Ronald E. Robertson
Data Voids and Warning Banners on Google Search
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:The content moderation systems used by social media sites are a topic of widespread interest and research, but less is known about the use of similar systems by web search engines. For example, Google Search attempts to help its users navigate three distinct types of data voids--when the available search results are deemed low-quality, low-relevance, or rapidly-changing--by placing one of three corresponding warning banners at the top of the search page. Here we collected 1.4M unique search queries shared on social media to surface Google's warning banners, examine when and why those banners were applied, and train deep learning models to identify data voids beyond Google's classifications. Across three data collection waves (Oct 2023, Mar 2024, Sept 2024), we found that Google returned a warning banner for about 1% of our search queries, with substantial churn in the set of queries that received a banner across waves. The low-quality banners, which warn users that their results "may not have reliable information on this topic," were especially rare, and their presence was associated with low-quality domains in the search results and conspiracy-related keywords in the search query. Low-quality banner presence was also inconsistent over short time spans, even when returning highly similar search results. In August 2024, low-quality banners stopped appearing on the SERPs we collected, but average search result quality remained largely unchanged, suggesting they may have been discontinued by Google. Using our deep learning models to analyze both queries and search results in context, we identify 29 to 58 times more low-quality data voids than there were low-quality banners, and find a similar number after the banners had disappeared. Our findings point to the need for greater transparency on search engines' content moderation practices, especially around important events like elections.
Subscriptions and external links help drive resentful users to alternative and extremist YouTube videos
Apr 22, 2022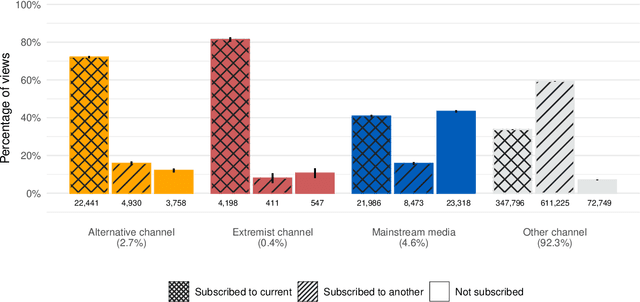
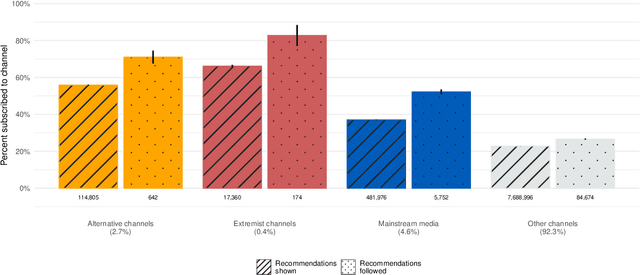
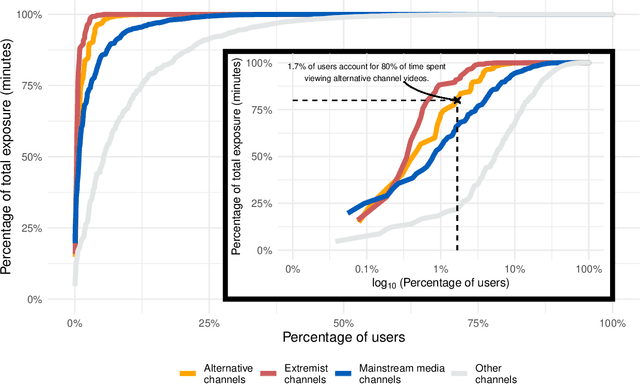
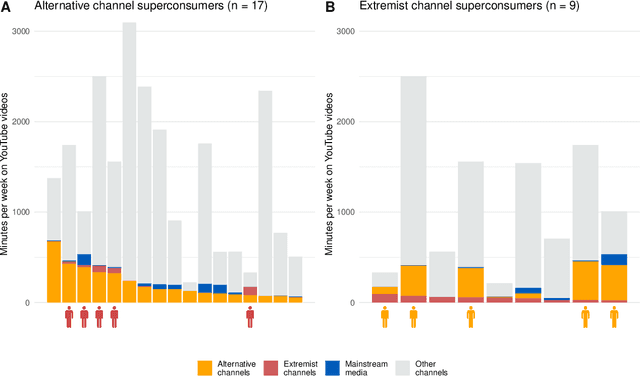
Abstract:Do online platforms facilitate the consumption of potentially harmful content? Despite widespread concerns that YouTube's algorithms send people down "rabbit holes" with recommendations to extremist videos, little systematic evidence exists to support this conjecture. Using paired behavioral and survey data provided by participants recruited from a representative sample (n=1,181), we show that exposure to alternative and extremist channel videos on YouTube is heavily concentrated among a small group of people with high prior levels of gender and racial resentment. These viewers typically subscribe to these channels (causing YouTube to recommend their videos more often) and often follow external links to them. Contrary to the "rabbit holes" narrative, non-subscribers are rarely recommended videos from alternative and extremist channels and seldom follow such recommendations when offered.
Googling for Abortion: Search Engine Mediation of Abortion Accessibility in the United States
Feb 23, 2022



Abstract:Among the myriad barriers to abortion access, crisis pregnancy centers (CPCs) pose an additional difficulty by targeting women with unexpected or "crisis" pregnancies in order to dissuade them from the procedure. Web search engines may prove to be another barrier, being in a powerful position to direct their users to health information, and above all, health services. In this study we ask, to what degree does Google Search provide quality responses to users searching for an abortion provider, specifically in terms of directing them to abortion clinics (ACs) or CPCs. To answer this question, we considered the scenario of a woman searching for abortion services online, and conducted 10 abortion-related queries from 467 locations across the United States once a week for 14 weeks. Overall, among Google's location results that feature businesses alongside a map, 79.4% were ACs, and 6.9% were CPCs. When an AC was returned, it was the closest known AC location 86.9% of the time. However, when a CPC appeared in a result set, it was the closest one to the search location 75.9% of the time. Examining correlates of AC results, we found that fewer AC results were returned for searches from poorer and rural areas, and those with TRAP laws governing AC facility and clinician requirements. We also observed that Google's performance on our queries significantly improved following a major algorithm update. These results have important implications concerning health access quality and equity, both for individual users and public health policy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge