Matei Ciocarlie
ReactEMG Stroke: Healthy-to-Stroke Few-shot Adaptation for sEMG-Based Intent Detection
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Surface electromyography (sEMG) is a promising control signal for assist-as-needed hand rehabilitation after stroke, but detecting intent from paretic muscles often requires lengthy, subject-specific calibration and remains brittle to variability. We propose a healthy-to-stroke adaptation pipeline that initializes an intent detector from a model pretrained on large-scale able-bodied sEMG, then fine-tunes it for each stroke participant using only a small amount of subject-specific data. Using a newly collected dataset from three individuals with chronic stroke, we compare adaptation strategies (head-only tuning, parameter-efficient LoRA adapters, and full end-to-end fine-tuning) and evaluate on held-out test sets that include realistic distribution shifts such as within-session drift, posture changes, and armband repositioning. Across conditions, healthy-pretrained adaptation consistently improves stroke intent detection relative to both zero-shot transfer and stroke-only training under the same data budget; the best adaptation methods improve average transition accuracy from 0.42 to 0.61 and raw accuracy from 0.69 to 0.78. These results suggest that transferring a reusable healthy-domain EMG representation can reduce calibration burden while improving robustness for real-time post-stroke intent detection.
SpikeATac: A Multimodal Tactile Finger with Taxelized Dynamic Sensing for Dexterous Manipulation
Oct 30, 2025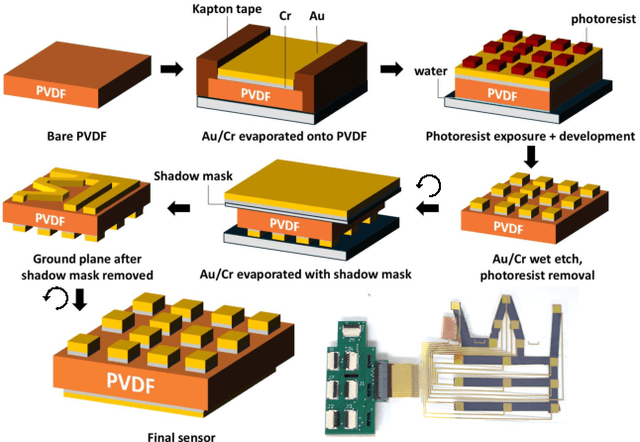
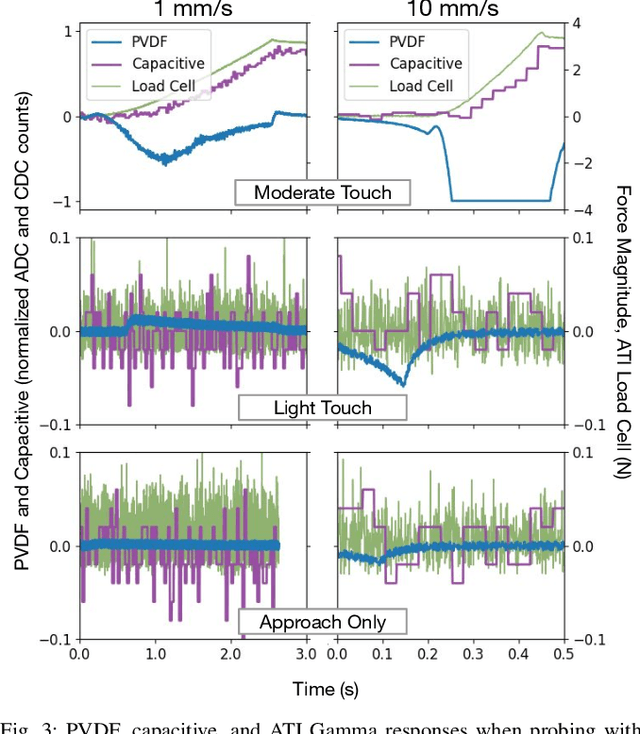
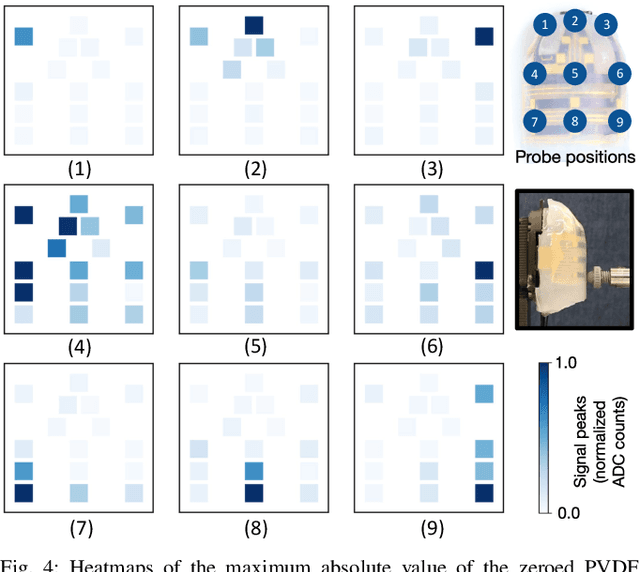
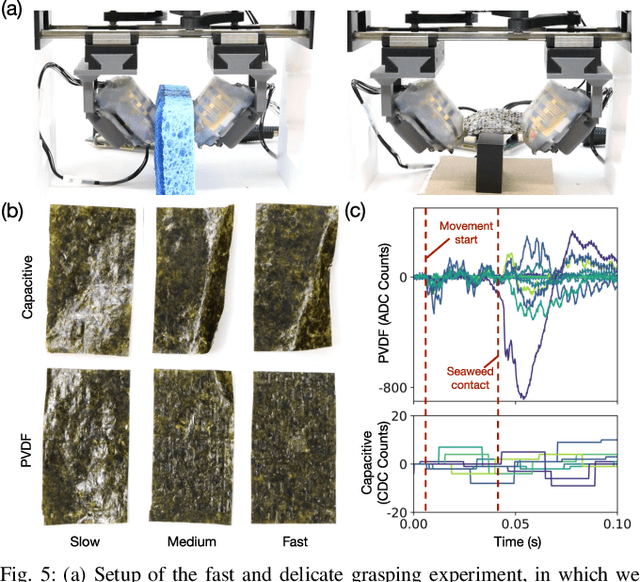
Abstract:In this work, we introduce SpikeATac, a multimodal tactile finger combining a taxelized and highly sensitive dynamic response (PVDF) with a static transduction method (capacitive) for multimodal touch sensing. Named for its `spiky' response, SpikeATac's 16-taxel PVDF film sampled at 4 kHz provides fast, sensitive dynamic signals to the very onset and breaking of contact. We characterize the sensitivity of the different modalities, and show that SpikeATac provides the ability to stop quickly and delicately when grasping fragile, deformable objects. Beyond parallel grasping, we show that SpikeATac can be used in a learning-based framework to achieve new capabilities on a dexterous multifingered robot hand. We use a learning recipe that combines reinforcement learning from human feedback with tactile-based rewards to fine-tune the behavior of a policy to modulate force. Our hardware platform and learning pipeline together enable a difficult dexterous and contact-rich task that has not previously been achieved: in-hand manipulation of fragile objects. Videos are available at \href{https://roamlab.github.io/spikeatac/}{roamlab.github.io/spikeatac}.
MiniBEE: A New Form Factor for Compact Bimanual Dexterity
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Bimanual robot manipulators can achieve impressive dexterity, but typically rely on two full six- or seven- degree-of-freedom arms so that paired grippers can coordinate effectively. This traditional framework increases system complexity while only exploiting a fraction of the overall workspace for dexterous interaction. We introduce the MiniBEE (Miniature Bimanual End-effector), a compact system in which two reduced-mobility arms (3+ DOF each) are coupled into a kinematic chain that preserves full relative positioning between grippers. To guide our design, we formulate a kinematic dexterity metric that enlarges the dexterous workspace while keeping the mechanism lightweight and wearable. The resulting system supports two complementary modes: (i) wearable kinesthetic data collection with self-tracked gripper poses, and (ii) deployment on a standard robot arm, extending dexterity across its entire workspace. We present kinematic analysis and design optimization methods for maximizing dexterous range, and demonstrate an end-to-end pipeline in which wearable demonstrations train imitation learning policies that perform robust, real-world bimanual manipulation.
ReactEMG: Zero-Shot, Low-Latency Intent Detection via sEMG
Jun 24, 2025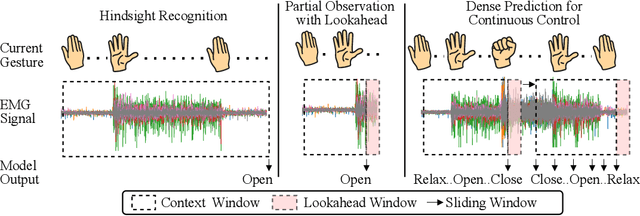
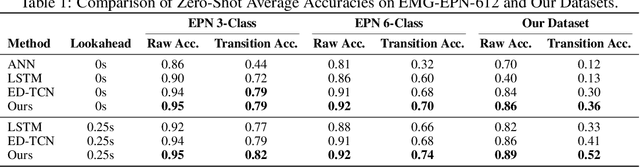
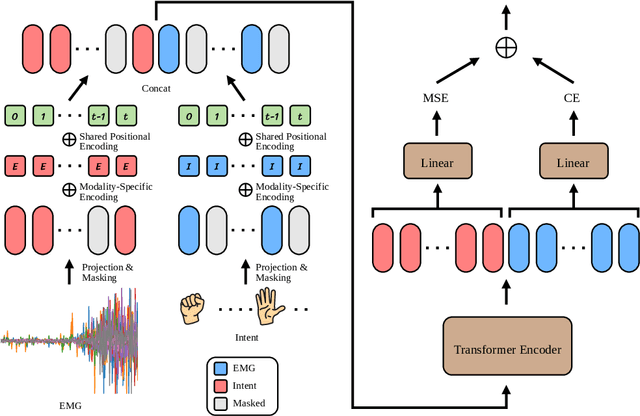
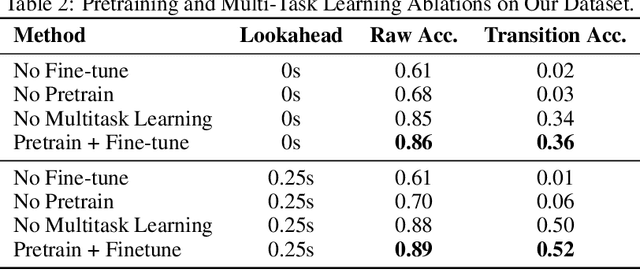
Abstract:Surface electromyography (sEMG) signals show promise for effective human-computer interfaces, particularly in rehabilitation and prosthetics. However, challenges remain in developing systems that respond quickly and reliably to user intent, across different subjects and without requiring time-consuming calibration. In this work, we propose a framework for EMG-based intent detection that addresses these challenges. Unlike traditional gesture recognition models that wait until a gesture is completed before classifying it, our approach uses a segmentation strategy to assign intent labels at every timestep as the gesture unfolds. We introduce a novel masked modeling strategy that aligns muscle activations with their corresponding user intents, enabling rapid onset detection and stable tracking of ongoing gestures. In evaluations against baseline methods, considering both accuracy and stability for device control, our approach surpasses state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot transfer conditions, demonstrating its potential for wearable robotics and next-generation prosthetic systems. Our project page is available at: https://reactemg.github.io
VibeCheck: Using Active Acoustic Tactile Sensing for Contact-Rich Manipulation
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:The acoustic response of an object can reveal a lot about its global state, for example its material properties or the extrinsic contacts it is making with the world. In this work, we build an active acoustic sensing gripper equipped with two piezoelectric fingers: one for generating signals, the other for receiving them. By sending an acoustic vibration from one finger to the other through an object, we gain insight into an object's acoustic properties and contact state. We use this system to classify objects, estimate grasping position, estimate poses of internal structures, and classify the types of extrinsic contacts an object is making with the environment. Using our contact type classification model, we tackle a standard long-horizon manipulation problem: peg insertion. We use a simple simulated transition model based on the performance of our sensor to train an imitation learning policy that is robust to imperfect predictions from the classifier. We finally demonstrate the policy on a UR5 robot with active acoustic sensing as the only feedback.
Train Robots in a JIF: Joint Inverse and Forward Dynamics with Human and Robot Demonstrations
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:Pre-training on large datasets of robot demonstrations is a powerful technique for learning diverse manipulation skills but is often limited by the high cost and complexity of collecting robot-centric data, especially for tasks requiring tactile feedback. This work addresses these challenges by introducing a novel method for pre-training with multi-modal human demonstrations. Our approach jointly learns inverse and forward dynamics to extract latent state representations, towards learning manipulation specific representations. This enables efficient fine-tuning with only a small number of robot demonstrations, significantly improving data efficiency. Furthermore, our method allows for the use of multi-modal data, such as combination of vision and touch for manipulation. By leveraging latent dynamics modeling and tactile sensing, this approach paves the way for scalable robot manipulation learning based on human demonstrations.
Reciprocal Learning of Intent Inferral with Augmented Visual Feedback for Stroke
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Intent inferral, the process by which a robotic device predicts a user's intent from biosignals, offers an effective and intuitive way to control wearable robots. Classical intent inferral methods treat biosignal inputs as unidirectional ground truths for training machine learning models, where the internal state of the model is not directly observable by the user. In this work, we propose reciprocal learning, a bidirectional paradigm that facilitates human adaptation to an intent inferral classifier. Our paradigm consists of iterative, interwoven stages that alternate between updating machine learning models and guiding human adaptation with the use of augmented visual feedback. We demonstrate this paradigm in the context of controlling a robotic hand orthosis for stroke, where the device predicts open, close, and relax intents from electromyographic (EMG) signals and provides appropriate assistance. We use LED progress-bar displays to communicate to the user the predicted probabilities for open and close intents by the classifier. Our experiments with stroke subjects show reciprocal learning improving performance in a subset of subjects (two out of five) without negatively impacting performance on the others. We hypothesize that, during reciprocal learning, subjects can learn to reproduce more distinguishable muscle activation patterns and generate more separable biosignals.
A Compact, Low-cost Force and Torque Sensor for Robot Fingers with LED-based Displacement Sensing
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Force/torque sensing is an important modality for robotic manipulation, but commodity solutions, generally developed with other applications in mind, do not generally fit the needs of robot hands. This paper introduces a novel method for six-axis force/torque sensing, using LEDs to sense the displacement between two plates connected by a transparent elastomer. Our method allows for finger-size packaging with no amplification electronics, low cost manufacturing, and easy integration into a complete hand. On test forces between 0-2 N, our prototype sensor exhibits a mean error between 0.05 and 0.07 N across the three force directions, suggesting future applicability to fine manipulation tasks.
ChatEMG: Synthetic Data Generation to Control a Robotic Hand Orthosis for Stroke
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Intent inferral on a hand orthosis for stroke patients is challenging due to the difficulty of data collection from impaired subjects. Additionally, EMG signals exhibit significant variations across different conditions, sessions, and subjects, making it hard for classifiers to generalize. Traditional approaches require a large labeled dataset from the new condition, session, or subject to train intent classifiers; however, this data collection process is burdensome and time-consuming. In this paper, we propose ChatEMG, an autoregressive generative model that can generate synthetic EMG signals conditioned on prompts (i.e., a given sequence of EMG signals). ChatEMG enables us to collect only a small dataset from the new condition, session, or subject and expand it with synthetic samples conditioned on prompts from this new context. ChatEMG leverages a vast repository of previous data via generative training while still remaining context-specific via prompting. Our experiments show that these synthetic samples are classifier-agnostic and can improve intent inferral accuracy for different types of classifiers. We demonstrate that our complete approach can be integrated into a single patient session, including the use of the classifier for functional orthosis-assisted tasks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time an intent classifier trained partially on synthetic data has been deployed for functional control of an orthosis by a stroke survivor. Videos and additional information can be found at https://jxu.ai/chatemg.
Task-Based Design and Policy Co-Optimization for Tendon-driven Underactuated Kinematic Chains
May 23, 2024



Abstract:Underactuated manipulators reduce the number of bulky motors, thereby enabling compact and mechanically robust designs. However, fewer actuators than joints means that the manipulator can only access a specific manifold within the joint space, which is particular to a given hardware configuration and can be low-dimensional and/or discontinuous. Determining an appropriate set of hardware parameters for this class of mechanisms, therefore, is difficult - even for traditional task-based co-optimization methods. In this paper, our goal is to implement a task-based design and policy co-optimization method for underactuated, tendon-driven manipulators. We first formulate a general model for an underactuated, tendon-driven transmission. We then use this model to co-optimize a three-link, two-actuator kinematic chain using reinforcement learning. We demonstrate that our optimized tendon transmission and control policy can be transferred reliably to physical hardware with real-world reaching experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge