Ni Zhang
Hybrid-Balance GFlowNet for Solving Vehicle Routing Problems
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Existing GFlowNet-based methods for vehicle routing problems (VRPs) typically employ Trajectory Balance (TB) to achieve global optimization but often neglect important aspects of local optimization. While Detailed Balance (DB) addresses local optimization more effectively, it alone falls short in solving VRPs, which inherently require holistic trajectory optimization. To address these limitations, we introduce the Hybrid-Balance GFlowNet (HBG) framework, which uniquely integrates TB and DB in a principled and adaptive manner by aligning their intrinsically complementary strengths. Additionally, we propose a specialized inference strategy for depot-centric scenarios like the Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP), leveraging the depot node's greater flexibility in selecting successors. Despite this specialization, HBG maintains broad applicability, extending effectively to problems without explicit depots, such as the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). We evaluate HBG by integrating it into two established GFlowNet-based solvers, i.e., AGFN and GFACS, and demonstrate consistent and significant improvements across both CVRP and TSP, underscoring the enhanced solution quality and generalization afforded by our approach.
Adversarial Generative Flow Network for Solving Vehicle Routing Problems
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Recent research into solving vehicle routing problems (VRPs) has gained significant traction, particularly through the application of deep (reinforcement) learning for end-to-end solution construction. However, many current construction-based neural solvers predominantly utilize Transformer architectures, which can face scalability challenges and struggle to produce diverse solutions. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel framework beyond Transformer-based approaches, i.e., Adversarial Generative Flow Networks (AGFN). This framework integrates the generative flow network (GFlowNet)-a probabilistic model inherently adept at generating diverse solutions (routes)-with a complementary model for discriminating (or evaluating) the solutions. These models are trained alternately in an adversarial manner to improve the overall solution quality, followed by a proposed hybrid decoding method to construct the solution. We apply the AGFN framework to solve the capacitated vehicle routing problem (CVRP) and travelling salesman problem (TSP), and our experimental results demonstrate that AGFN surpasses the popular construction-based neural solvers, showcasing strong generalization capabilities on synthetic and real-world benchmark instances.
Vehicular Multi-Tier Distributed Computing with Hybrid THz-RF Transmission in Satellite-Terrestrial Integrated Networks
Jan 26, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a Satellite-Terrestrial Integrated Network (STIN) assisted vehicular multi-tier distributed computing (VMDC) system leveraging hybrid terahertz (THz) and radio frequency (RF) communication technologies. Task offloading for satellite edge computing is enabled by THz communication using the orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) technique. For terrestrial edge computing, we employ non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and vehicle clustering to realize task offloading. We formulate a non-convex optimization problem aimed at maximizing computation efficiency by jointly optimizing bandwidth allocation, task allocation, subchannel-vehicle matching and power allocation. To address this non-convex optimization problem, we decompose the original problem into four sub-problems and solve them using an alternating iterative optimization approach. For the subproblem of task allocation, we solve it by linear programming. To solve the subproblem of sub-channel allocation, we exploit many-to-one matching theory to obtain the result. The subproblem of bandwidth allocation of OFDMA and the subproblem of power allocation of NOMA are solved by quadratic transformation method. Finally, the simulation results show that our proposed scheme significantly enhances the computation efficiency of the STIN-based VMDC system compared with the benchmark schemes.
VST++: Efficient and Stronger Visual Saliency Transformer
Oct 18, 2023



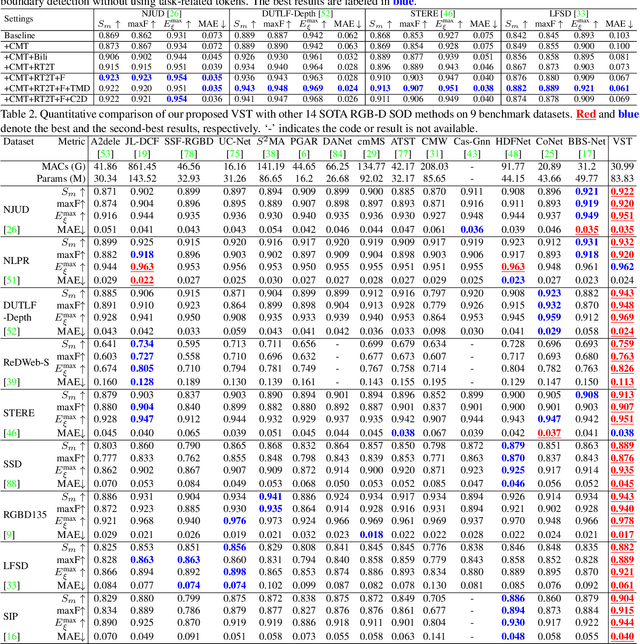
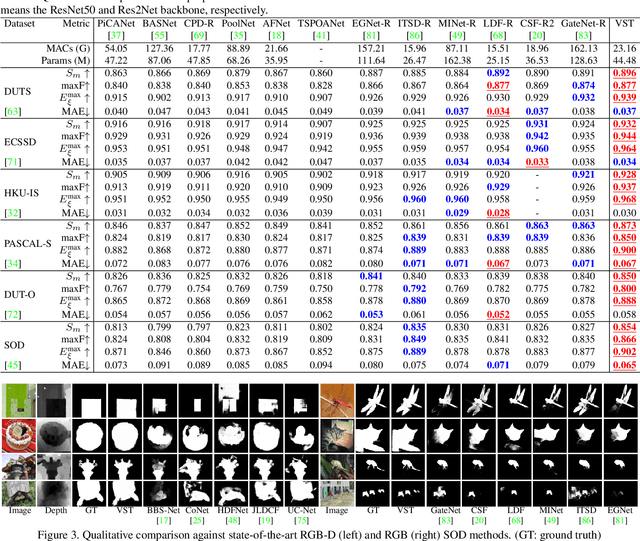
Abstract:While previous CNN-based models have exhibited promising results for salient object detection (SOD), their ability to explore global long-range dependencies is restricted. Our previous work, the Visual Saliency Transformer (VST), addressed this constraint from a transformer-based sequence-to-sequence perspective, to unify RGB and RGB-D SOD. In VST, we developed a multi-task transformer decoder that concurrently predicts saliency and boundary outcomes in a pure transformer architecture. Moreover, we introduced a novel token upsampling method called reverse T2T for predicting a high-resolution saliency map effortlessly within transformer-based structures. Building upon the VST model, we further propose an efficient and stronger VST version in this work, i.e. VST++. To mitigate the computational costs of the VST model, we propose a Select-Integrate Attention (SIA) module, partitioning foreground into fine-grained segments and aggregating background information into a single coarse-grained token. To incorporate 3D depth information with low cost, we design a novel depth position encoding method tailored for depth maps. Furthermore, we introduce a token-supervised prediction loss to provide straightforward guidance for the task-related tokens. We evaluate our VST++ model across various transformer-based backbones on RGB, RGB-D, and RGB-T SOD benchmark datasets. Experimental results show that our model outperforms existing methods while achieving a 25% reduction in computational costs without significant performance compromise. The demonstrated strong ability for generalization, enhanced performance, and heightened efficiency of our VST++ model highlight its potential.
Discriminative Co-Saliency and Background Mining Transformer for Co-Salient Object Detection
May 06, 2023



Abstract:Most previous co-salient object detection works mainly focus on extracting co-salient cues via mining the consistency relations across images while ignoring explicit exploration of background regions. In this paper, we propose a Discriminative co-saliency and background Mining Transformer framework (DMT) based on several economical multi-grained correlation modules to explicitly mine both co-saliency and background information and effectively model their discrimination. Specifically, we first propose a region-to-region correlation module for introducing inter-image relations to pixel-wise segmentation features while maintaining computational efficiency. Then, we use two types of pre-defined tokens to mine co-saliency and background information via our proposed contrast-induced pixel-to-token correlation and co-saliency token-to-token correlation modules. We also design a token-guided feature refinement module to enhance the discriminability of the segmentation features under the guidance of the learned tokens. We perform iterative mutual promotion for the segmentation feature extraction and token construction. Experimental results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method. The source code is available at: https://github.com/dragonlee258079/DMT.
AGAD: Adversarial Generative Anomaly Detection
Apr 09, 2023Abstract:Anomaly detection suffered from the lack of anomalies due to the diversity of abnormalities and the difficulties of obtaining large-scale anomaly data. Semi-supervised anomaly detection methods are often used to solely leverage normal data to detect abnormalities that deviated from the learnt normality distributions. Meanwhile, given the fact that limited anomaly data can be obtained with a minor cost in practice, some researches also investigated anomaly detection methods under supervised scenarios with limited anomaly data. In order to address the lack of abnormal data for robust anomaly detection, we propose Adversarial Generative Anomaly Detection (AGAD), a self-contrast-based anomaly detection paradigm that learns to detect anomalies by generating \textit{contextual adversarial information} from the massive normal examples. Essentially, our method generates pseudo-anomaly data for both supervised and semi-supervised anomaly detection scenarios. Extensive experiments are carried out on multiple benchmark datasets and real-world datasets, the results show significant improvement in both supervised and semi-supervised scenarios. Importantly, our approach is data-efficient that can boost up the detection accuracy with no more than 5% anomalous training data.
Dissolving Is Amplifying: Towards Fine-Grained Anomaly Detection
Feb 28, 2023



Abstract:Medical anomalous data normally contains fine-grained instance-wise additive feature patterns (e.g. tumor, hemorrhage), that are oftenly critical but insignificant. Interestingly, apart from the remarkable image generation abilities of diffusion models, we observed that diffusion models can dissolve image details for a given image, resulting in generalized feature representations. We hereby propose DIA, dissolving is amplifying, that amplifies fine-grained image features by contrasting an image against its feature dissolved counterpart. In particular, we show that diffusion models can serve as semantic preserving feature dissolvers that help learning fine-grained anomalous patterns for anomaly detection tasks, especially for medical domains with fine-grained feature differences. As a result, our method yields a novel fine-grained anomaly detection method, aims at amplifying instance-level feature patterns, that significantly improves medical anomaly detection accuracy in a large margin without any prior knowledge of explicit fine-grained anomalous feature patterns.
Summarize and Search: Learning Consensus-aware Dynamic Convolution for Co-Saliency Detection
Oct 01, 2021
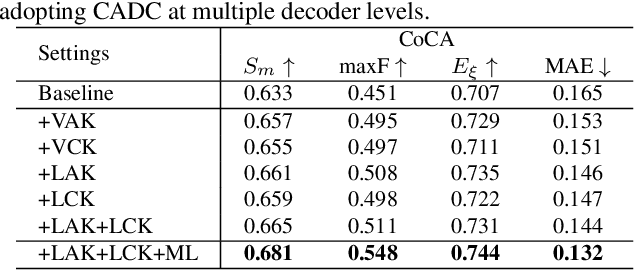
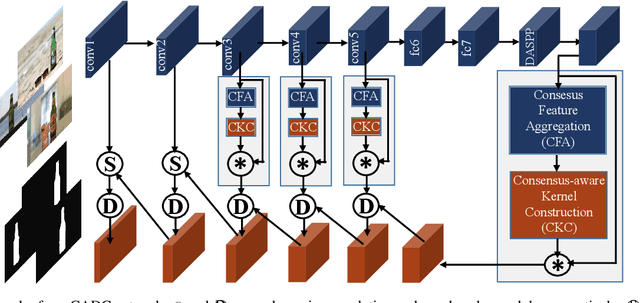
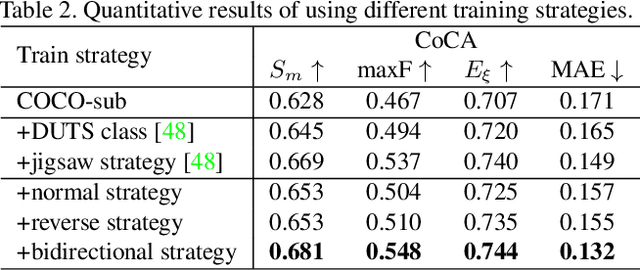
Abstract:Humans perform co-saliency detection by first summarizing the consensus knowledge in the whole group and then searching corresponding objects in each image. Previous methods usually lack robustness, scalability, or stability for the first process and simply fuse consensus features with image features for the second process. In this paper, we propose a novel consensus-aware dynamic convolution model to explicitly and effectively perform the "summarize and search" process. To summarize consensus image features, we first summarize robust features for every single image using an effective pooling method and then aggregate cross-image consensus cues via the self-attention mechanism. By doing this, our model meets the scalability and stability requirements. Next, we generate dynamic kernels from consensus features to encode the summarized consensus knowledge. Two kinds of kernels are generated in a supplementary way to summarize fine-grained image-specific consensus object cues and the coarse group-wise common knowledge, respectively. Then, we can effectively perform object searching by employing dynamic convolution at multiple scales. Besides, a novel and effective data synthesis method is also proposed to train our network. Experimental results on four benchmark datasets verify the effectiveness of our proposed method. Our code and saliency maps are available at \url{https://github.com/nnizhang/CADC}.
Visual Saliency Transformer
Apr 25, 2021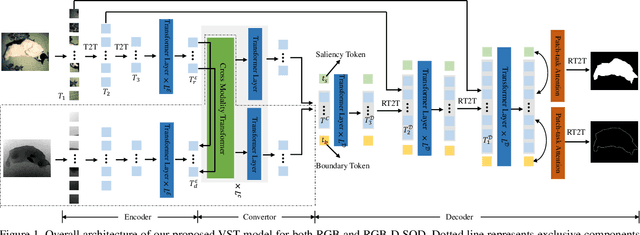
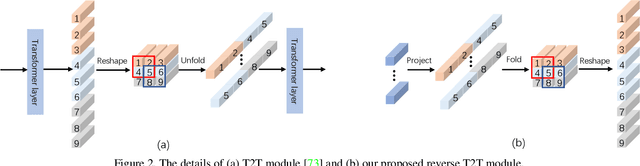
Abstract:Recently, massive saliency detection methods have achieved promising results by relying on CNN-based architectures. Alternatively, we rethink this task from a convolution-free sequence-to-sequence perspective and predict saliency by modeling long-range dependencies, which can not be achieved by convolution. Specifically, we develop a novel unified model based on a pure transformer, namely, Visual Saliency Transformer (VST), for both RGB and RGB-D salient object detection (SOD). It takes image patches as inputs and leverages the transformer to propagate global contexts among image patches. Apart from the traditional transformer architecture used in Vision Transformer (ViT), we leverage multi-level token fusion and propose a new token upsampling method under the transformer framework to get high-resolution detection results. We also develop a token-based multi-task decoder to simultaneously perform saliency and boundary detection by introducing task-related tokens and a novel patch-task-attention mechanism. Experimental results show that our model outperforms existing state-of-the-art results on both RGB and RGB-D SOD benchmark datasets. Most importantly, our whole framework not only provides a new perspective for the SOD field but also shows a new paradigm for transformer-based dense prediction models.
Learning Selective Mutual Attention and Contrast for RGB-D Saliency Detection
Oct 12, 2020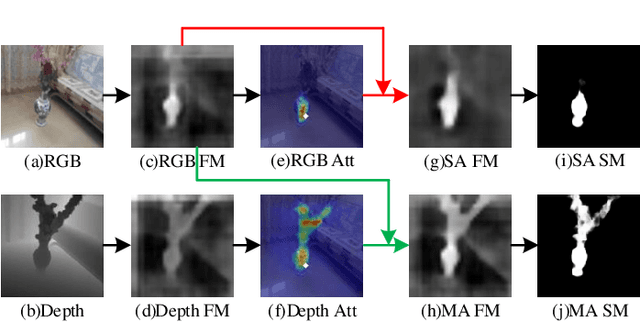
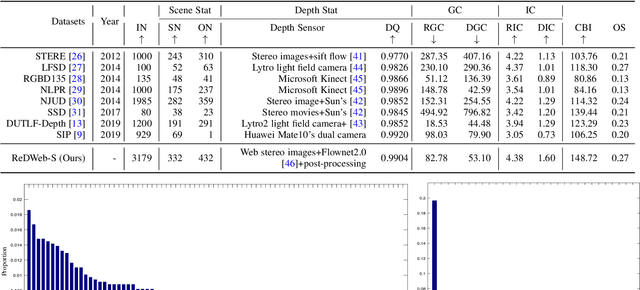
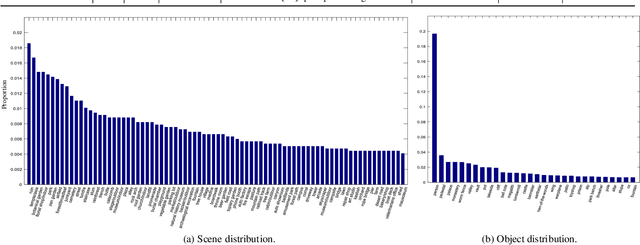

Abstract:How to effectively fuse cross-modal information is the key problem for RGB-D salient object detection. Early fusion and the result fusion schemes fuse RGB and depth information at the input and output stages, respectively, hence incur the problem of distribution gap or information loss. Many models use the feature fusion strategy but are limited by the low-order point-to-point fusion methods. In this paper, we propose a novel mutual attention model by fusing attention and contexts from different modalities. We use the non-local attention of one modality to propagate long-range contextual dependencies for the other modality, thus leveraging complementary attention cues to perform high-order and trilinear cross-modal interaction. We also propose to induce contrast inference from the mutual attention and obtain a unified model. Considering low-quality depth data may detriment the model performance, we further propose selective attention to reweight the added depth cues. We embed the proposed modules in a two-stream CNN for RGB-D SOD. Experimental results have demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed model. Moreover, we also construct a new challenging large-scale RGB-D SOD dataset with high-quality, thus can both promote the training and evaluation of deep models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge