Nobuaki Minematsu
Kanade: A Simple Disentangled Tokenizer for Spoken Language Modeling
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:A good language model starts with a good tokenizer. Tokenization is especially important for speech modeling, which must handle continuous signals that mix linguistic and non-linguistic information. A speech tokenizer should extract phonetics and prosody, suppress linguistically irrelevant information like speaker identity, and enable high-quality synthesis. We present Kanade, a single-layer disentangled speech tokenizer that realizes this ideal. Kanade separates out acoustic constants to create a single stream of tokens that captures rich phonetics and prosody. It does so without the need for auxiliary methods that existing disentangled codecs often rely on. Experiments show that Kanade achieves state-of-the-art speaker disentanglement and lexical availability, while maintaining excellent reconstruction quality.
Re:Member: Emotional Question Generation from Personal Memories
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:We present Re:Member, a system that explores how emotionally expressive, memory-grounded interaction can support more engaging second language (L2) learning. By drawing on users' personal videos and generating stylized spoken questions in the target language, Re:Member is designed to encourage affective recall and conversational engagement. The system aligns emotional tone with visual context, using expressive speech styles such as whispers or late-night tones to evoke specific moods. It combines WhisperX-based transcript alignment, 3-frame visual sampling, and Style-BERT-VITS2 for emotional synthesis within a modular generation pipeline. Designed as a stylized interaction probe, Re:Member highlights the role of affect and personal media in learner-centered educational technologies.
A Perception-Based L2 Speech Intelligibility Indicator: Leveraging a Rater's Shadowing and Sequence-to-sequence Voice Conversion
May 30, 2025Abstract:Evaluating L2 speech intelligibility is crucial for effective computer-assisted language learning (CALL). Conventional ASR-based methods often focus on native-likeness, which may fail to capture the actual intelligibility perceived by human listeners. In contrast, our work introduces a novel, perception based L2 speech intelligibility indicator that leverages a native rater's shadowing data within a sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) voice conversion framework. By integrating an alignment mechanism and acoustic feature reconstruction, our approach simulates the auditory perception of native listeners, identifying segments in L2 speech that are likely to cause comprehension difficulties. Both objective and subjective evaluations indicate that our method aligns more closely with native judgments than traditional ASR-based metrics, offering a promising new direction for CALL systems in a global, multilingual contexts.
Prosodically Enhanced Foreign Accent Simulation by Discrete Token-based Resynthesis Only with Native Speech Corpora
May 22, 2025Abstract:Recently, a method for synthesizing foreign-accented speech only with native speech data using discrete tokens obtained from self-supervised learning (SSL) models was proposed. Considering limited availability of accented speech data, this method is expected to make it much easier to simulate foreign accents. By using the synthesized accented speech as listening materials for humans or training data for automatic speech recognition (ASR), both of them will acquire higher robustness against foreign accents. However, the previous method has a fatal flaw that it cannot reproduce duration-related accents. Durational accents are commonly seen when L2 speakers, whose native language has syllable-timed or mora-timed rhythm, speak stress-timed languages, such as English. In this paper, we integrate duration modification to the previous method to simulate foreign accents more accurately. Experiments show that the proposed method successfully replicates durational accents seen in real L2 speech.
Discrete Tokens Exhibit Interlanguage Speech Intelligibility Benefit: an Analytical Study Towards Accent-robust ASR Only with Native Speech Data
May 22, 2025Abstract:In this study, we gained insight that contributes to achieving accent-robust ASR using only native speech data. In human perception of non-native speech, the phenomenon known as "interlanguage speech intelligibility benefit" (ISIB) is observed, where non-native listeners who share the native language with the speaker understand the speech better compared even to native listeners. Based on the idea that discrete tokens extracted from self-supervised learning (SSL) models represent the human perception of speech, we conducted an analytical study on the robustness of discrete token-based ASR to non-native speech, varying the language used for training the tokenization, which is viewed as a technical implementation of ISIB. The results showed that ISIB actually occurred in the discrete token-based ASR. Since our approach relies only on native speech data to simulate the behavior of human perception, it is expected to be applicable to a wide range of accents for which speech data is scarce.
Analytic Study of Text-Free Speech Synthesis for Raw Audio using a Self-Supervised Learning Model
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:We examine the text-free speech representations of raw audio obtained from a self-supervised learning (SSL) model by analyzing the synthesized speech using the SSL representations instead of conventional text representations. Since raw audio does not have paired speech representations as transcribed texts do, obtaining speech representations from unpaired speech is crucial for augmenting available datasets for speech synthesis. Specifically, the proposed speech synthesis is conducted using discrete symbol representations from the SSL model in comparison with text representations, and analytical examinations of the synthesized speech have been carried out. The results empirically show that using text representations is advantageous for preserving semantic information, while using discrete symbol representations is superior for preserving acoustic content, including prosodic and intonational information.
A Pilot Study of Applying Sequence-to-Sequence Voice Conversion to Evaluate the Intelligibility of L2 Speech Using a Native Speaker's Shadowings
Oct 03, 2024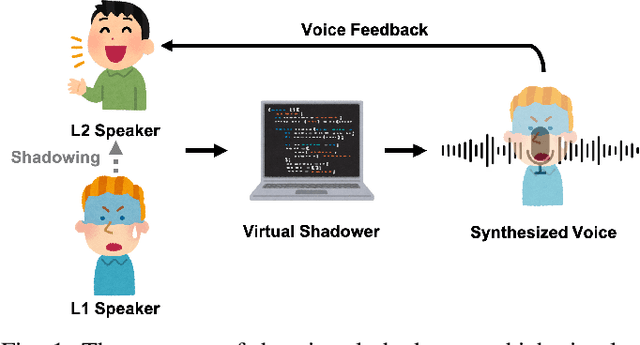
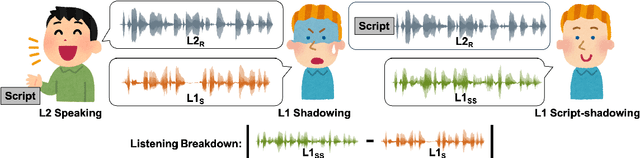

Abstract:Utterances by L2 speakers can be unintelligible due to mispronunciation and improper prosody. In computer-aided language learning systems, textual feedback is often provided using a speech recognition engine. However, an ideal form of feedback for L2 speakers should be so fine-grained that it enables them to detect and diagnose unintelligible parts of L2 speakers' utterances. Inspired by language teachers who correct students' pronunciation through a voice-to-voice process, this pilot study utilizes a unique semi-parallel dataset composed of non-native speakers' (L2) reading aloud, shadowing of native speakers (L1) and their script-shadowing utterances. We explore the technical possibility of replicating the process of an L1 speaker's shadowing L2 speech using Voice Conversion techniques, to create a virtual shadower system. Experimental results demonstrate the feasibility of the VC system in simulating L1's shadowing behavior. The output of the virtual shadower system shows a reasonable similarity to the real L1 shadowing utterances in both linguistic and acoustic aspects.
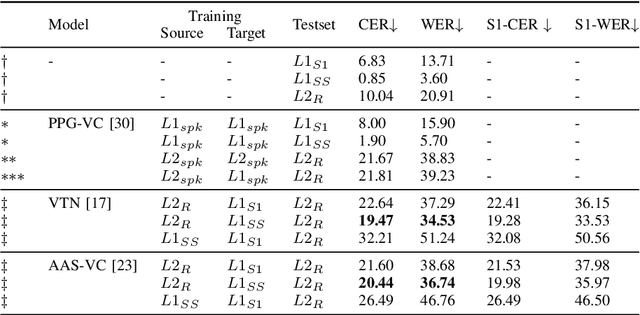
Simulating Native Speaker Shadowing for Nonnative Speech Assessment with Latent Speech Representations
Sep 19, 2024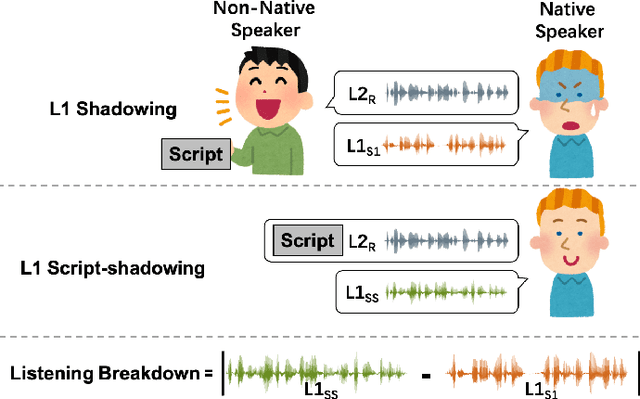
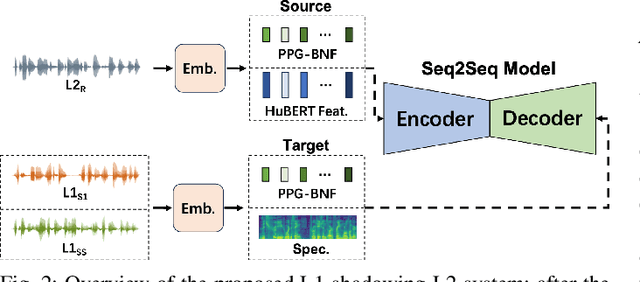
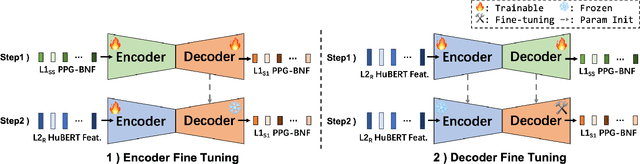
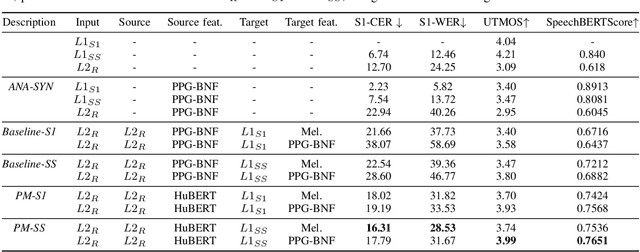
Abstract:Evaluating speech intelligibility is a critical task in computer-aided language learning systems. Traditional methods often rely on word error rates (WER) provided by automatic speech recognition (ASR) as intelligibility scores. However, this approach has significant limitations due to notable differences between human speech recognition (HSR) and ASR. A promising alternative is to involve a native (L1) speaker in shadowing what nonnative (L2) speakers say. Breakdowns or mispronunciations in the L1 speaker's shadowing utterance can serve as indicators for assessing L2 speech intelligibility. In this study, we propose a speech generation system that simulates the L1 shadowing process using voice conversion (VC) techniques and latent speech representations. Our experimental results demonstrate that this method effectively replicates the L1 shadowing process, offering an innovative tool to evaluate L2 speech intelligibility. Notably, systems that utilize self-supervised speech representations (S3R) show a higher degree of similarity to real L1 shadowing utterances in both linguistic accuracy and naturalness.
A Pilot Study of GSLM-based Simulation of Foreign Accentuation Only Using Native Speech Corpora
Jul 16, 2024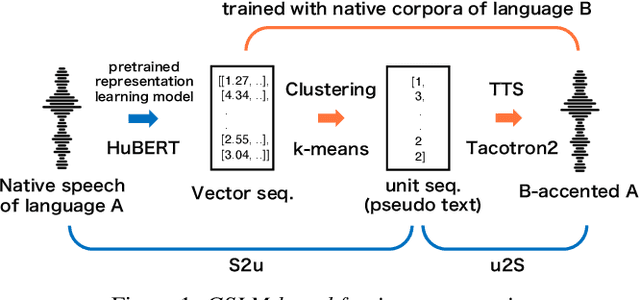
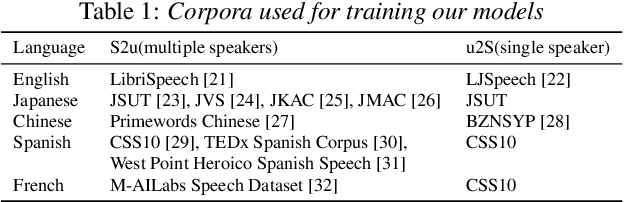
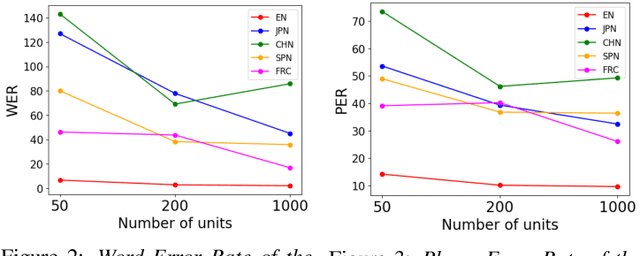

Abstract:We propose a method of simulating the human process of foreign accentuation using Generative Spoken Language Model (GSLM) only with native speech corpora. When one listens to spoken words of a foreign language and repeats them, the repeated speech is often with the accent of that listener's L1. This is said to be because the spoken words are mentally represented as a sequence of phonological units of the L1, and those units are used for oral reproduction. We simulate this process by inputting speech of language A into GSLM of language B to add B's accent onto the input speech. The process of running ASR of the L1 for foreign input speech and giving the ASR result to TTS of the L1 can be viewed as a naive implementation of this approach. The results of our experiments show that the synthesized accent of the output speech is highly natural, compared to real samples of A generated by speakers whose L1 is B, and that the degree of accentuation is controllable.
Exploring Isolated Musical Notes as Pre-training Data for Predominant Instrument Recognition in Polyphonic Music
Jun 15, 2023Abstract:With the growing amount of musical data available, automatic instrument recognition, one of the essential problems in Music Information Retrieval (MIR), is drawing more and more attention. While automatic recognition of single instruments has been well-studied, it remains challenging for polyphonic, multi-instrument musical recordings. This work presents our efforts toward building a robust end-to-end instrument recognition system for polyphonic multi-instrument music. We train our model using a pre-training and fine-tuning approach: we use a large amount of monophonic musical data for pre-training and subsequently fine-tune the model for the polyphonic ensemble. In pre-training, we apply data augmentation techniques to alleviate the domain gap between monophonic musical data and real-world music. We evaluate our method on the IRMAS testing data, a polyphonic musical dataset comprising professionally-produced commercial music recordings. Experimental results show that our best model achieves a micro F1-score of 0.674 and an LRAP of 0.814, meaning 10.9% and 8.9% relative improvement compared with the previous state-of-the-art end-to-end approach. Also, we are able to build a lightweight model, achieving competitive performance with only 519K trainable parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge