Nathan Cooper
It's All in The [MASK]: Simple Instruction-Tuning Enables BERT-like Masked Language Models As Generative Classifiers
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:While encoder-only models such as BERT and ModernBERT are ubiquitous in real-world NLP applications, their conventional reliance on task-specific classification heads can limit their applicability compared to decoder-based large language models (LLMs). In this work, we introduce ModernBERT-Large-Instruct, a 0.4B-parameter encoder model that leverages its masked language modelling (MLM) head for generative classification. Our approach employs an intentionally simple training loop and inference mechanism that requires no heavy pre-processing, heavily engineered prompting, or architectural modifications. ModernBERT-Large-Instruct exhibits strong zero-shot performance on both classification and knowledge-based tasks, outperforming similarly sized LLMs on MMLU and achieving 93% of Llama3-1B's MMLU performance with 60% less parameters. We also demonstrate that, when fine-tuned, the generative approach using the MLM head matches or even surpasses traditional classification-head methods across diverse NLU tasks.This capability emerges specifically in models trained on contemporary, diverse data mixes, with models trained on lower volume, less-diverse data yielding considerably weaker performance. Although preliminary, these results demonstrate the potential of using the original generative masked language modelling head over traditional task-specific heads for downstream tasks. Our work suggests that further exploration into this area is warranted, highlighting many avenues for future improvements.
Smarter, Better, Faster, Longer: A Modern Bidirectional Encoder for Fast, Memory Efficient, and Long Context Finetuning and Inference
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Encoder-only transformer models such as BERT offer a great performance-size tradeoff for retrieval and classification tasks with respect to larger decoder-only models. Despite being the workhorse of numerous production pipelines, there have been limited Pareto improvements to BERT since its release. In this paper, we introduce ModernBERT, bringing modern model optimizations to encoder-only models and representing a major Pareto improvement over older encoders. Trained on 2 trillion tokens with a native 8192 sequence length, ModernBERT models exhibit state-of-the-art results on a large pool of evaluations encompassing diverse classification tasks and both single and multi-vector retrieval on different domains (including code). In addition to strong downstream performance, ModernBERT is also the most speed and memory efficient encoder and is designed for inference on common GPUs.
Rephrasing natural text data with different languages and quality levels for Large Language Model pre-training
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Recently published work on rephrasing natural text data for pre-training LLMs has shown promising results when combining the original dataset with the synthetically rephrased data. We build upon previous work by replicating existing results on C4 and extending them with our optimized rephrasing pipeline to the English, German, Italian, and Spanish Oscar subsets of CulturaX. Our pipeline leads to increased performance on standard evaluation benchmarks in both the mono- and multilingual setup. In addition, we provide a detailed study of our pipeline, investigating the choice of the base dataset and LLM for the rephrasing, as well as the relationship between the model size and the performance after pre-training. By exploring data with different perceived quality levels, we show that gains decrease with higher quality. Furthermore, we find the difference in performance between model families to be bigger than between different model sizes. This highlights the necessity for detailed tests before choosing an LLM to rephrase large amounts of data. Moreover, we investigate the effect of pre-training with synthetic data on supervised fine-tuning. Here, we find increasing but inconclusive results that highly depend on the used benchmark. These results (again) highlight the need for better benchmarking setups. In summary, we show that rephrasing multilingual and low-quality data is a very promising direction to extend LLM pre-training data.
Semantic GUI Scene Learning and Video Alignment for Detecting Duplicate Video-based Bug Reports
Jul 11, 2024Abstract:Video-based bug reports are increasingly being used to document bugs for programs centered around a graphical user interface (GUI). However, developing automated techniques to manage video-based reports is challenging as it requires identifying and understanding often nuanced visual patterns that capture key information about a reported bug. In this paper, we aim to overcome these challenges by advancing the bug report management task of duplicate detection for video-based reports. To this end, we introduce a new approach, called JANUS, that adapts the scene-learning capabilities of vision transformers to capture subtle visual and textual patterns that manifest on app UI screens - which is key to differentiating between similar screens for accurate duplicate report detection. JANUS also makes use of a video alignment technique capable of adaptive weighting of video frames to account for typical bug manifestation patterns. In a comprehensive evaluation on a benchmark containing 7,290 duplicate detection tasks derived from 270 video-based bug reports from 90 Android app bugs, the best configuration of our approach achieves an overall mRR/mAP of 89.8%/84.7%, and for the large majority of duplicate detection tasks, outperforms prior work by around 9% to a statistically significant degree. Finally, we qualitatively illustrate how the scene-learning capabilities provided by Janus benefits its performance.
Stable Code Technical Report
Apr 01, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Stable Code, the first in our new-generation of code language models series, which serves as a general-purpose base code language model targeting code completion, reasoning, math, and other software engineering-based tasks. Additionally, we introduce an instruction variant named Stable Code Instruct that allows conversing with the model in a natural chat interface for performing question-answering and instruction-based tasks. In this technical report, we detail the data and training procedure leading to both models. Their weights are available via Hugging Face for anyone to download and use at https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-code-3b and https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-code-instruct-3b. This report contains thorough evaluations of the models, including multilingual programming benchmarks, and the MT benchmark focusing on multi-turn dialogues. At the time of its release, Stable Code is the state-of-the-art open model under 3B parameters and even performs comparably to larger models of sizes 7 billion and 15 billion parameters on the popular Multi-PL benchmark. Stable Code Instruct also exhibits state-of-the-art performance on the MT-Bench coding tasks and on Multi-PL completion compared to other instruction tuned models. Given its appealing small size, we also provide throughput measurements on a number of edge devices. In addition, we open source several quantized checkpoints and provide their performance metrics compared to the original model.
Stable LM 2 1.6B Technical Report
Feb 27, 2024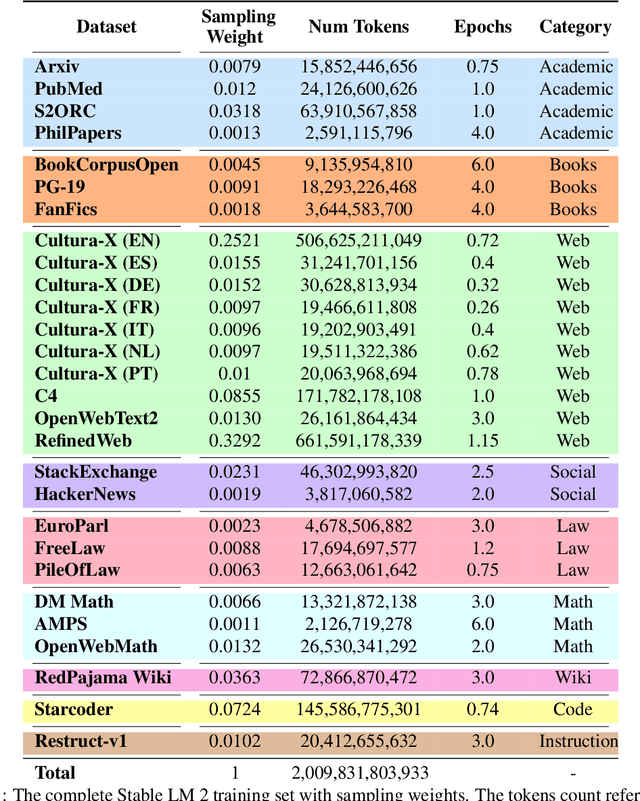
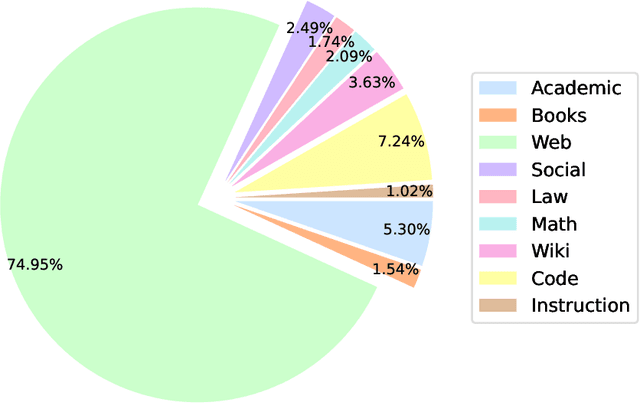
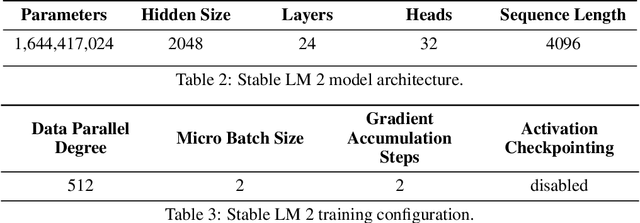
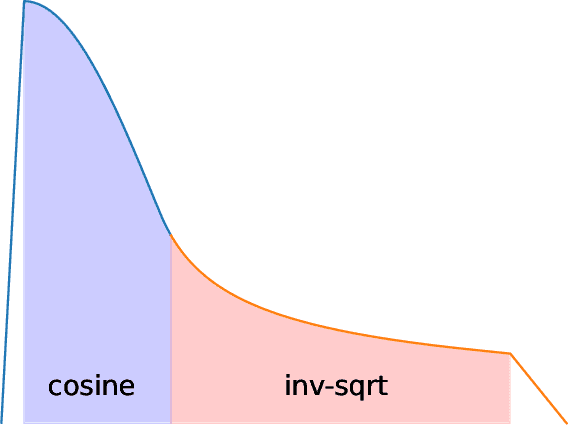
Abstract:We introduce StableLM 2 1.6B, the first in a new generation of our language model series. In this technical report, we present in detail the data and training procedure leading to the base and instruction-tuned versions of StableLM 2 1.6B. The weights for both models are available via Hugging Face for anyone to download and use. The report contains thorough evaluations of these models, including zero- and few-shot benchmarks, multilingual benchmarks, and the MT benchmark focusing on multi-turn dialogues. At the time of publishing this report, StableLM 2 1.6B was the state-of-the-art open model under 2B parameters by a significant margin. Given its appealing small size, we also provide throughput measurements on a number of edge devices. In addition, we open source several quantized checkpoints and provide their performance metrics compared to the original model.
Intelligent Software Tooling for Improving Software Development
Oct 17, 2023



Abstract:Software has eaten the world with many of the necessities and quality of life services people use requiring software. Therefore, tools that improve the software development experience can have a significant impact on the world such as generating code and test cases, detecting bugs, question and answering, etc., The success of Deep Learning (DL) over the past decade has shown huge advancements in automation across many domains, including Software Development processes. One of the main reasons behind this success is the availability of large datasets such as open-source code available through GitHub or image datasets of mobile Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) with RICO and ReDRAW to be trained on. Therefore, the central research question my dissertation explores is: In what ways can the software development process be improved through leveraging DL techniques on the vast amounts of unstructured software engineering artifacts?
Toward a Theory of Causation for Interpreting Neural Code Models
Feb 07, 2023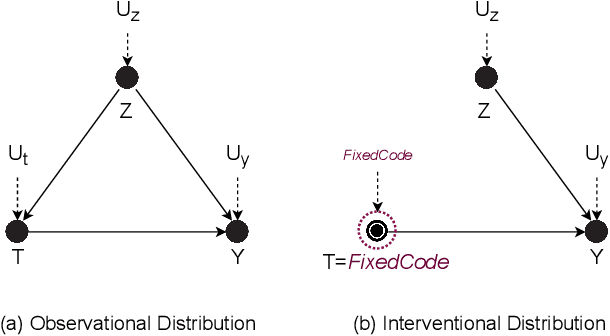
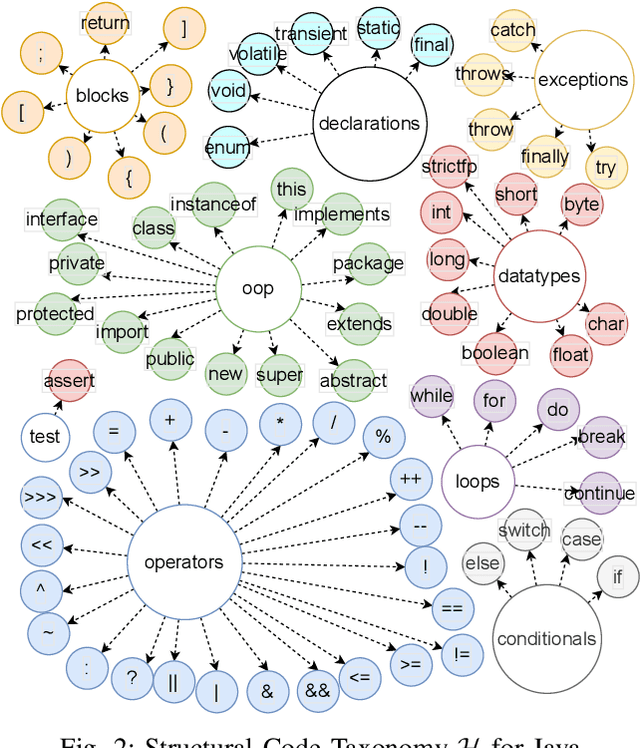
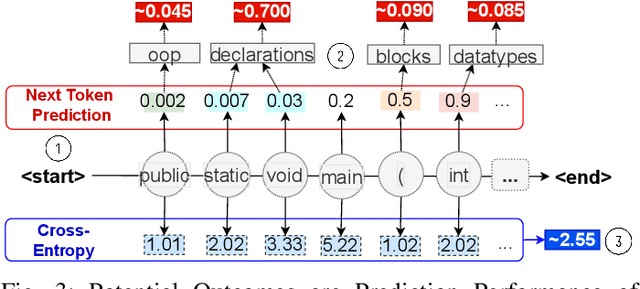
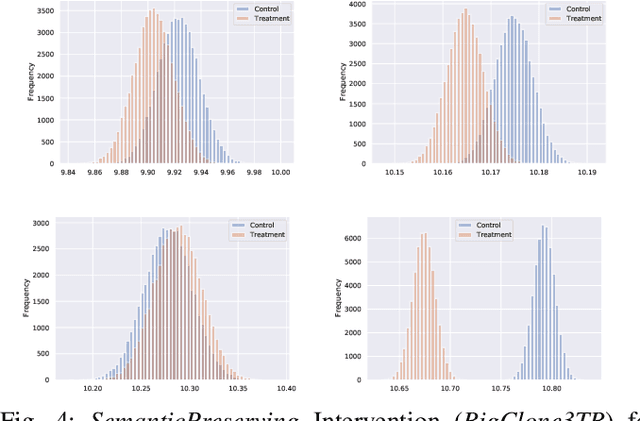
Abstract:Neural Language Models of Code, or Neural Code Models (NCMs), are rapidly progressing from research prototypes to commercial developer tools. As such, understanding the capabilities and limitations of such models is becoming critical. However, the abilities of these models are typically measured using automated metrics that often only reveal a portion of their real-world performance. While, in general, the performance of NCMs appears promising, currently much is unknown about how such models arrive at decisions. To this end, this paper introduces $do_{code}$, a post-hoc interpretability methodology specific to NCMs that is capable of explaining model predictions. $do_{code}$ is based upon causal inference to enable programming language-oriented explanations. While the theoretical underpinnings of $do_{code}$ are extensible to exploring different model properties, we provide a concrete instantiation that aims to mitigate the impact of spurious correlations by grounding explanations of model behavior in properties of programming languages. To demonstrate the practical benefit of $do_{code}$, we illustrate the insights that our framework can provide by performing a case study on two popular deep learning architectures and nine NCMs. The results of this case study illustrate that our studied NCMs are sensitive to changes in code syntax and statistically learn to predict tokens related to blocks of code (e.g., brackets, parenthesis, semicolon) with less confounding bias as compared to other programming language constructs. These insights demonstrate the potential of $do_{code}$ as a useful model debugging mechanism that may aid in discovering biases and limitations in NCMs.
It Takes Two to Tango: Combining Visual and Textual Information for Detecting Duplicate Video-Based Bug Reports
Feb 05, 2021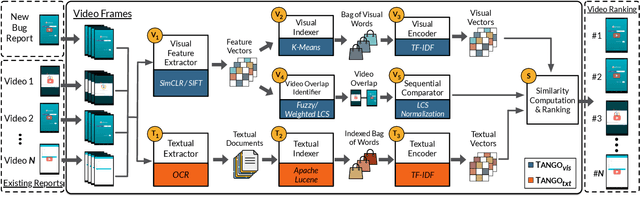
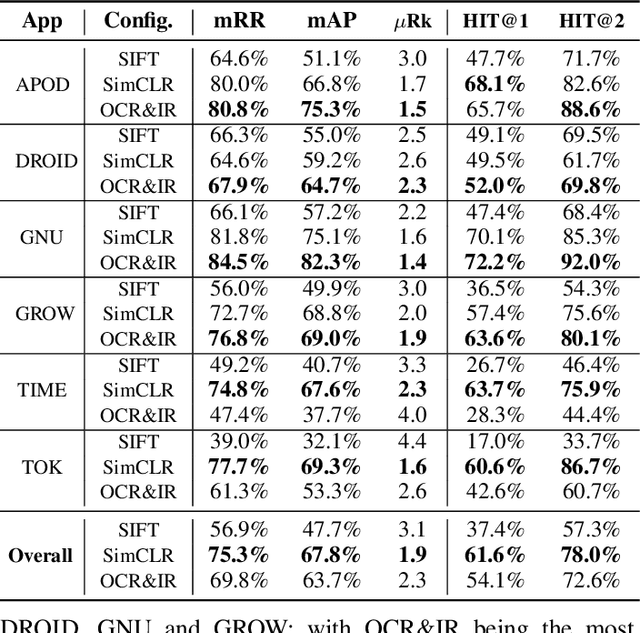

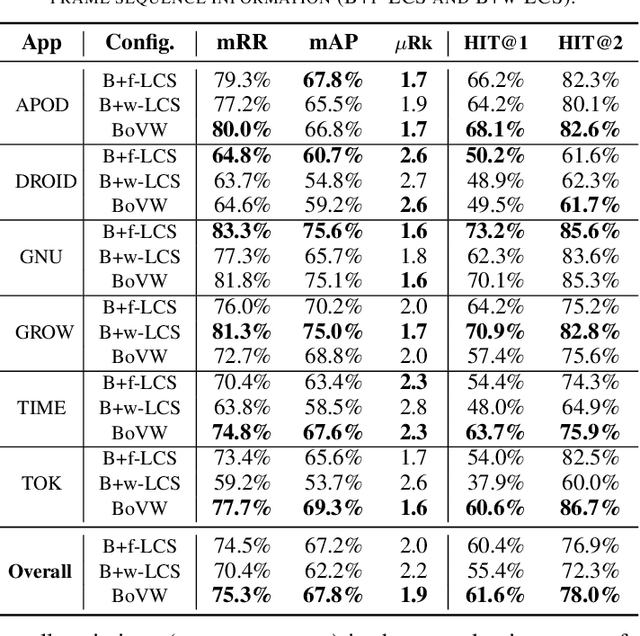
Abstract:When a bug manifests in a user-facing application, it is likely to be exposed through the graphical user interface (GUI). Given the importance of visual information to the process of identifying and understanding such bugs, users are increasingly making use of screenshots and screen-recordings as a means to report issues to developers. However, when such information is reported en masse, such as during crowd-sourced testing, managing these artifacts can be a time-consuming process. As the reporting of screen-recordings in particular becomes more popular, developers are likely to face challenges related to manually identifying videos that depict duplicate bugs. Due to their graphical nature, screen-recordings present challenges for automated analysis that preclude the use of current duplicate bug report detection techniques. To overcome these challenges and aid developers in this task, this paper presents Tango, a duplicate detection technique that operates purely on video-based bug reports by leveraging both visual and textual information. Tango combines tailored computer vision techniques, optical character recognition, and text retrieval. We evaluated multiple configurations of Tango in a comprehensive empirical evaluation on 4,860 duplicate detection tasks that involved a total of 180 screen-recordings from six Android apps. Additionally, we conducted a user study investigating the effort required for developers to manually detect duplicate video-based bug reports and compared this to the effort required to use Tango. The results reveal that Tango's optimal configuration is highly effective at detecting duplicate video-based bug reports, accurately ranking target duplicate videos in the top-2 returned results in 83% of the tasks. Additionally, our user study shows that, on average, Tango can reduce developer effort by over 60%, illustrating its practicality.
A Systematic Literature Review on the Use of Deep Learning in Software Engineering Research
Sep 14, 2020



Abstract:An increasingly popular set of techniques adopted by software engineering (SE) researchers to automate development tasks are those rooted in the concept of Deep Learning (DL). The popularity of such techniques largely stems from their automated feature engineering capabilities, which aid in modeling software artifacts. However, due to the rapid pace at which DL techniques have been adopted, it is difficult to distill the current successes, failures, and opportunities of the current research landscape. In an effort to bring clarity to this cross-cutting area of work, from its modern inception to the present, this paper presents a systematic literature review of research at the intersection of SE & DL. The review canvases work appearing in the most prominent SE and DL conferences and journals and spans 84 papers across 22 unique SE tasks. We center our analysis around the components of learning, a set of principles that govern the application of machine learning techniques (ML) to a given problem domain, discussing several aspects of the surveyed work at a granular level. The end result of our analysis is a research roadmap that both delineates the foundations of DL techniques applied to SE research, and likely areas of fertile exploration for the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge