Nilanjan Chakraborty
A Unified Complementarity-based Approach for Rigid-Body Manipulation and Motion Prediction
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Robotic manipulation in unstructured environments requires planners to reason jointly about free-space motion and sustained, frictional contact with the environment. Existing (local) planning and simulation frameworks typically separate these regimes or rely on simplified contact representations, particularly when modeling non-convex or distributed contact patches. Such approximations limit the fidelity of contact-mode transitions and hinder the robust execution of contact-rich behaviors in real time. This paper presents a unified discrete-time modeling framework for robotic manipulation that consistently captures both free motion and frictional contact within a single mathematical formalism (Unicomp). Building on complementarity-based rigid-body dynamics, we formulate free-space motion and contact interactions as coupled linear and nonlinear complementarity problems, enabling principled transitions between contact modes without enforcing fixed-contact assumptions. For planar patch contact, we derive a frictional contact model from the maximum power dissipation principle in which the set of admissible contact wrenches is represented by an ellipsoidal limit surface. This representation captures coupled force-moment effects, including torsional friction, while remaining agnostic to the underlying pressure distribution across the contact patch. The resulting formulation yields a discrete-time predictive model that relates generalized velocities and contact wrenches through quadratic constraints and is suitable for real-time optimization-based planning. Experimental results show that the proposed approach enables stable, physically consistent behavior at interactive speeds across tasks, from planar pushing to contact-rich whole-body maneuvers.
Unifying Complementarity Constraints and Control Barrier Functions for Safe Whole-Body Robot Control
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Safety-critical whole-body robot control demands reactive methods that ensure collision avoidance in real-time. Complementarity constraints and control barrier functions (CBF) have emerged as core tools for ensuring such safety constraints, and each represents a well-developed field. Despite addressing similar problems, their connection remains largely unexplored. This paper bridges this gap by formally proving the equivalence between these two methodologies for sampled-data, first-order systems, considering both single and multiple constraint scenarios. By demonstrating this equivalence, we provide a unified perspective on these techniques. This unification has theoretical and practical implications, facilitating the cross-application of robustness guarantees and algorithmic improvements between complementarity and CBF frameworks. We discuss these synergistic benefits and motivate future work in the comparison of the methods in more general cases.
Transferring Kinesthetic Demonstrations across Diverse Objects for Manipulation Planning
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Given a demonstration of a complex manipulation task such as pouring liquid from one container to another, we seek to generate a motion plan for a new task instance involving objects with different geometries. This is non-trivial since we need to simultaneously ensure that the implicit motion constraints are satisfied (glass held upright while moving), the motion is collision-free, and that the task is successful (e.g. liquid is poured into the target container). We solve this problem by identifying positions of critical locations and associating a reference frame (called motion transfer frames) on the manipulated object and the target, selected based on their geometries and the task at hand. By tracking and transferring the path of the motion transfer frames, we generate motion plans for arbitrary task instances with objects of different geometries and poses. We show results from simulation as well as robot experiments on physical objects to evaluate the effectiveness of our solution.
Synthesizing Grasps and Regrasps for Complex Manipulation Tasks
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:In complex manipulation tasks, e.g., manipulation by pivoting, the motion of the object being manipulated has to satisfy path constraints that can change during the motion. Therefore, a single grasp may not be sufficient for the entire path, and the object may need to be regrasped. Additionally, geometric data for objects from a sensor are usually available in the form of point clouds. The problem of computing grasps and regrasps from point-cloud representation of objects for complex manipulation tasks is a key problem in endowing robots with manipulation capabilities beyond pick-and-place. In this paper, we formalize the problem of grasping/regrasping for complex manipulation tasks with objects represented by (partial) point clouds and present an algorithm to solve it. We represent a complex manipulation task as a sequence of constant screw motions. Using a manipulation plan skeleton as a sequence of constant screw motions, we use a grasp metric to find graspable regions on the object for every constant screw segment. The overlap of the graspable regions for contiguous screws are then used to determine when and how many times the object needs to be regrasped. We present experimental results on point cloud data collected from RGB-D sensors to illustrate our approach.
On the Synthesis of Reactive Collision-Free Whole-Body Robot Motions: A Complementarity-based Approach
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:This paper is about generating motion plans for high degree-of-freedom systems that account for collisions along the entire body. A particular class of mathematical programs with complementarity constraints become useful in this regard. Optimization-based planners can tackle confined-space trajectory planning while being cognizant of robot constraints. However, introducing obstacles in this setting transforms the formulation into a non-convex problem (oftentimes with ill-posed bilinear constraints), which is non-trivial in a real-time setting. To this end, we present the FLIQC (Fast LInear Quadratic Complementarity based) motion planner. Our planner employs a novel motion model that captures the entire rigid robot as well as the obstacle geometry and ensures non-penetration between the surfaces due to the imposed constraint. We perform thorough comparative studies with the state-of-the-art, which demonstrate improved performance. Extensive simulation and hardware experiments validate our claim of generating continuous and reactive motion plans at 1 kHz for modern collaborative robots with constant minimal parameters.
Screw Geometry Meets Bandits: Incremental Acquisition of Demonstrations to Generate Manipulation Plans
Oct 23, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we study the problem of methodically obtaining a sufficient set of kinesthetic demonstrations, one at a time, such that a robot can be confident of its ability to perform a complex manipulation task in a given region of its workspace. Although Learning from Demonstrations has been an active area of research, the problems of checking whether a set of demonstrations is sufficient, and systematically seeking additional demonstrations have remained open. We present a novel approach to address these open problems using (i) a screw geometric representation to generate manipulation plans from demonstrations, which makes the sufficiency of a set of demonstrations measurable; (ii) a sampling strategy based on PAC-learning from multi-armed bandit optimization to evaluate the robot's ability to generate manipulation plans in a subregion of its task space; and (iii) a heuristic to seek additional demonstration from areas of weakness. Thus, we present an approach for the robot to incrementally and actively ask for new demonstration examples until the robot can assess with high confidence that it can perform the task successfully. We present experimental results on two example manipulation tasks, namely, pouring and scooping, to illustrate our approach. A short video on the method: https://youtu.be/R-qICICdEos
Provable Methods for Searching with an Imperfect Sensor
Oct 08, 2024
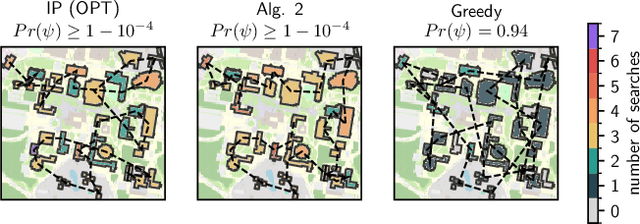
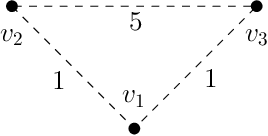
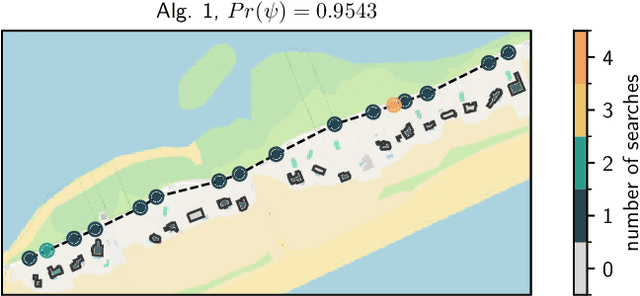
Abstract:Assume that a target is known to be present at an unknown point among a finite set of locations in the plane. We search for it using a mobile robot that has imperfect sensing capabilities. It takes time for the robot to move between locations and search a location; we have a total time budget within which to conduct the search. We study the problem of computing a search path/strategy for the robot that maximizes the probability of detection of the target. Considering non-uniform travel times between points (e.g., based on the distance between them) is crucial for search and rescue applications; such problems have been investigated to a limited extent due to their inherent complexity. In this paper, we describe fast algorithms with performance guarantees for this search problem and some variants, complement them with complexity results, and perform experiments to observe their performance.
A General Formulation for Path Constrained Time-Optimized Trajectory Planning with Environmental and Object Contacts
Oct 08, 2024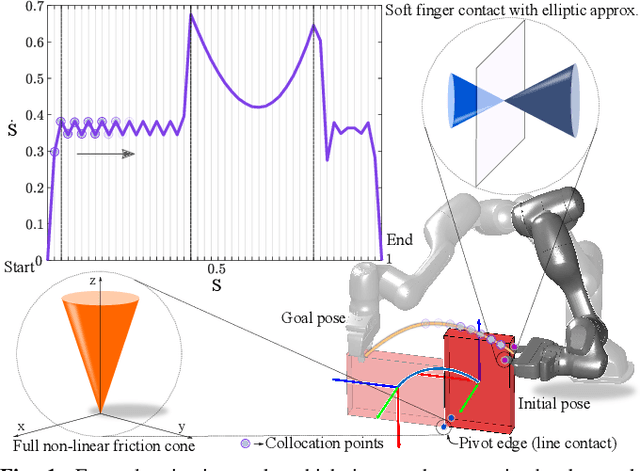
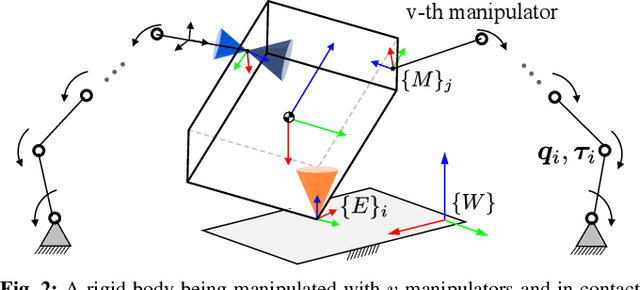
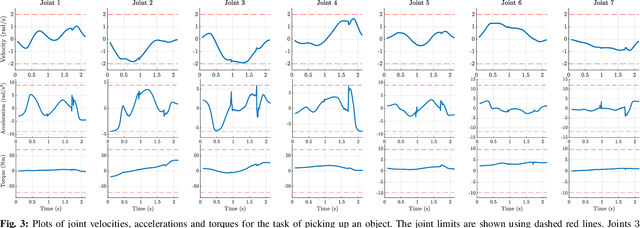
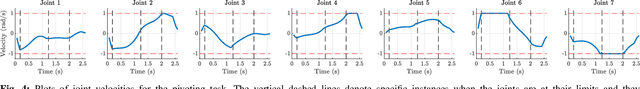
Abstract:A typical manipulation task consists of a manipulator equipped with a gripper to grasp and move an object with constraints on the motion of the hand-held object, which may be due to the nature of the task itself or from object-environment contacts. In this paper, we study the problem of computing joint torques and grasping forces for time-optimal motion of an object, while ensuring that the grasp is not lost and any constraints on the motion of the object, either due to dynamics, environment contact, or no-slip requirements, are also satisfied. We present a second-order cone program (SOCP) formulation of the time-optimal trajectory planning problem that considers nonlinear friction cone constraints at the hand-object and object-environment contacts. Since SOCPs are convex optimization problems that can be solved optimally in polynomial time using interior point methods, we can solve the trajectory optimization problem efficiently. We present simulation results on three examples, including a non-prehensile manipulation task, which shows the generality and effectiveness of our approach.
Containerized Vertical Farming Using Cobots
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:Containerized vertical farming is a type of vertical farming practice using hydroponics in which plants are grown in vertical layers within a mobile shipping container. Space limitations within shipping containers make the automation of different farming operations challenging. In this paper, we explore the use of cobots (i.e., collaborative robots) to automate two key farming operations, namely, the transplantation of saplings and the harvesting of grown plants. Our method uses a single demonstration from a farmer to extract the motion constraints associated with the tasks, namely, transplanting and harvesting, and can then generalize to different instances of the same task. For transplantation, the motion constraint arises during insertion of the sapling within the growing tube, whereas for harvesting, it arises during extraction from the growing tube. We present experimental results to show that using RGBD camera images (obtained from an eye-in-hand configuration) and one demonstration for each task, it is feasible to perform transplantation of saplings and harvesting of leafy greens using a cobot, without task-specific programming.
Task-Oriented Grasping with Point Cloud Representation of Objects
Sep 20, 2023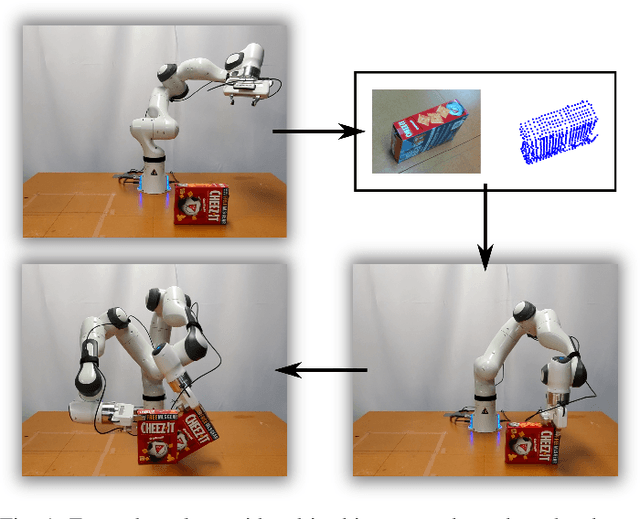
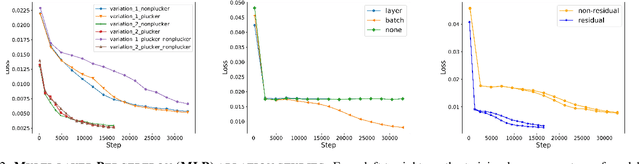
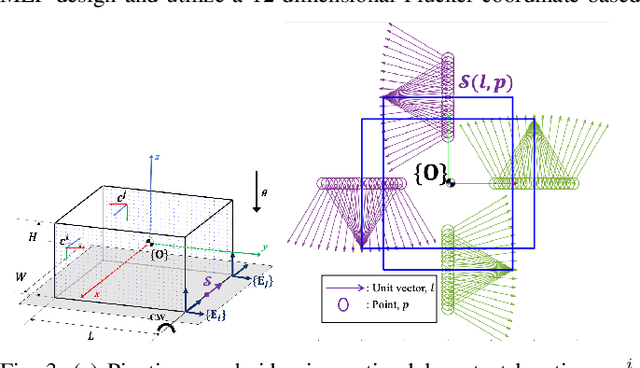
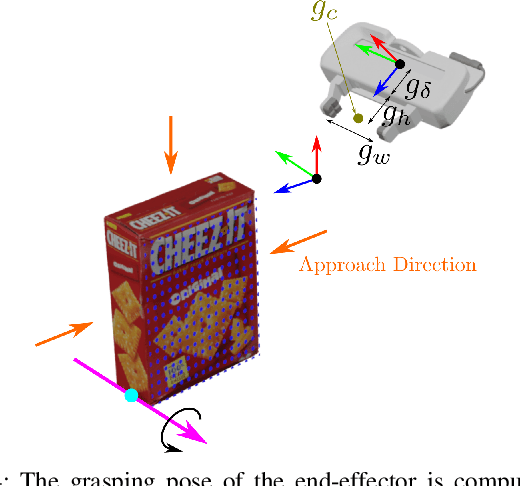
Abstract:In this paper, we study the problem of task-oriented grasp synthesis from partial point cloud data using an eye-in-hand camera configuration. In task-oriented grasp synthesis, a grasp has to be selected so that the object is not lost during manipulation, and it is also ensured that adequate force/moment can be applied to perform the task. We formalize the notion of a gross manipulation task as a constant screw motion (or a sequence of constant screw motions) to be applied to the object after grasping. Using this notion of task, and a corresponding grasp quality metric developed in our prior work, we use a neural network to approximate a function for predicting the grasp quality metric on a cuboid shape. We show that by using a bounding box obtained from the partial point cloud of an object, and the grasp quality metric mentioned above, we can generate a good grasping region on the bounding box that can be used to compute an antipodal grasp on the actual object. Our algorithm does not use any manually labeled data or grasping simulator, thus making it very efficient to implement and integrate with screw linear interpolation-based motion planners. We present simulation as well as experimental results that show the effectiveness of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge