Zhaolin Wang
Exploiting Segmented Waveguide-Enabled Pinching-Antenna Systems (SWANs) for Uplink Tri-Hybrid Beamforming
Mar 04, 2026Abstract:A segmented waveguide-enabled pinching-antenna system (SWAN)-based tri-hybrid beamforming architecture is proposed for uplink multi-user MIMO communications, which jointly optimizes digital, analog, and pinching beamforming. Both fully-connected (FC) and partially-connected (PC) structures between RF chains and segment feed points are considered. For the FC architecture, tri-hybrid beamforming is optimized using the weighted minimum mean-square error (WMMSE) and zero-forcing (ZF) approaches. Specifically, the digital, analog, and pinching beamforming components are optimized via a closed-form solution, Riemannian manifold optimization, and a Gauss-Seidel search, respectively. For the PC architecture, an interleaved topology tailored to the SWAN receiver is proposed, in which segments assigned to each RF chain (sub-array) are interleaved with those from other sub-arrays. Based on this structure, a WMMSE-based tri-hybrid design is developed, in which the Riemannian-manifold update used for the FC structure is replaced by element-wise phase calibration to exploit sparsity in analog beamforming. To gain insight into the performance of the proposed system, the rate-scaling laws with respect to the number of segments are derived for both the FC and PC structures. Our results demonstrate that: i)~SWAN with the proposed tri-hybrid beamforming consistently outperforms conventional hybrid beamforming and conventional pinching-antenna systems with pinching beamforming for both the FC and PC structures; and ii)~the PC structure can strike a good balance between sum rate and energy consumption when the number of segments is large; and iii) the achievable rate does not necessarily increase with the number of segments.
Failure Detection for Pinching-Antenna Systems
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:A signal processing-based framework is proposed for detecting random segment failures in segmented waveguide-enabled pinching-antenna systems. To decouple the passively combined uplink signal and to provide per-segment observability, tagged pilots are employed. A simple tag is attached to each segment and is used to apply a known low-rate modulation at the segment feed, which assigns a unique signature to each segment. Based on the tagged-pilot model, a low-complexity per-segment maximum-likelihood (ML) detector is developed for the case in which the pilot length is no smaller than the number of segments. For the case in which the pilot length is smaller than the number of segments, sparsity in the failure-indicator vector is exploited and a compressive sensing-based detector is adopted. Numerical results show that the per-segment detector approaches joint ML performance, while the compressive sensing-based detector achieves reliable detection with a short pilot and can outperform baselines that require much longer pilots.
Generative Site-Specific Beamforming via Information-Maximizing Codebook
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:A novel generative site-specific beamforming (GenSSBF) framework is proposed, which integrates a site-information-maximizing (SIM) codebook with a conditional flow matching (CFM)-based beam generator. By this framework, the site-specific radio propagation environment is learned at the base station (BS), enabling the generation of high fidelity communication beams from coarse reference-signal-received-power (RSRP) feedback provided by user equipments (UEs). In the proposed design, a low-dimensional SIM probing codebook is first constructed by maximizing the mutual information between the RSRP feedback and the site-specific channel. This design not only reduces the initial beam sweeping overhead, but also enhances the amount of channel state information conveyed through UE feedback. By treating the RSRP feedback as a conditional prior, a CFM-based generative model is further developed to explicitly capture the uncertainty in beam generation. Specifically, a small set of UE-specific candidate beams is generated by inferring the learned generative model and sampling from the corresponding posterior distribution, after which the final data transmission beam is selected by the UE. Extensive simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of both the proposed SIM codebook and the CFM-based beam generator. The proposed GenSSBF framework achieves beamforming performance nearly identical to maximum ratio transmission while requiring only eight probing beams and eight candidate beams.
On the Maintainability of Pinching-Antenna Systems: A Failure-Repair Perspective
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:The pinching-antenna system (PASS) enables wireless channel reconfiguration through optimized placement of pinching antennas along dielectric waveguides. In this article, a unified analytical framework is proposed to characterize the maintainability of PASS. Within this framework, random waveguide failures and repairs are modeled by treating the waveguide lifetime and repair time as exponentially distributed random variables, which are characterized by the failure rate and the repair rate, respectively. The operational state of the waveguide is described by a two-state continuous-time Markov chain, for which the transition probabilities and steady-state probabilities of the waveguide being working or failed are analyzed. By incorporating the randomness of the waveguide operational state into the transmission rate, system maintainability is characterized using the probability of non-zero rate (PNR) and outage probability (OP). The proposed framework is applied to both a conventional PASS employing a single long waveguide and a segmented waveguide-enabled pinching-antenna system (SWAN) composed of multiple short waveguide segments under two operational protocols: segment switching (SS) and segment aggregation (SA). Closed-form expressions for the PNR and OP are derived for both architectures, and the corresponding scaling laws are analyzed with respect to the service-region size and the number of segments. It is proven that both SS-based and SA-based SWAN achieve higher PNR and lower OP than conventional PASS, which confirms the maintainability advantage of segmentation. Numerical results demonstrate that: i) the maintainability gain of SWAN over conventional PASS increases with the number of segments, and ii) SA provides stronger maintainability than SS.
A Survey of Pinching-Antenna Systems (PASS)
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:The pinching-antenna system (PASS), recently proposed as a flexible-antenna technology, has been regarded as a promising solution for several challenges in next-generation wireless networks. It provides large-scale antenna reconfiguration, establishes stable line-of-sight links, mitigates signal blockage, and exploits near-field advantages through its distinctive architecture. This article aims to present a comprehensive overview of the state of the art in PASS. The fundamental principles of PASS are first discussed, including its hardware architecture, circuit and physical models, and signal models. Several emerging PASS designs, such as segmented PASS (S-PASS), center-fed PASS (C-PASS), and multi-mode PASS (M-PASS), are subsequently introduced, and their design features are discussed. In addition, the properties and promising applications of PASS for wireless sensing are reviewed. On this basis, recent progress in the performance analysis of PASS for both communications and sensing is surveyed, and the performance gains achieved by PASS are highlighted. Existing research contributions in optimization and machine learning are also summarized, with the practical challenges of beamforming and resource allocation being identified in relation to the unique transmission structure and propagation characteristics of PASS. Finally, several variants of PASS are presented, and key implementation challenges that remain open for future study are discussed.
Beam-Brainstorm: A Generative Site-Specific Beamforming Approach
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Accurately understanding the propagation environment is a fundamental challenge in site-specific beamforming (SSBF). This paper proposes a novel generative SSBF (GenSSBF) solution, which represents a paradigm shift from conventional unstructured prediction to joint-structure modeling. First, considering the fundamental differences between beam generation and conventional image synthesis, a unified GenSSBF framework is proposed, which includes a site profile, a wireless prompting module, and a generator. Second, a beam-brainstorm (BBS) solution is proposed as an instantiation of this GenSSBF framework. Specifically, the site profile is configured by transforming channel data from spatial domain to a reversible latent space via discrete Fourier transform (DFT). To facilitate practical deployment, the wireless prompt is constructed from the reference signal received power (RSRP) measured using a small number of DFT-beams. Finally, the generator is developed using a customized conditional diffusion model. Rather than relying on a meticulously designed global codebook, BBS directly generates diverse and high-fidelity user-specific beams guided by the wireless prompts. Simulation results on accurate ray-tracing datasets demonstrate that BBS can achieve near-optimal beamforming gain while drastically reducing the beam sweeping overhead, even in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) environments.
Segmented Waveguide-Enabled Pinching-Antenna Systems (SWANs) for ISAC
Dec 08, 2025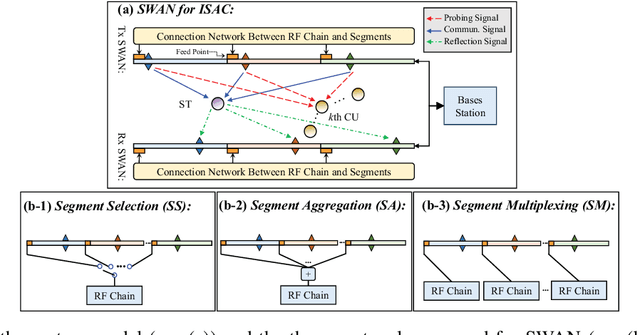
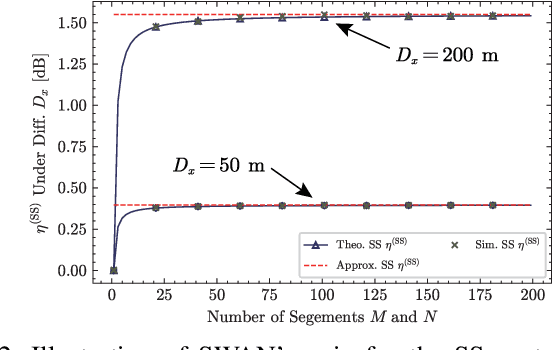
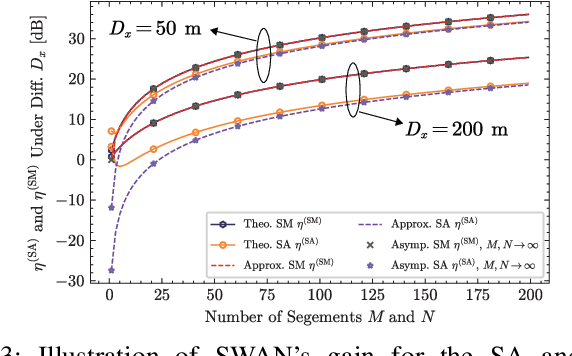
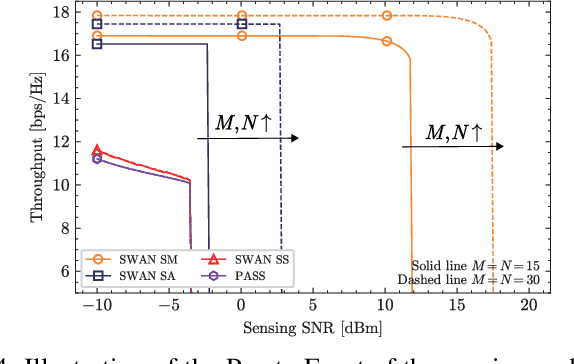
Abstract:A segmented waveguide-enabled pinching-antenna system (SWAN)-assisted integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) framework is proposed. Unlike conventional pinching antenna systems (PASS), which use a single long waveguide, SWAN divides the waveguide into multiple short segments, each with a dedicated feed point. Thanks to the segmented structure, SWAN enhances sensing performance by significantly simplifying the reception model and reducing the in-waveguide propagation loss. To balance performance and complexity, three segment controlling protocols are proposed for the transceivers, namely i) \emph{segment selection} to select a single segment for signal transceiving, ii) \emph{segment aggregation} to aggregate signals from all segments using a single RF chain, and iii) \emph{segment multiplexing} to jointly process the signals from all segments using individual RF chains. The theoretical sensing performance limit is first analyzed for different protocols, unveiling how the sensing performance gain of SWAN scales with the number of segments. Based on this performance limit, the Pareto fronts of sensing and communication performance are characterized for the simple one-user one-target case, which is then extended to the general multi-user single-target case based on time-division multiple access (TDMA). Numerical results are presented to verify the correctness of the derivations and the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms, which jointly confirm the advantages of SWAN-assisted ISAC.
Tri-Hybrid Beamforming Design for Fully-Connected Pinching Antenna Systems
Nov 18, 2025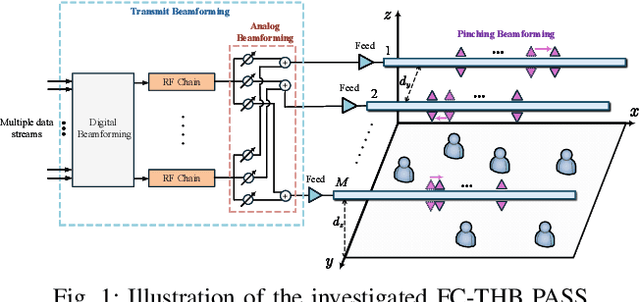
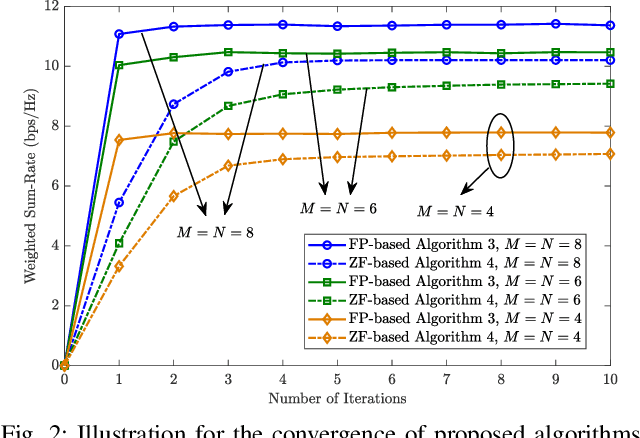
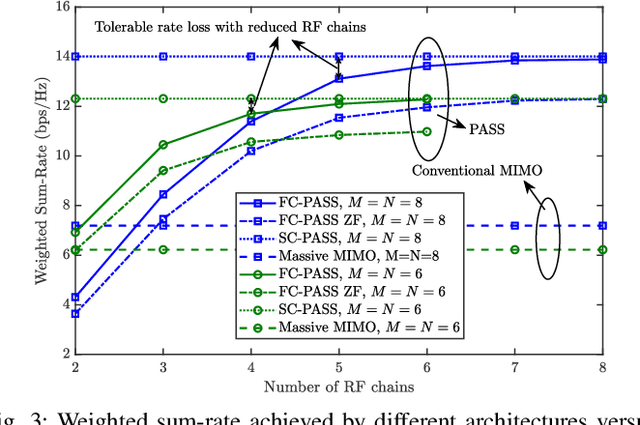
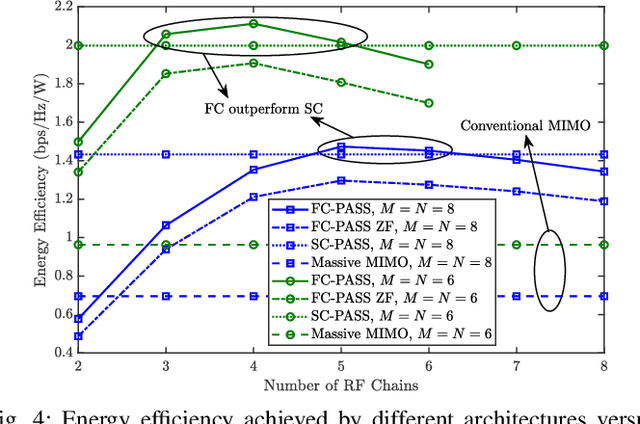
Abstract:A novel fully-connected (FC) tri-hybrid beamforming (THB) architecture is proposed for pinching antenna systems (PASS). In contrast to conventional sub-connected (SC) PASS, the proposed FC architecture employs a tunable phase-shifter network to interconnect all radio frequency (RF) chains with all waveguides. This facilitates a THB framework that integrates conventional hybrid analog-digital beamforming with pinching beamforming. A weighted sum-rate (WSR) optimization problem is then formulated to jointly optimize the transmit beamformers and pinching antenna (PA) positions. Two algorithms are developed to address this challenging non-convex problem. 1) Fractional programming (FP)-based algorithm: This algorithm directly maximizes the WSR using an FP-based alternating optimization framework. Particularly, a success-history based adaptive differential evolution (SHADE) method is proposed to optimize PA positions, effectively addressing the intractable multimodal objective function. 2) Zero-forcing (ZF)-based algorithm: To reduce design complexity, zero-forcing is employed for transmit beamforming. The PA positions are subsequently optimized to maximize the WSR via a modified SHADE method. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms, revealing that the FC-THB PASS achieves WSR comparable to the SC architecture while delivering superior energy efficiency with fewer RF chains.
Flexible Continuous Aperture Arrays
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:A novel electromagnetic (EM) structure termed flexible continuous aperture array (FCAPA) is proposed, which incorporates inherent surface flexibility into typical continuous aperture array (CAPA) systems, thereby enhancing the degrees-of-freedom (DoF) of multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems equipped with this technology. By formulating and solving a downlink multi-user beamforming optimization problem to maximize the weighted sum rate (WSR) of the multiple users with FCAPA, it is shown that the proposed structure outperforms typical CAPA systems by a wide margin, with performance increasing with increasing morphability.
Joint DOA and Attitude Sensing Based on Tri-Polarized Continuous Aperture Array
Oct 02, 2025



Abstract:This paper investigates joint direction-of-arrival (DOA) and attitude sensing using tri-polarized continuous aperture arrays (CAPAs). By employing electromagnetic (EM) information theory, the spatially continuous received signals in tri-polarized CAPA are modeled, thereby enabling accurate DOA and attitude estimation. To facilitate subspace decomposition for continuous operators, an equivalent continuous-discrete transformation technique is developed. Moreover, both self- and cross-covariances of tri-polarized signals are exploited to construct a tri-polarized spectrum, significantly enhancing DOA estimation performance. Theoretical analyses reveal that the identifiability of attitude information fundamentally depends on the availability of prior target snapshots. Accordingly, two attitude estimation algorithms are proposed: one capable of estimating partial attitude information without prior knowledge, and the other achieving full attitude estimation when such knowledge is available. Numerical results demonstrate the feasibility and superiority of the proposed framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge