsub, a framework that applies targeted perturbations to image sources to study and improve the robustness of VLMs against three different types of knowledge conflicts, namely parametric, source, and counterfactual conflicts. Contrary to prior findings that showed that LLMs are sensitive to parametric conflicts arising from textual perturbations, we find VLMs are largely robust to image perturbation. On the other hand, VLMs perform poorly on counterfactual examples (<30% accuracy) and fail to reason over source conflicts (<1% accuracy). We also find a link between hallucinations and image context, with GPT-4o prone to hallucination when presented with highly contextualized counterfactual examples. While challenges persist with source conflicts, finetuning models significantly improves reasoning over counterfactual samples. Our findings highlight the need for VLM training methodologies that enhance their reasoning capabilities, particularly in addressing complex knowledge conflicts between multimodal sources.
What is a Social Media Bot? A Global Comparison of Bot and Human Characteristics
Jan 01, 2025Abstract:Chatter on social media is 20% bots and 80% humans. Chatter by bots and humans is consistently different: bots tend to use linguistic cues that can be easily automated while humans use cues that require dialogue understanding. Bots use words that match the identities they choose to present, while humans may send messages that are not related to the identities they present. Bots and humans differ in their communication structure: sampled bots have a star interaction structure, while sampled humans have a hierarchical structure. These conclusions are based on a large-scale analysis of social media tweets across ~200mil users across 7 events. Social media bots took the world by storm when social-cybersecurity researchers realized that social media users not only consisted of humans but also of artificial agents called bots. These bots wreck havoc online by spreading disinformation and manipulating narratives. Most research on bots are based on special-purposed definitions, mostly predicated on the event studied. This article first begins by asking, "What is a bot?", and we study the underlying principles of how bots are different from humans. We develop a first-principle definition of a social media bot. With this definition as a premise, we systematically compare characteristics between bots and humans across global events, and reflect on how the software-programmed bot is an Artificial Intelligent algorithm, and its potential for evolution as technology advances. Based on our results, we provide recommendations for the use and regulation of bots. Finally, we discuss open challenges and future directions: Detect, to systematically identify these automated and potentially evolving bots; Differentiate, to evaluate the goodness of the bot in terms of their content postings and relationship interactions; Disrupt, to moderate the impact of malicious bots.
Dredge Word, Social Media, and Webgraph Networks for Unreliable Website Classification and Identification
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:In an attempt to mimic the complex paths through which unreliable content spreads between search engines and social media, we explore the impact of incorporating both webgraph and large-scale social media contexts into website credibility classification and discovery systems. We further explore the usage of what we define as \textit{dredge words} on social media -- terms or phrases for which unreliable domains rank highly. Through comprehensive graph neural network ablations, we demonstrate that curriculum-based heterogeneous graph models that leverage context from both webgraphs and social media data outperform homogeneous and single-mode approaches. We further demonstrate that the incorporation of dredge words into our model strongly associates unreliable websites with social media and online commerce platforms. Finally, we show our heterogeneous model greatly outperforms competing systems in the top-k identification of unlabeled unreliable websites. We demonstrate the strong unreliability signals present in the diverse paths that users follow to uncover unreliable content, and we release a novel dataset of dredge words.
Multimodal LLMs Struggle with Basic Visual Network Analysis: a VNA Benchmark
May 10, 2024



Abstract:We evaluate the zero-shot ability of GPT-4 and LLaVa to perform simple Visual Network Analysis (VNA) tasks on small-scale graphs. We evaluate the Vision Language Models (VLMs) on 5 tasks related to three foundational network science concepts: identifying nodes of maximal degree on a rendered graph, identifying whether signed triads are balanced or unbalanced, and counting components. The tasks are structured to be easy for a human who understands the underlying graph theoretic concepts, and can all be solved by counting the appropriate elements in graphs. We find that while GPT-4 consistently outperforms LLaVa, both models struggle with every visual network analysis task we propose. We publicly release the first benchmark for the evaluation of VLMs on foundational VNA tasks.
Misinformation Resilient Search Rankings with Webgraph-based Interventions
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:The proliferation of unreliable news domains on the internet has had wide-reaching negative impacts on society. We introduce and evaluate interventions aimed at reducing traffic to unreliable news domains from search engines while maintaining traffic to reliable domains. We build these interventions on the principles of fairness (penalize sites for what is in their control), generality (label/fact-check agnostic), targeted (increase the cost of adversarial behavior), and scalability (works at webscale). We refine our methods on small-scale webdata as a testbed and then generalize the interventions to a large-scale webgraph containing 93.9M domains and 1.6B edges. We demonstrate that our methods penalize unreliable domains far more than reliable domains in both settings and we explore multiple avenues to mitigate unintended effects on both the small-scale and large-scale webgraph experiments. These results indicate the potential of our approach to reduce the spread of misinformation and foster a more reliable online information ecosystem. This research contributes to the development of targeted strategies to enhance the trustworthiness and quality of search engine results, ultimately benefiting users and the broader digital community.
Purpose in the Machine: Do Traffic Simulators Produce Distributionally Equivalent Outcomes for Reinforcement Learning Applications?
Nov 14, 2023


Abstract:Traffic simulators are used to generate data for learning in intelligent transportation systems (ITSs). A key question is to what extent their modelling assumptions affect the capabilities of ITSs to adapt to various scenarios when deployed in the real world. This work focuses on two simulators commonly used to train reinforcement learning (RL) agents for traffic applications, CityFlow and SUMO. A controlled virtual experiment varying driver behavior and simulation scale finds evidence against distributional equivalence in RL-relevant measures from these simulators, with the root mean squared error and KL divergence being significantly greater than 0 for all assessed measures. While granular real-world validation generally remains infeasible, these findings suggest that traffic simulators are not a deus ex machina for RL training: understanding the impacts of inter-simulator differences is necessary to train and deploy RL-based ITSs.
Identity Construction in a Misogynist Incels Forum
Jul 09, 2023



Abstract:Online communities of involuntary celibates (incels) are a prominent source of misogynist hate speech. In this paper, we use quantitative text and network analysis approaches to examine how identity groups are discussed on incels-dot-is, the largest black-pilled incels forum. We find that this community produces a wide range of novel identity terms and, while terms for women are most common, mentions of other minoritized identities are increasing. An analysis of the associations made with identity groups suggests an essentialist ideology where physical appearance, as well as gender and racial hierarchies, determine human value. We discuss implications for research into automated misogynist hate speech detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge