Martin Magnusson
HiCrowd: Hierarchical Crowd Flow Alignment for Dense Human Environments
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Navigating through dense human crowds remains a significant challenge for mobile robots. A key issue is the freezing robot problem, where the robot struggles to find safe motions and becomes stuck within the crowd. To address this, we propose HiCrowd, a hierarchical framework that integrates reinforcement learning (RL) with model predictive control (MPC). HiCrowd leverages surrounding pedestrian motion as guidance, enabling the robot to align with compatible crowd flows. A high-level RL policy generates a follow point to align the robot with a suitable pedestrian group, while a low-level MPC safely tracks this guidance with short horizon planning. The method combines long-term crowd aware decision making with safe short-term execution. We evaluate HiCrowd against reactive and learning-based baselines in offline setting (replaying recorded human trajectories) and online setting (human trajectories are updated to react to the robot in simulation). Experiments on a real-world dataset and a synthetic crowd dataset show that our method outperforms in navigation efficiency and safety, while reducing freezing behaviors. Our results suggest that leveraging human motion as guidance, rather than treating humans solely as dynamic obstacles, provides a powerful principle for safe and efficient robot navigation in crowds.
Large-scale visual SLAM for in-the-wild videos
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Accurate and robust 3D scene reconstruction from casual, in-the-wild videos can significantly simplify robot deployment to new environments. However, reliable camera pose estimation and scene reconstruction from such unconstrained videos remains an open challenge. Existing visual-only SLAM methods perform well on benchmark datasets but struggle with real-world footage which often exhibits uncontrolled motion including rapid rotations and pure forward movements, textureless regions, and dynamic objects. We analyze the limitations of current methods and introduce a robust pipeline designed to improve 3D reconstruction from casual videos. We build upon recent deep visual odometry methods but increase robustness in several ways. Camera intrinsics are automatically recovered from the first few frames using structure-from-motion. Dynamic objects and less-constrained areas are masked with a predictive model. Additionally, we leverage monocular depth estimates to regularize bundle adjustment, mitigating errors in low-parallax situations. Finally, we integrate place recognition and loop closure to reduce long-term drift and refine both intrinsics and pose estimates through global bundle adjustment. We demonstrate large-scale contiguous 3D models from several online videos in various environments. In contrast, baseline methods typically produce locally inconsistent results at several points, producing separate segments or distorted maps. In lieu of ground-truth pose data, we evaluate map consistency, execution time and visual accuracy of re-rendered NeRF models. Our proposed system establishes a new baseline for visual reconstruction from casual uncontrolled videos found online, demonstrating more consistent reconstructions over longer sequences of in-the-wild videos than previously achieved.
Multimodal Interaction and Intention Communication for Industrial Robots
Feb 25, 2025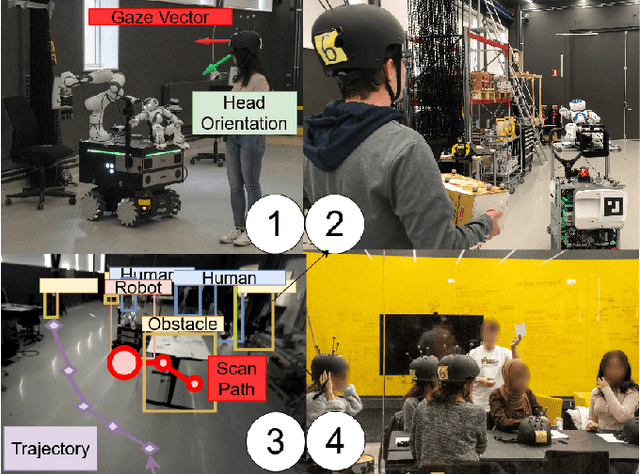
Abstract:Successful adoption of industrial robots will strongly depend on their ability to safely and efficiently operate in human environments, engage in natural communication, understand their users, and express intentions intuitively while avoiding unnecessary distractions. To achieve this advanced level of Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), robots need to acquire and incorporate knowledge of their users' tasks and environment and adopt multimodal communication approaches with expressive cues that combine speech, movement, gazes, and other modalities. This paper presents several methods to design, enhance, and evaluate expressive HRI systems for non-humanoid industrial robots. We present the concept of a small anthropomorphic robot communicating as a proxy for its non-humanoid host, such as a forklift. We developed a multimodal and LLM-enhanced communication framework for this robot and evaluated it in several lab experiments, using gaze tracking and motion capture to quantify how users perceive the robot and measure the task progress.
Evaluating Efficiency and Engagement in Scripted and LLM-Enhanced Human-Robot Interactions
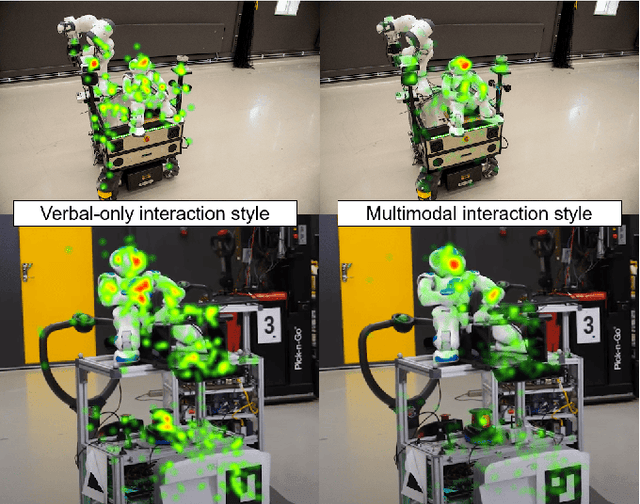
Jan 21, 2025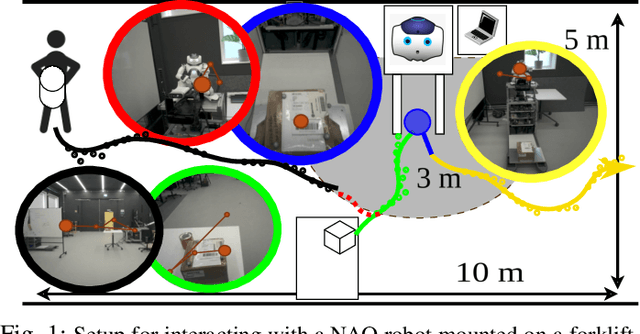
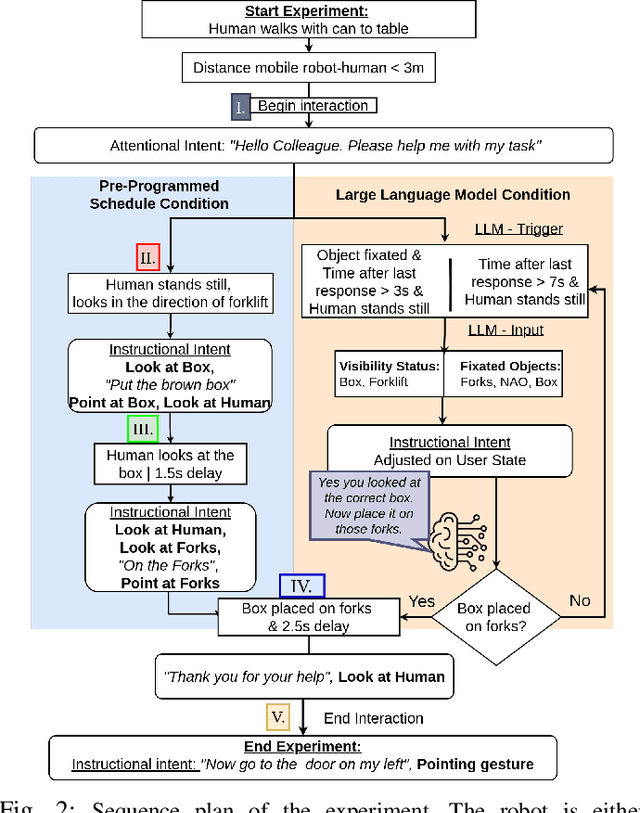
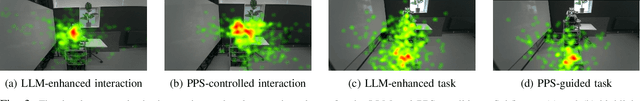
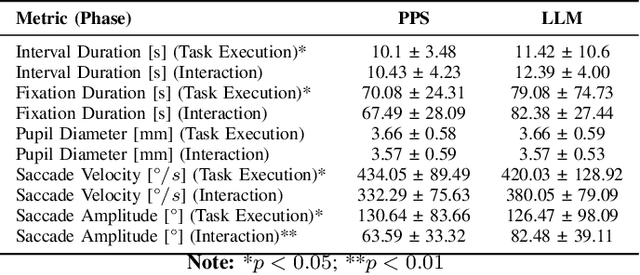
Abstract:To achieve natural and intuitive interaction with people, HRI frameworks combine a wide array of methods for human perception, intention communication, human-aware navigation and collaborative action. In practice, when encountering unpredictable behavior of people or unexpected states of the environment, these frameworks may lack the ability to dynamically recognize such states, adapt and recover to resume the interaction. Large Language Models (LLMs), owing to their advanced reasoning capabilities and context retention, present a promising solution for enhancing robot adaptability. This potential, however, may not directly translate to improved interaction metrics. This paper considers a representative interaction with an industrial robot involving approach, instruction, and object manipulation, implemented in two conditions: (1) fully scripted and (2) including LLM-enhanced responses. We use gaze tracking and questionnaires to measure the participants' task efficiency, engagement, and robot perception. The results indicate higher subjective ratings for the LLM condition, but objective metrics show that the scripted condition performs comparably, particularly in efficiency and focus during simple tasks. We also note that the scripted condition may have an edge over LLM-enhanced responses in terms of response latency and energy consumption, especially for trivial and repetitive interactions.
Fast Online Learning of CLiFF-maps in Changing Environments
Oct 16, 2024
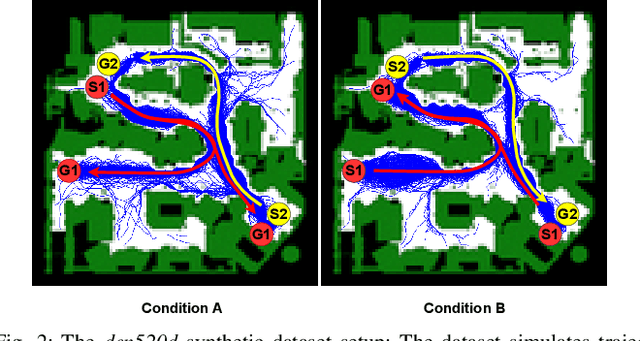
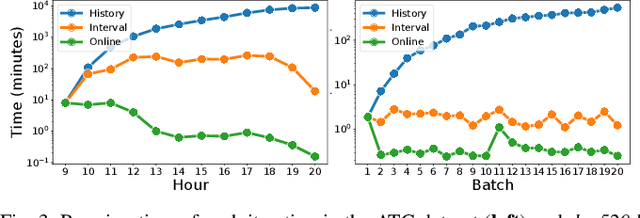

Abstract:Maps of dynamics are effective representations of motion patterns learned from prior observations, with recent research demonstrating their ability to enhance performance in various downstream tasks such as human-aware robot navigation, long-term human motion prediction, and robot localization. Current advancements have primarily concentrated on methods for learning maps of human flow in environments where the flow is static, i.e., not assumed to change over time. In this paper we propose a method to update the CLiFF-map, one type of map of dynamics, for achieving efficient life-long robot operation. As new observations are collected, our goal is to update a CLiFF-map to effectively and accurately integrate new observations, while retaining relevant historic motion patterns. The proposed online update method maintains a probabilistic representation in each observed location, updating parameters by continuously tracking sufficient statistics. In experiments using both synthetic and real-world datasets, we show that our method is able to maintain accurate representations of human motion dynamics, contributing to high performance flow-compliant planning downstream tasks, while being orders of magnitude faster than the comparable baselines.
Human Gaze and Head Rotation during Navigation, Exploration and Object Manipulation in Shared Environments with Robots
Jun 10, 2024
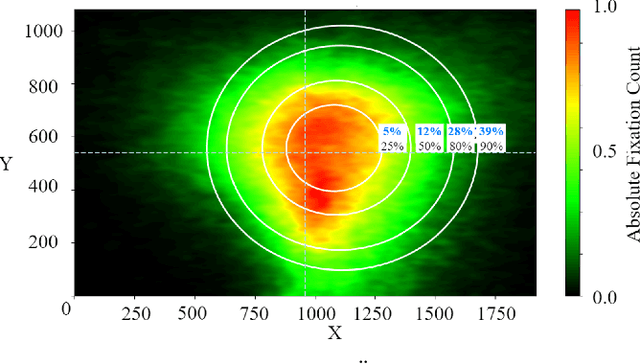
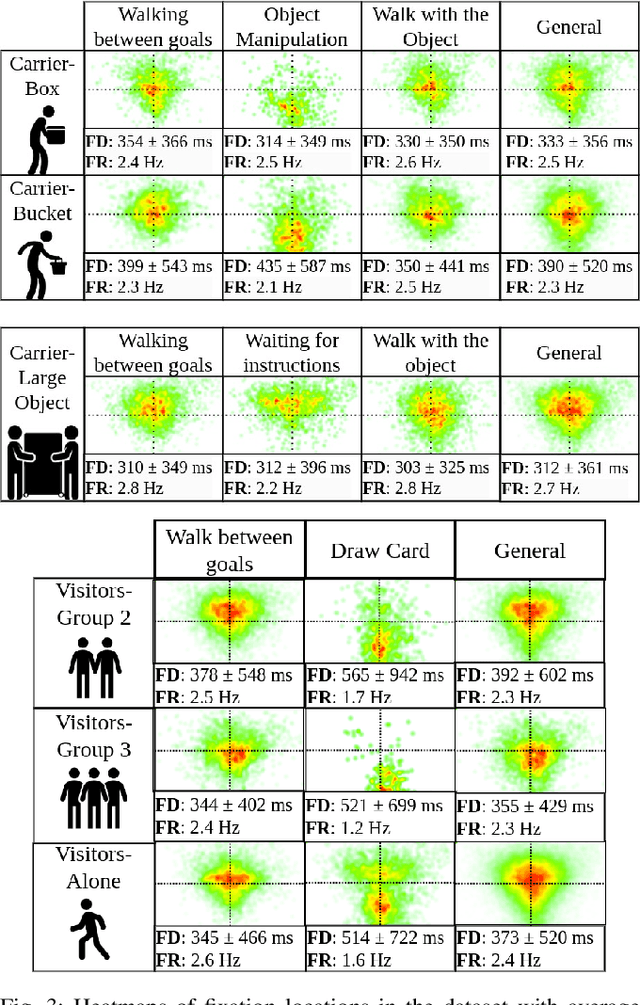
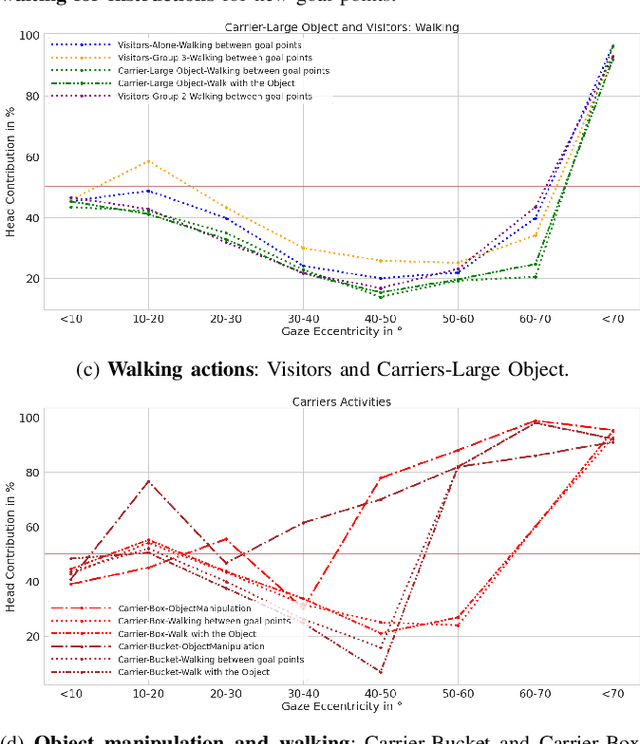
Abstract:The human gaze is an important cue to signal intention, attention, distraction, and the regions of interest in the immediate surroundings. Gaze tracking can transform how robots perceive, understand, and react to people, enabling new modes of robot control, interaction, and collaboration. In this paper, we use gaze tracking data from a rich dataset of human motion (TH\"OR-MAGNI) to investigate the coordination between gaze direction and head rotation of humans engaged in various indoor activities involving navigation, interaction with objects, and collaboration with a mobile robot. In particular, we study the spread and central bias of fixations in diverse activities and examine the correlation between gaze direction and head rotation. We introduce various human motion metrics to enhance the understanding of gaze behavior in dynamic interactions. Finally, we apply semantic object labeling to decompose the gaze distribution into activity-relevant regions.
* This is the final version of the accepted version of the manuscript that will be published in the 2024 33rd IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (ROMAN). Copyright 2024 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses
Human Detection from 4D Radar Data in Low-Visibility Field Conditions
Apr 08, 2024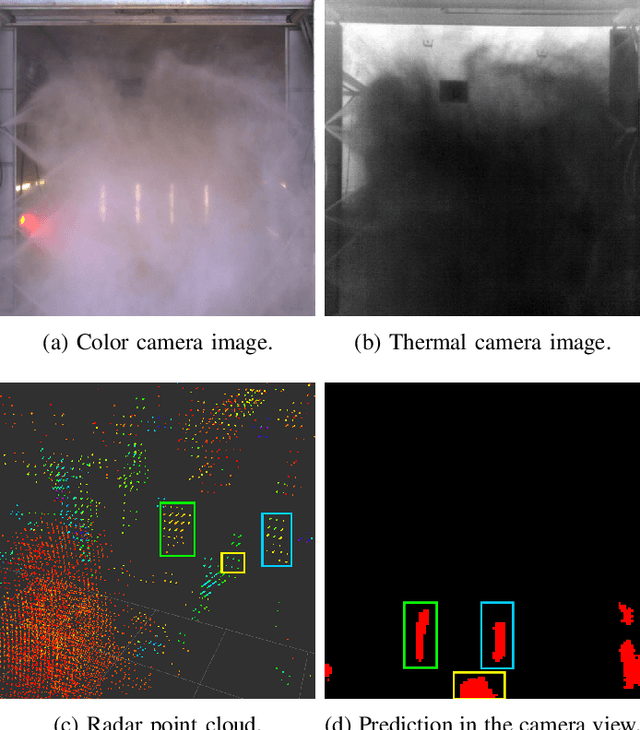



Abstract:Autonomous driving technology is increasingly being used on public roads and in industrial settings such as mines. While it is essential to detect pedestrians, vehicles, or other obstacles, adverse field conditions negatively affect the performance of classical sensors such as cameras or lidars. Radar, on the other hand, is a promising modality that is less affected by, e.g., dust, smoke, water mist or fog. In particular, modern 4D imaging radars provide target responses across the range, vertical angle, horizontal angle and Doppler velocity dimensions. We propose TMVA4D, a CNN architecture that leverages this 4D radar modality for semantic segmentation. The CNN is trained to distinguish between the background and person classes based on a series of 2D projections of the 4D radar data that include the elevation, azimuth, range, and Doppler velocity dimensions. We also outline the process of compiling a novel dataset consisting of data collected in industrial settings with a car-mounted 4D radar and describe how the ground-truth labels were generated from reference thermal images. Using TMVA4D on this dataset, we achieve an mIoU score of 78.2% and an mDice score of 86.1%, evaluated on the two classes background and person
LaCE-LHMP: Airflow Modelling-Inspired Long-Term Human Motion Prediction By Enhancing Laminar Characteristics in Human Flow
Mar 20, 2024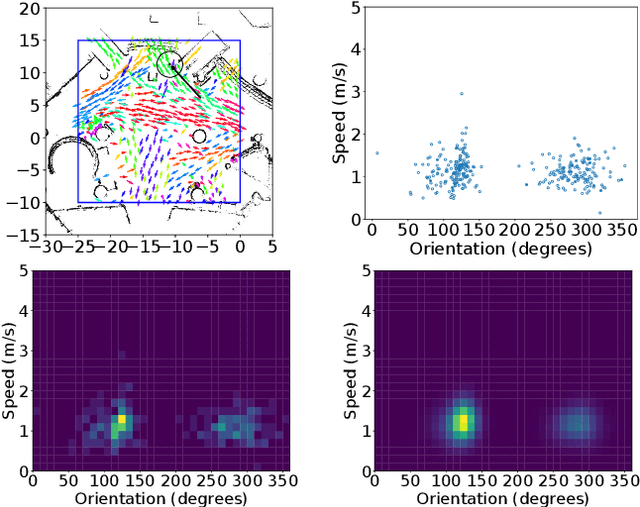
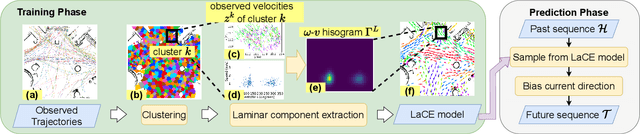
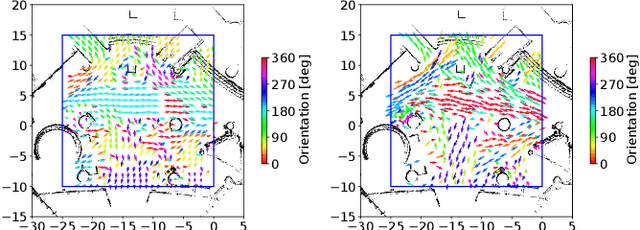
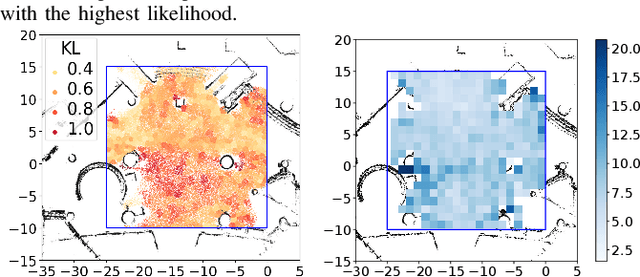
Abstract:Long-term human motion prediction (LHMP) is essential for safely operating autonomous robots and vehicles in populated environments. It is fundamental for various applications, including motion planning, tracking, human-robot interaction and safety monitoring. However, accurate prediction of human trajectories is challenging due to complex factors, including, for example, social norms and environmental conditions. The influence of such factors can be captured through Maps of Dynamics (MoDs), which encode spatial motion patterns learned from (possibly scattered and partial) past observations of motion in the environment and which can be used for data-efficient, interpretable motion prediction (MoD-LHMP). To address the limitations of prior work, especially regarding accuracy and sensitivity to anomalies in long-term prediction, we propose the Laminar Component Enhanced LHMP approach (LaCE-LHMP). Our approach is inspired by data-driven airflow modelling, which estimates laminar and turbulent flow components and uses predominantly the laminar components to make flow predictions. Based on the hypothesis that human trajectory patterns also manifest laminar flow (that represents predictable motion) and turbulent flow components (that reflect more unpredictable and arbitrary motion), LaCE-LHMP extracts the laminar patterns in human dynamics and uses them for human motion prediction. We demonstrate the superior prediction performance of LaCE-LHMP through benchmark comparisons with state-of-the-art LHMP methods, offering an unconventional perspective and a more intuitive understanding of human movement patterns.
High-Fidelity SLAM Using Gaussian Splatting with Rendering-Guided Densification and Regularized Optimization
Mar 19, 2024



Abstract:We propose a dense RGBD SLAM system based on 3D Gaussian Splatting that provides metrically accurate pose tracking and visually realistic reconstruction. To this end, we first propose a Gaussian densification strategy based on the rendering loss to map unobserved areas and refine reobserved areas. Second, we introduce extra regularization parameters to alleviate the forgetting problem in the continuous mapping problem, where parameters tend to overfit the latest frame and result in decreasing rendering quality for previous frames. Both mapping and tracking are performed with Gaussian parameters by minimizing re-rendering loss in a differentiable way. Compared to recent neural and concurrently developed gaussian splatting RGBD SLAM baselines, our method achieves state-of-the-art results on the synthetic dataset Replica and competitive results on the real-world dataset TUM.
THÖR-MAGNI: A Large-scale Indoor Motion Capture Recording of Human Movement and Robot Interaction
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:We present a new large dataset of indoor human and robot navigation and interaction, called TH\"OR-MAGNI, that is designed to facilitate research on social navigation: e.g., modelling and predicting human motion, analyzing goal-oriented interactions between humans and robots, and investigating visual attention in a social interaction context. TH\"OR-MAGNI was created to fill a gap in available datasets for human motion analysis and HRI. This gap is characterized by a lack of comprehensive inclusion of exogenous factors and essential target agent cues, which hinders the development of robust models capable of capturing the relationship between contextual cues and human behavior in different scenarios. Unlike existing datasets, TH\"OR-MAGNI includes a broader set of contextual features and offers multiple scenario variations to facilitate factor isolation. The dataset includes many social human-human and human-robot interaction scenarios, rich context annotations, and multi-modal data, such as walking trajectories, gaze tracking data, and lidar and camera streams recorded from a mobile robot. We also provide a set of tools for visualization and processing of the recorded data. TH\"OR-MAGNI is, to the best of our knowledge, unique in the amount and diversity of sensor data collected in a contextualized and socially dynamic environment, capturing natural human-robot interactions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge