Mingjun Sun
Robust Beamforming for Pinching-Antenna Systems
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Pinching-antenna system (PASS) mitigates large-scale path loss by enabling flexible placement of pinching antennas (PAs) along the dielectric waveguide. However, most existing studies assume perfect channel state information (CSI), overlooking the impact of channel uncertainty. This paper addresses this gap by proposing a robust beamforming framework for both lossy and lossless waveguides. For baseband beamforming, the lossy case yields an second-order cone programming-based solution, while the lossless case admits a closed-form solution via maximum ratio transmission. The PAs' positions in both cases are optimized through the Gauss-Seidel-based method. Numerical results validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm and demonstrate that PASS exhibits superior robustness against channel uncertainty compared with conventional fixed-antenna systems. Notably, its worst-case achievable rate can even exceed the fixed-antenna baseline under perfect CSI.
Multiuser Beamforming for Pinching-Antenna Systems: An Element-wise Optimization Framework
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:The pinching-antenna system (PASS) reconstructs wireless channels through pinching beamforming, i.e., optimizing the activated locations of pinching antennas (PAs) along the waveguide. The aim of this article is to investigate the joint design of baseband beamforming and pinching beamforming. A low-complexity element-wise sequential optimization framework is proposed to address the sum-rate maximization problem in PASS-enabled downlink and uplink channels. i) For the downlink scenario, maximum ratio transmission (MRT), zero-forcing (ZF), and minimum mean square error (MMSE) beamforming schemes are employed as baseband beamformers. For each beamformer, a closed-form expression for the downlink sum-rate is derived as a single-variable function with respect to the pinching beamformer. Based on this, a sequential optimization method is proposed, where the positions of the PAs are updated element-wise using a low-complexity one-dimensional search. ii) For the uplink scenario, signal detection is performed using maximum ratio combining (MRC), ZF, and MMSE combiners. A closed-form sum-rate expression is derived for each linear combiner, and a similar element-wise design is applied to optimize the pinching beamforming. Numerical results are provided to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method and demonstrate that: (i) For all considered linear beamformers, the proposed PASS architecture outperforms conventional fixed-antenna systems in terms of sum-rate performance; (ii) in both downlink and uplink channels, ZF achieves performance close to that of MMSE and significantly outperforms MRT or MRC; and (iii) the proposed element-wise design eliminates the need for alternating updates between the baseband and pinching beamformers, thereby ensuring low computational complexity.
Multi-Target Position Error Bound and Power Allocation Scheme for Cell-Free mMIMO-OTFS ISAC Systems
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates multi-target position estimation in cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (CF mMIMO) architectures, where orthogonal time frequency and space (OTFS) is used as an integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) signal. Closed-form expressions for the Cram\'{e}r-Rao lower bound and the positioning error bound (PEB) in multi-target position estimation are derived, providing quantitative evaluations of sensing performance. To enhance the overall performance of the ISAC system, a power allocation algorithm is developed to maximize the minimum user communication signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio while ensuring a specified sensing PEB requirement. The results validate the proposed PEB expression and its approximation, clearly illustrating the coordination gain enabled by ISAC. Further, the superiority of using the multi-static CF mMIMO architecture over traditional cellular ISAC is demonstrated, and the advantages of OTFS signals in high-mobility scenarios are highlighted.
Physical Layer Security for Pinching-Antenna Systems (PASS)
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:The pinching-antenna system (PASS) introduces new degrees of freedom (DoFs) for physical layer security (PLS) through pinching beamforming. In this paper, a couple of scenarios for secure beamforming for PASS are studied. 1) For the case with a single legitimate user (Bob) and a single eavesdropper (Eve), a closed-form expression for the optimal baseband beamformer is derived. On this basis, a gradient-based method is proposed to optimize the activated positions of pinching antennas (PAs). 2) For the case with multiple Bobs and multiple Eves, a fractional programming (FP)-based block coordinate descent (BCD) algorithm, termed FP-BCD, is proposed for optimizing the weighted secrecy sum-rate (WSSR). Specifically, a closed-form baseband beamformer is obtained via Lagrange multiplier method. Furthermore, owing to the non-convex objective function exhibiting numerous stationary points, a low-complexity one-dimensional search is used to find a high-quality solution of the PAs' activated locations. Numerical results are provided to demonstrate that: i) All proposed algorithms achieve stable convergence within a few iterations, ii) across all considered power ranges, the FP-BCD algorithm outperforms baseline methods using zero-forcing (ZF) and maximal-ratio transmission (MRT) beamforming in terms of the WSSR, and iii) PASS achieves a significantly higher secrecy rate than traditional fixed-antenna systems.
Secure Beamforming for Continuous Aperture Array (CAPA) Systems
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:Continuous aperture array (CAPA) is considered a promising technology for 6G networks, offering the potential to fully exploit spatial DoFs and achieve the theoretical limits of channel capacity. This paper investigates the performance gain of a CAPA-based downlink secure transmission system, where multiple legitimate user terminals (LUTs) coexist with multiple eavesdroppers (Eves). The system's secrecy performance is evaluated using a weighted secrecy sum-rate (WSSR) under a power constraint. We then propose two solutions for the secure current pattern design. The first solution is a block coordinate descent (BCD) optimization method based on fractional programming, which introduces a continuous-function inversion theory corresponding to matrix inversion in the discrete domain. This approach derives a closed-form expression for the optimal source current pattern. Based on this, it can be found that the optimal current pattern is essentially a linear combination of the channel spatial responses, thus eliminating the need for complex integration operations during the algorithm's optimization process. The second solution is a heuristic algorithm based on Zero-Forcing (ZF), which constructs a zero-leakage current pattern using the channel correlation matrix. It further employs a water-filling approach to design an optimal power allocation scheme that maximizes the WSSR. In high SNR regions, this solution gradually approaches the first solution, ensuring zero leakage while offering lower computational complexity. Simulation results demonstrate that: 1) CAPA-based systems achieve better WSSR compared to discrete multiple-input multiple-output systems. 2) The proposed methods, whether optimization-based or heuristic, provide significant performance improvements over existing state-of-the-art Fourier-based discretization methods, while considerably reducing computational complexity.
A Homogeneous Graph Neural Network for Precoding and Power Allocation in Scalable Wireless Networks
Aug 30, 2024



Abstract:Deep learning is widely used in wireless communications but struggles with fixed neural network sizes, which limit their adaptability in environments where the number of users and antennas varies. To overcome this, this paper introduced a generalization strategy for precoding and power allocation in scalable wireless networks. Initially, we employ an innovative approach to abstract the wireless network into a homogeneous graph. This primarily focuses on bypassing the heterogeneous features between transmitter (TX) and user entities to construct a virtual homogeneous graph serving optimization objectives, thereby enabling all nodes in the virtual graph to share the same neural network. This "TX entity" is known as a base station (BS) in cellular networks and an access point (AP) in cell-free networks. Subsequently, we design a universal graph neural network, termed the information carrying graph neural network (ICGNN), to capture and integrate information from this graph, maintaining permutation invariance. Lastly, using ICGNN as the core algorithm, we tailor the neural network's input and output for specific problem requirements and validate its performance in two scenarios: 1) in cellular networks, we develop a matrix-inverse-free multi-user multi-input multi-output (MU-MIMO) precoding scheme using the conjugate gradient (CG) method, adaptable to varying user and antenna numbers; 2) in a cell-free network, facing dynamic variations in the number of users served by APs, the number of APs serving each user, and the number of antennas per AP, we propose a universal power allocation scheme. Simulations demonstrate that the proposed approach not only significantly reduces computational complexity but also achieves, and potentially exceeds, the spectral efficiency (SE) of conventional algorithms.
WIDER Face and Pedestrian Challenge 2018: Methods and Results
Feb 19, 2019

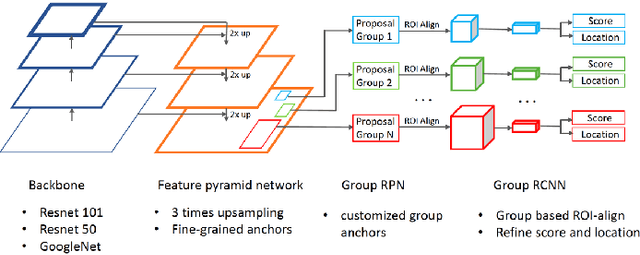

Abstract:This paper presents a review of the 2018 WIDER Challenge on Face and Pedestrian. The challenge focuses on the problem of precise localization of human faces and bodies, and accurate association of identities. It comprises of three tracks: (i) WIDER Face which aims at soliciting new approaches to advance the state-of-the-art in face detection, (ii) WIDER Pedestrian which aims to find effective and efficient approaches to address the problem of pedestrian detection in unconstrained environments, and (iii) WIDER Person Search which presents an exciting challenge of searching persons across 192 movies. In total, 73 teams made valid submissions to the challenge tracks. We summarize the winning solutions for all three tracks. and present discussions on open problems and potential research directions in these topics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge