Nghia Nguyen
Robotic-CLIP: Fine-tuning CLIP on Action Data for Robotic Applications
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Vision language models have played a key role in extracting meaningful features for various robotic applications. Among these, Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) is widely used in robotic tasks that require both vision and natural language understanding. However, CLIP was trained solely on static images paired with text prompts and has not yet been fully adapted for robotic tasks involving dynamic actions. In this paper, we introduce Robotic-CLIP to enhance robotic perception capabilities. We first gather and label large-scale action data, and then build our Robotic-CLIP by fine-tuning CLIP on 309,433 videos (~7.4 million frames) of action data using contrastive learning. By leveraging action data, Robotic-CLIP inherits CLIP's strong image performance while gaining the ability to understand actions in robotic contexts. Intensive experiments show that our Robotic-CLIP outperforms other CLIP-based models across various language-driven robotic tasks. Additionally, we demonstrate the practical effectiveness of Robotic-CLIP in real-world grasping applications.
Lightweight Language-driven Grasp Detection using Conditional Consistency Model
Jul 25, 2024



Abstract:Language-driven grasp detection is a fundamental yet challenging task in robotics with various industrial applications. In this work, we present a new approach for language-driven grasp detection that leverages the concept of lightweight diffusion models to achieve fast inference time. By integrating diffusion processes with grasping prompts in natural language, our method can effectively encode visual and textual information, enabling more accurate and versatile grasp positioning that aligns well with the text query. To overcome the long inference time problem in diffusion models, we leverage the image and text features as the condition in the consistency model to reduce the number of denoising timesteps during inference. The intensive experimental results show that our method outperforms other recent grasp detection methods and lightweight diffusion models by a clear margin. We further validate our method in real-world robotic experiments to demonstrate its fast inference time capability.
Language-driven Grasp Detection
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:Grasp detection is a persistent and intricate challenge with various industrial applications. Recently, many methods and datasets have been proposed to tackle the grasp detection problem. However, most of them do not consider using natural language as a condition to detect the grasp poses. In this paper, we introduce Grasp-Anything++, a new language-driven grasp detection dataset featuring 1M samples, over 3M objects, and upwards of 10M grasping instructions. We utilize foundation models to create a large-scale scene corpus with corresponding images and grasp prompts. We approach the language-driven grasp detection task as a conditional generation problem. Drawing on the success of diffusion models in generative tasks and given that language plays a vital role in this task, we propose a new language-driven grasp detection method based on diffusion models. Our key contribution is the contrastive training objective, which explicitly contributes to the denoising process to detect the grasp pose given the language instructions. We illustrate that our approach is theoretically supportive. The intensive experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches and allows real-world robotic grasping. Finally, we demonstrate our large-scale dataset enables zero-short grasp detection and is a challenging benchmark for future work. Project website: https://airvlab.github.io/grasp-anything/
Predicting Lattice Phonon Vibrational Frequencies Using Deep Graph Neural Networks
Nov 10, 2021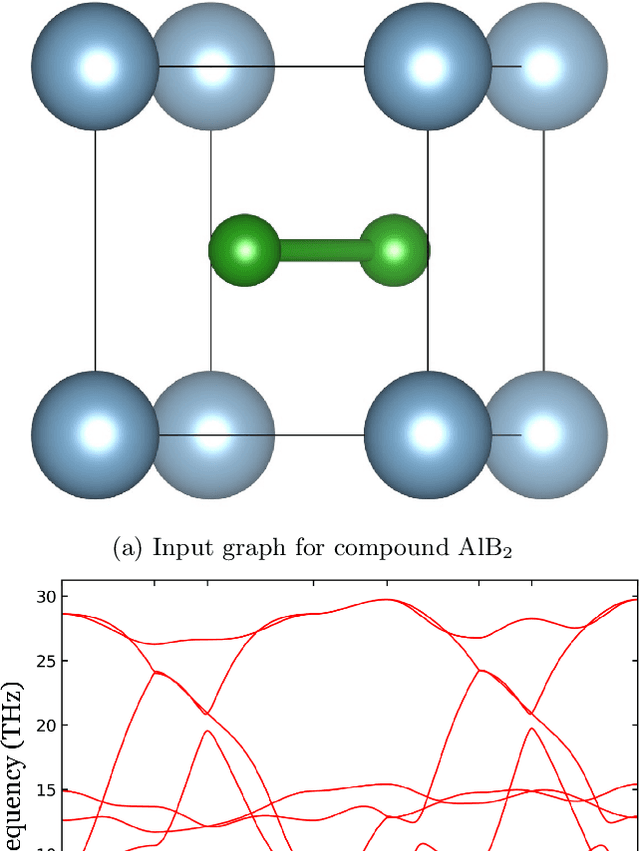
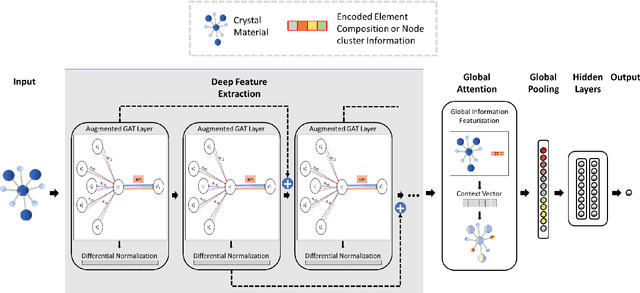
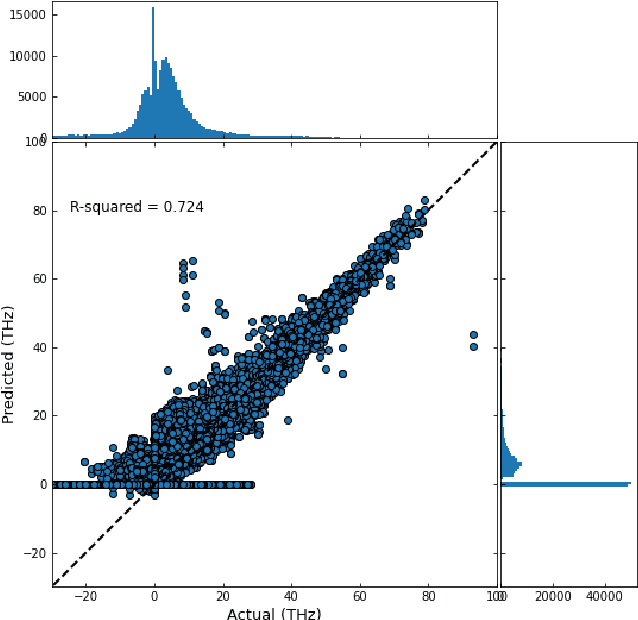
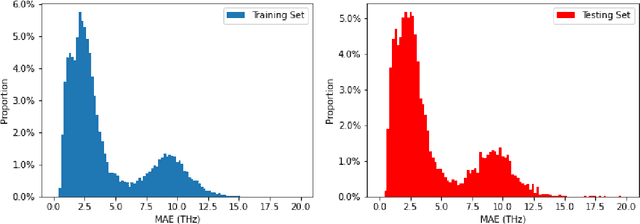
Abstract:Lattice vibration frequencies are related to many important materials properties such as thermal and electrical conductivity as well as superconductivity. However, computational calculation of vibration frequencies using density functional theory (DFT) methods is too computationally demanding for a large number of samples in materials screening. Here we propose a deep graph neural network-based algorithm for predicting crystal vibration frequencies from crystal structures with high accuracy. Our algorithm addresses the variable dimension of vibration frequency spectrum using the zero padding scheme. Benchmark studies on two data sets with 15,000 and 35,552 samples show that the aggregated $R^2$ scores of the prediction reaches 0.554 and 0.724 respectively. Our work demonstrates the capability of deep graph neural networks to learn to predict phonon spectrum properties of crystal structures in addition to phonon density of states (DOS) and electronic DOS in which the output dimension is constant.
A long short-term memory stochastic volatility model
Jun 07, 2019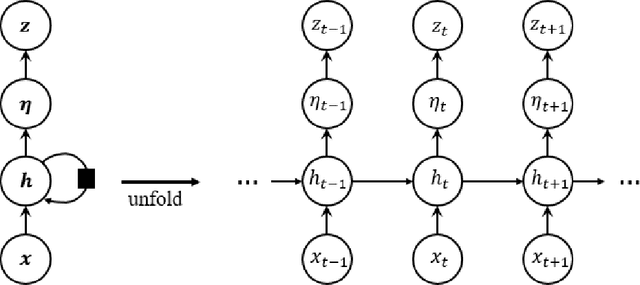
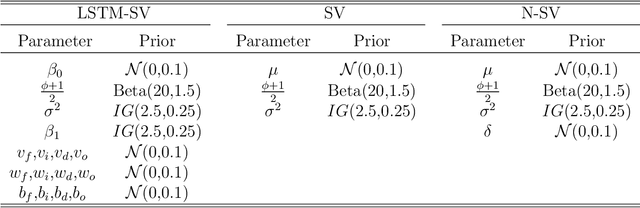
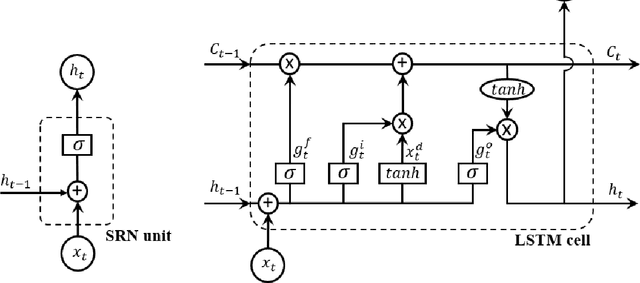

Abstract:Stochastic Volatility (SV) models are widely used in the financial sector while Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models have been successfully used in many large-scale industrial applications of Deep Learning. Our article combines these two methods non trivially and proposes a model for capturing the dynamics of financial volatility process, which we call the LSTM-SV model. The proposed model overcomes the short-term memory problem in conventional SV models, is able to capture non-linear dependence in the latent volatility process, and often has a better out-of-sample forecast performance than SV models. The conclusions are illustrated through simulation studies and applications to three financial time series datasets: US stock market weekly index SP500, Australian stock weekly index ASX200 and Australian-US dollar daily exchange rates. We argue that there are significant differences in the underlying dynamics between the volatility process of SP500 and ASX200 datasets and that of the exchange rate dataset. For the stock index data, there is strong evidence of long-term memory and non-linear dependence in the volatility process, while this is not the case for the exchange rates. An user-friendly software package together with the examples reported in the paper are available at https://github.com/vbayeslab.
Automatic Face Aging in Videos via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Nov 27, 2018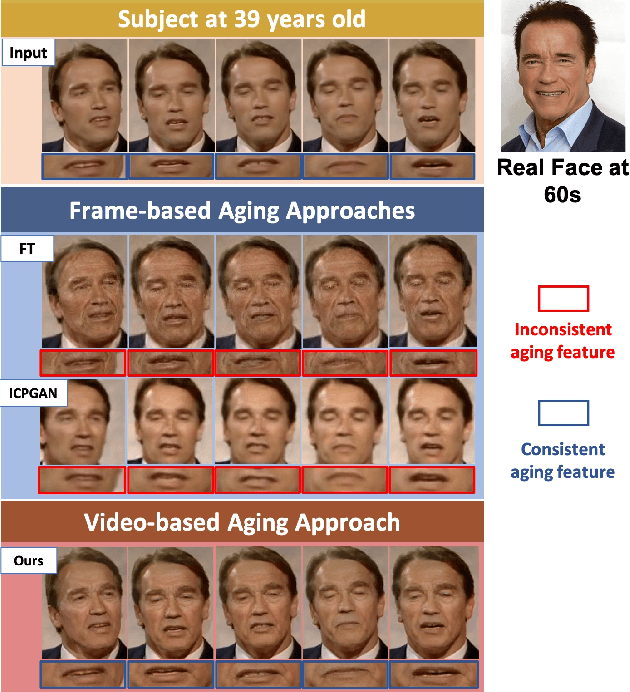


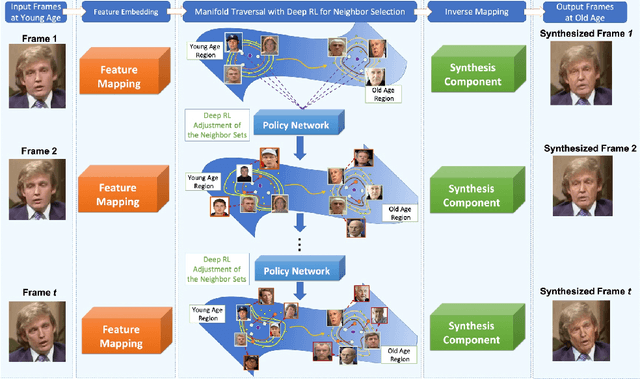
Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach for synthesizing automatically age-progressed facial images in video sequences using Deep Reinforcement Learning. The proposed method models facial structures and the longitudinal face-aging process of given subjects coherently across video frames. The approach is optimized using a long-term reward, Reinforcement Learning function with deep feature extraction from Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Unlike previous age-progression methods that are only able to synthesize an aged likeness of a face from a single input image, the proposed approach is capable of age-progressing facial likenesses in videos with consistently synthesized facial features across frames. In addition, the deep reinforcement learning method guarantees preservation of the visual identity of input faces after age-progression. Results on videos of our new collected aging face AGFW-v2 database demonstrate the advantages of the proposed solution in terms of both quality of age-progressed faces, temporal smoothness, and cross-age face verification.
MobiFace: A Lightweight Deep Learning Face Recognition on Mobile Devices
Nov 27, 2018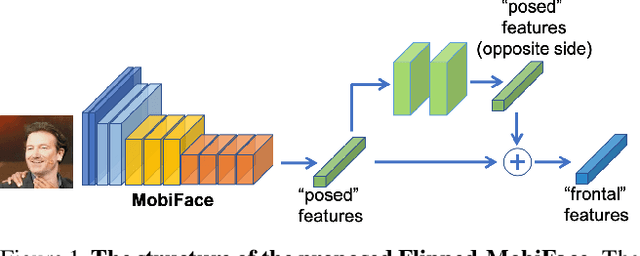
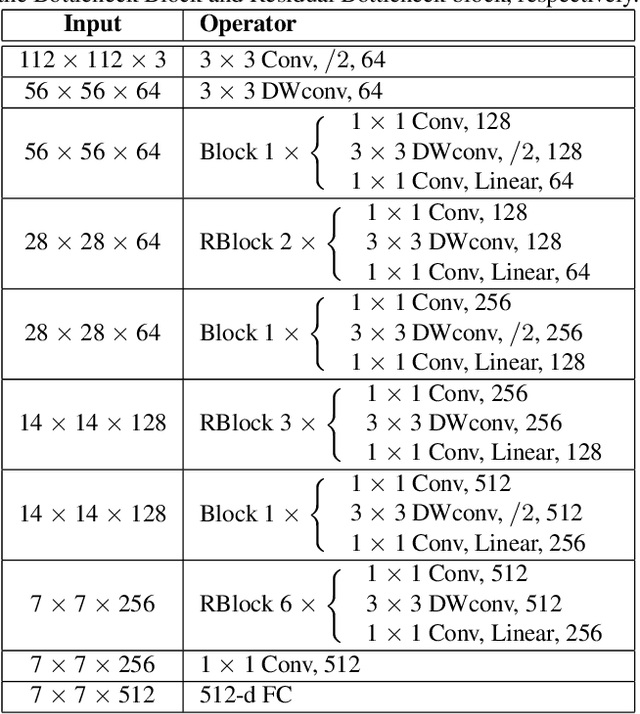
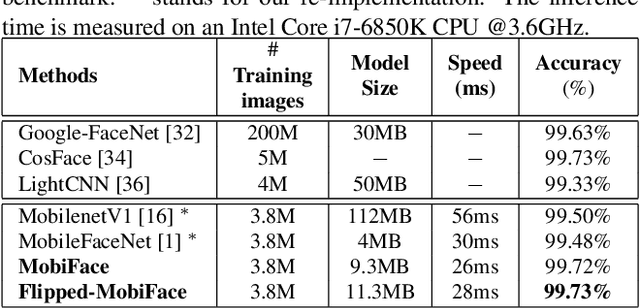
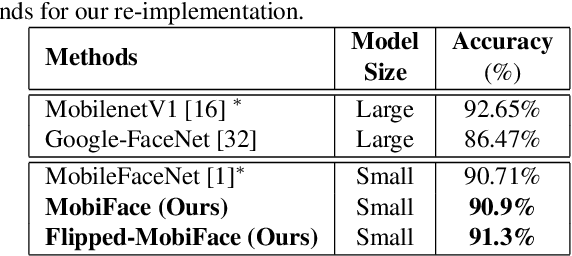
Abstract:Deep neural networks have been widely used in numerous computer vision applications, particularly in face recognition. However, deploying deep neural network face recognition on mobile devices is still limited since most high-accuracy deep models are both time and GPU consumption in the inference stage. Therefore, developing a lightweight deep neural network is one of the most promising solutions to deploy face recognition on mobile devices. Such the lightweight deep neural network requires efficient memory with small number of weights representation and low cost operators. In this paper a novel deep neural network named MobiFace, which is simple but effective, is proposed for productively deploying face recognition on mobile devices. The experimental results have shown that our lightweight MobiFace is able to achieve high performance with 99.7% on LFW database and 91.3% on large-scale challenging Megaface database. It is also eventually competitive against large-scale deep-networks face recognition while significant reducing computational time and memory consumption.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge