Peter Carragher
Quantifying Memorization and Retriever Performance in Retrieval-Augmented Vision-Language Models
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities in question answering (QA), but metrics for assessing their reliance on memorization versus retrieval remain underdeveloped. Moreover, while finetuned models are state-of-the-art on closed-domain tasks, general-purpose models like GPT-4o exhibit strong zero-shot performance. This raises questions about the trade-offs between memorization, generalization, and retrieval. In this work, we analyze the extent to which multimodal retrieval-augmented VLMs memorize training data compared to baseline VLMs. Using the WebQA benchmark, we contrast finetuned models with baseline VLMs on multihop retrieval and question answering, examining the impact of finetuning on data memorization. To quantify memorization in end-to-end retrieval and QA systems, we propose several proxy metrics by investigating instances where QA succeeds despite retrieval failing. Our results reveal the extent to which finetuned models rely on memorization. In contrast, retrieval-augmented VLMs have lower memorization scores, at the cost of accuracy (72% vs 52% on WebQA test set). As such, our measures pose a challenge for future work to reconcile memorization and generalization in both Open-Domain QA and joint Retrieval-QA tasks.
KOALA: Knowledge Conflict Augmentations for Robustness in Vision Language Models
Feb 19, 2025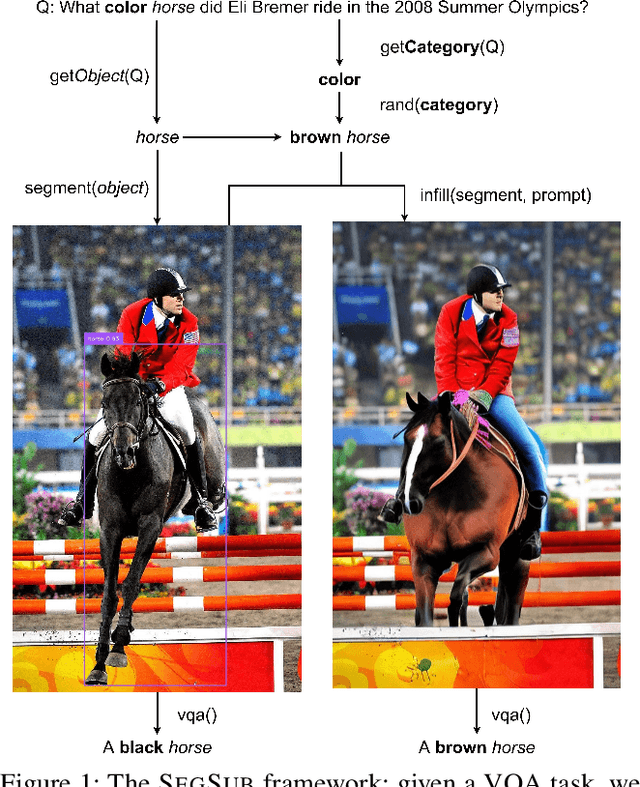


Abstract:The robustness of large language models (LLMs) against knowledge conflicts in unimodal question answering systems has been well studied. However, the effect of conflicts in information sources on vision language models (VLMs) in multimodal settings has not yet been explored. In this work, we propose \segsub, a framework that applies targeted perturbations to image sources to study and improve the robustness of VLMs against three different types of knowledge conflicts, namely parametric, source, and counterfactual conflicts. Contrary to prior findings that showed that LLMs are sensitive to parametric conflicts arising from textual perturbations, we find VLMs are largely robust to image perturbation. On the other hand, VLMs perform poorly on counterfactual examples (<30% accuracy) and fail to reason over source conflicts (<1% accuracy). We also find a link between hallucinations and image context, with GPT-4o prone to hallucination when presented with highly contextualized counterfactual examples. While challenges persist with source conflicts, finetuning models significantly improves reasoning over counterfactual samples. Our findings highlight the need for VLM training methodologies that enhance their reasoning capabilities, particularly in addressing complex knowledge conflicts between multimodal sources.
Dredge Word, Social Media, and Webgraph Networks for Unreliable Website Classification and Identification
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:In an attempt to mimic the complex paths through which unreliable content spreads between search engines and social media, we explore the impact of incorporating both webgraph and large-scale social media contexts into website credibility classification and discovery systems. We further explore the usage of what we define as \textit{dredge words} on social media -- terms or phrases for which unreliable domains rank highly. Through comprehensive graph neural network ablations, we demonstrate that curriculum-based heterogeneous graph models that leverage context from both webgraphs and social media data outperform homogeneous and single-mode approaches. We further demonstrate that the incorporation of dredge words into our model strongly associates unreliable websites with social media and online commerce platforms. Finally, we show our heterogeneous model greatly outperforms competing systems in the top-k identification of unlabeled unreliable websites. We demonstrate the strong unreliability signals present in the diverse paths that users follow to uncover unreliable content, and we release a novel dataset of dredge words.
Misinformation Resilient Search Rankings with Webgraph-based Interventions
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:The proliferation of unreliable news domains on the internet has had wide-reaching negative impacts on society. We introduce and evaluate interventions aimed at reducing traffic to unreliable news domains from search engines while maintaining traffic to reliable domains. We build these interventions on the principles of fairness (penalize sites for what is in their control), generality (label/fact-check agnostic), targeted (increase the cost of adversarial behavior), and scalability (works at webscale). We refine our methods on small-scale webdata as a testbed and then generalize the interventions to a large-scale webgraph containing 93.9M domains and 1.6B edges. We demonstrate that our methods penalize unreliable domains far more than reliable domains in both settings and we explore multiple avenues to mitigate unintended effects on both the small-scale and large-scale webgraph experiments. These results indicate the potential of our approach to reduce the spread of misinformation and foster a more reliable online information ecosystem. This research contributes to the development of targeted strategies to enhance the trustworthiness and quality of search engine results, ultimately benefiting users and the broader digital community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge