Siqi Shang
FORTE: Tactile Force and Slip Sensing on Compliant Fingers for Delicate Manipulation
Jun 23, 2025



Abstract:Handling delicate and fragile objects remains a major challenge for robotic manipulation, especially for rigid parallel grippers. While the simplicity and versatility of parallel grippers have led to widespread adoption, these grippers are limited by their heavy reliance on visual feedback. Tactile sensing and soft robotics can add responsiveness and compliance. However, existing methods typically involve high integration complexity or suffer from slow response times. In this work, we introduce FORTE, a tactile sensing system embedded in compliant gripper fingers. FORTE uses 3D-printed fin-ray grippers with internal air channels to provide low-latency force and slip feedback. FORTE applies just enough force to grasp objects without damaging them, while remaining easy to fabricate and integrate. We find that FORTE can accurately estimate grasping forces from 0-8 N with an average error of 0.2 N, and detect slip events within 100 ms of occurring. We demonstrate FORTE's ability to grasp a wide range of slippery, fragile, and deformable objects. In particular, FORTE grasps fragile objects like raspberries and potato chips with a 98.6% success rate, and achieves 93% accuracy in detecting slip events. These results highlight FORTE's potential as a robust and practical solution for enabling delicate robotic manipulation. Project page: https://merge-lab.github.io/FORTE
ChatEMG: Synthetic Data Generation to Control a Robotic Hand Orthosis for Stroke
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Intent inferral on a hand orthosis for stroke patients is challenging due to the difficulty of data collection from impaired subjects. Additionally, EMG signals exhibit significant variations across different conditions, sessions, and subjects, making it hard for classifiers to generalize. Traditional approaches require a large labeled dataset from the new condition, session, or subject to train intent classifiers; however, this data collection process is burdensome and time-consuming. In this paper, we propose ChatEMG, an autoregressive generative model that can generate synthetic EMG signals conditioned on prompts (i.e., a given sequence of EMG signals). ChatEMG enables us to collect only a small dataset from the new condition, session, or subject and expand it with synthetic samples conditioned on prompts from this new context. ChatEMG leverages a vast repository of previous data via generative training while still remaining context-specific via prompting. Our experiments show that these synthetic samples are classifier-agnostic and can improve intent inferral accuracy for different types of classifiers. We demonstrate that our complete approach can be integrated into a single patient session, including the use of the classifier for functional orthosis-assisted tasks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time an intent classifier trained partially on synthetic data has been deployed for functional control of an orthosis by a stroke survivor. Videos and additional information can be found at https://jxu.ai/chatemg.
R$\times$R: Rapid eXploration for Reinforcement Learning via Sampling-based Reset Distributions and Imitation Pre-training
Jan 27, 2024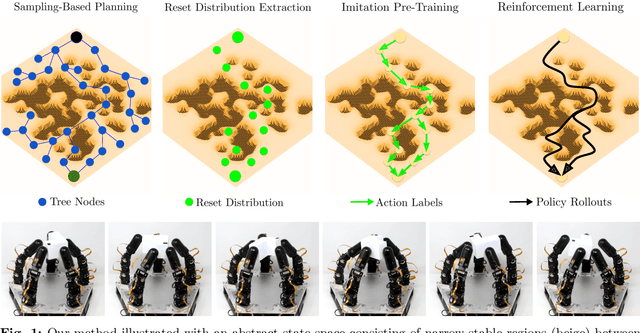

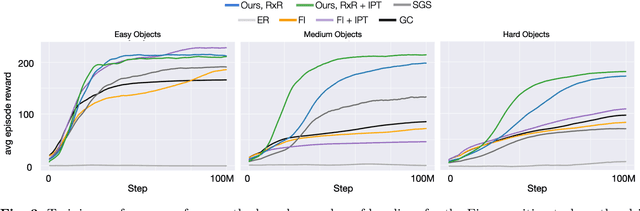
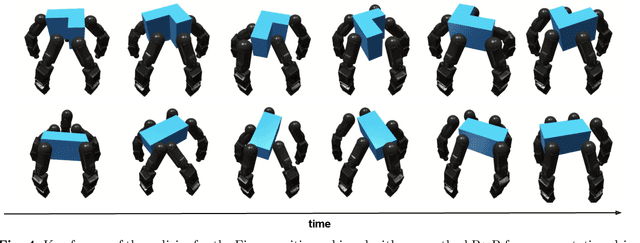
Abstract:We present a method for enabling Reinforcement Learning of motor control policies for complex skills such as dexterous manipulation. We posit that a key difficulty for training such policies is the difficulty of exploring the problem state space, as the accessible and useful regions of this space form a complex structure along manifolds of the original high-dimensional state space. This work presents a method to enable and support exploration with Sampling-based Planning. We use a generally applicable non-holonomic Rapidly-exploring Random Trees algorithm and present multiple methods to use the resulting structure to bootstrap model-free Reinforcement Learning. Our method is effective at learning various challenging dexterous motor control skills of higher difficulty than previously shown. In particular, we achieve dexterous in-hand manipulation of complex objects while simultaneously securing the object without the use of passive support surfaces. These policies also transfer effectively to real robots. A number of example videos can also be found on the project website: https://sbrl.cs.columbia.edu
Sampling-based Exploration for Reinforcement Learning of Dexterous Manipulation
Mar 11, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel method for achieving dexterous manipulation of complex objects, while simultaneously securing the object without the use of passive support surfaces. We posit that a key difficulty for training such policies in a Reinforcement Learning framework is the difficulty of exploring the problem state space, as the accessible regions of this space form a complex structure along manifolds of a high-dimensional space. To address this challenge, we use two versions of the non-holonomic Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees algorithm; one version is more general, but requires explicit use of the environment's transition function, while the second version uses manipulation-specific kinematic constraints to attain better sample efficiency. In both cases, we use states found via sampling-based exploration to generate reset distributions that enable training control policies under full dynamic constraints via model-free Reinforcement Learning. We show that these policies are effective at manipulation problems of higher difficulty than previously shown, and also transfer effectively to real robots. Videos of the real-hand demonstrations can be found on the project website: https://sbrl.cs.columbia.edu/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge