Minhao Jiang
Temperature-Centric Investigation of Speculative Decoding with Knowledge Distillation
Oct 14, 2024Abstract:Speculative decoding stands as a pivotal technique to expedite inference in autoregressive (large) language models. This method employs a smaller draft model to speculate a block of tokens, which the target model then evaluates for acceptance. Despite a wealth of studies aimed at increasing the efficiency of speculative decoding, the influence of generation configurations on the decoding process remains poorly understood, especially concerning decoding temperatures. This paper delves into the effects of decoding temperatures on speculative decoding's efficacy. Beginning with knowledge distillation (KD), we first highlight the challenge of decoding at higher temperatures, and demonstrate KD in a consistent temperature setting could be a remedy. We also investigate the effects of out-of-domain testing sets with out-of-range temperatures. Building upon these findings, we take an initial step to further the speedup for speculative decoding, particularly in a high-temperature generation setting. Our work offers new insights into how generation configurations drastically affect the performance of speculative decoding, and underscores the need for developing methods that focus on diverse decoding configurations. Code is publically available at https://github.com/ozyyshr/TempSpec.
Reasoning-Enhanced Healthcare Predictions with Knowledge Graph Community Retrieval
Oct 06, 2024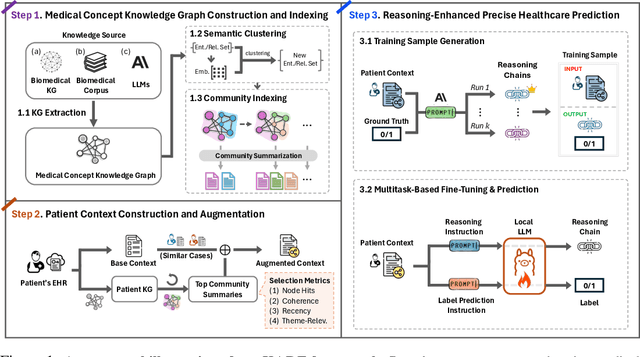
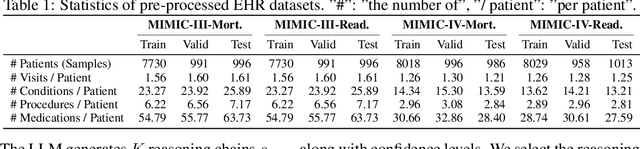
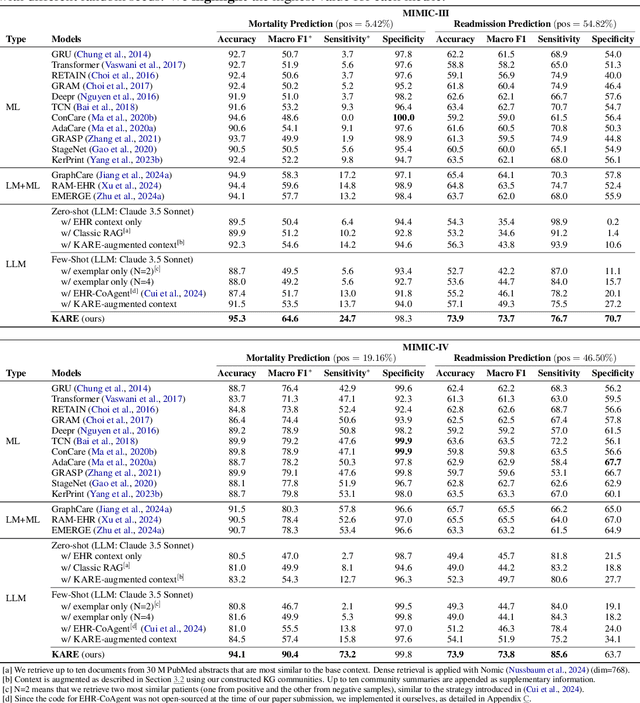
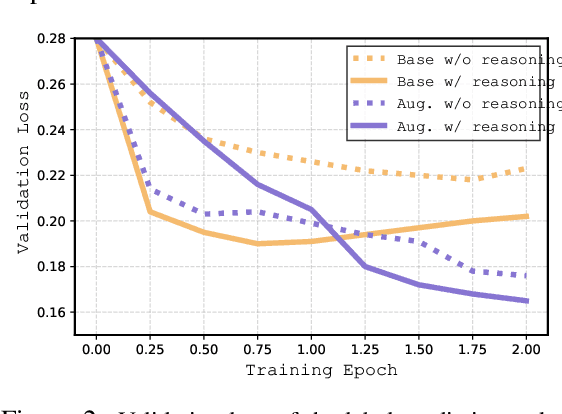
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in clinical decision support. Yet LLMs still suffer from hallucinations and lack fine-grained contextual medical knowledge, limiting their high-stake healthcare applications such as clinical diagnosis. Traditional retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) methods attempt to address these limitations but frequently retrieve sparse or irrelevant information, undermining prediction accuracy. We introduce KARE, a novel framework that integrates knowledge graph (KG) community-level retrieval with LLM reasoning to enhance healthcare predictions. KARE constructs a comprehensive multi-source KG by integrating biomedical databases, clinical literature, and LLM-generated insights, and organizes it using hierarchical graph community detection and summarization for precise and contextually relevant information retrieval. Our key innovations include: (1) a dense medical knowledge structuring approach enabling accurate retrieval of relevant information; (2) a dynamic knowledge retrieval mechanism that enriches patient contexts with focused, multi-faceted medical insights; and (3) a reasoning-enhanced prediction framework that leverages these enriched contexts to produce both accurate and interpretable clinical predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that KARE outperforms leading models by up to 10.8-15.0% on MIMIC-III and 12.6-12.7% on MIMIC-IV for mortality and readmission predictions. In addition to its impressive prediction accuracy, our framework leverages the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, enhancing the trustworthiness of clinical predictions.
Investigating Data Contamination for Pre-training Language Models
Jan 11, 2024



Abstract:Language models pre-trained on web-scale corpora demonstrate impressive capabilities on diverse downstream tasks. However, there is increasing concern whether such capabilities might arise from evaluation datasets being included in the pre-training corpus -- a phenomenon known as \textit{data contamination} -- in a manner that artificially increases performance. There has been little understanding of how this potential contamination might influence LMs' performance on downstream tasks. In this paper, we explore the impact of data contamination at the pre-training stage by pre-training a series of GPT-2 models \textit{from scratch}. We highlight the effect of both text contamination (\textit{i.e.}\ input text of the evaluation samples) and ground-truth contamination (\textit{i.e.}\ the prompts asked on the input and the desired outputs) from evaluation data. We also investigate the effects of repeating contamination for various downstream tasks. Additionally, we examine the prevailing n-gram-based definitions of contamination within current LLM reports, pinpointing their limitations and inadequacy. Our findings offer new insights into data contamination's effects on language model capabilities and underscore the need for independent, comprehensive contamination assessments in LLM studies.
ReactIE: Enhancing Chemical Reaction Extraction with Weak Supervision
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:Structured chemical reaction information plays a vital role for chemists engaged in laboratory work and advanced endeavors such as computer-aided drug design. Despite the importance of extracting structured reactions from scientific literature, data annotation for this purpose is cost-prohibitive due to the significant labor required from domain experts. Consequently, the scarcity of sufficient training data poses an obstacle to the progress of related models in this domain. In this paper, we propose ReactIE, which combines two weakly supervised approaches for pre-training. Our method utilizes frequent patterns within the text as linguistic cues to identify specific characteristics of chemical reactions. Additionally, we adopt synthetic data from patent records as distant supervision to incorporate domain knowledge into the model. Experiments demonstrate that ReactIE achieves substantial improvements and outperforms all existing baselines.
PromptClass: Weakly-Supervised Text Classification with Prompting Enhanced Noise-Robust Self-Training
May 23, 2023



Abstract:Recently proposed weakly-supervised text classification settings train a classifier using the label name of each target class as the only supervision. Such weakly-supervised settings have been gaining increasing attention since they can largely reduce human annotation efforts compared to fully-supervised and semi-supervised settings. Most existing methods follow the strategy that first uses the label names as static features to generate pseudo labels, which are then used for classifier training. While reasonable, such a commonly adopted framework suffers from two limitations: (1) words can have different meanings in different contexts, so using label names for context-free matching can induce very noisy pseudo labels; and (2) the errors made in the pseudo label generation stage will directly propagate to the classifier training stage without a chance of being corrected. In this paper, we propose a new method, PromptClass, consisting of two modules: (1) a pseudo label acquisition module that uses zero-shot prompting of pre-trained language models (PLM) to get pseudo labels based on contextualized text understanding, and (2) a noise-robust self-training module that iteratively trains the classifier and updates pseudo labels by utilizing two PLM fine-tuning strategies that regularize each other. Extensive experiments show that PromptClass achieves overall better performance than existing strong baselines on four benchmark datasets and even achieves similar performance to fully-supervised classifiers on sentiment classification tasks.
OntoType: Ontology-Guided Zero-Shot Fine-Grained Entity Typing with Weak Supervision from Pre-Trained Language Models
May 21, 2023Abstract:Fine-grained entity typing (FET), which assigns entities in text with context-sensitive, fine-grained semantic types, will play an important role in natural language understanding. A supervised FET method, which typically relies on human-annotated corpora for training, is costly and difficult to scale. Recent studies leverage pre-trained language models (PLMs) to generate rich and context-aware weak supervision for FET. However, a PLM may still generate a mixture of rough and fine-grained types, or tokens unsuitable for typing. In this study, we vision that an ontology provides a semantics-rich, hierarchical structure, which will help select the best results generated by multiple PLM models and head words. Specifically, we propose a novel zero-shot, ontology-guided FET method, OntoType, which follows a type ontological structure, from coarse to fine, ensembles multiple PLM prompting results to generate a set of type candidates, and refines its type resolution, under the local context with a natural language inference model. Our experiments on the Ontonotes, FIGER, and NYT datasets using their associated ontological structures demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art zero-shot fine-grained entity typing methods. Our error analysis shows that refinement of the existing ontology structures will further improve fine-grained entity typing.
TaxoEnrich: Self-Supervised Taxonomy Completion via Structure-Semantic Representations
Feb 10, 2022



Abstract:Taxonomies are fundamental to many real-world applications in various domains, serving as structural representations of knowledge. To deal with the increasing volume of new concepts needed to be organized as taxonomies, researchers turn to automatically completion of an existing taxonomy with new concepts. In this paper, we propose TaxoEnrich, a new taxonomy completion framework, which effectively leverages both semantic features and structural information in the existing taxonomy and offers a better representation of candidate position to boost the performance of taxonomy completion. Specifically, TaxoEnrich consists of four components: (1) taxonomy-contextualized embedding which incorporates both semantic meanings of concept and taxonomic relations based on powerful pretrained language models; (2) a taxonomy-aware sequential encoder which learns candidate position representations by encoding the structural information of taxonomy; (3) a query-aware sibling encoder which adaptively aggregates candidate siblings to augment candidate position representations based on their importance to the query-position matching; (4) a query-position matching model which extends existing work with our new candidate position representations. Extensive experiments on four large real-world datasets from different domains show that \TaxoEnrich achieves the best performance among all evaluation metrics and outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge