Martijn de Vos
Mosaic Learning: A Framework for Decentralized Learning with Model Fragmentation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Decentralized learning (DL) enables collaborative machine learning (ML) without a central server, making it suitable for settings where training data cannot be centrally hosted. We introduce Mosaic Learning, a DL framework that decomposes models into fragments and disseminates them independently across the network. Fragmentation reduces redundant communication across correlated parameters and enables more diverse information propagation without increasing communication cost. We theoretically show that Mosaic Learning (i) shows state-of-the-art worst-case convergence rate, and (ii) leverages parameter correlation in an ML model, improving contraction by reducing the highest eigenvalue of a simplified system. We empirically evaluate Mosaic Learning on four learning tasks and observe up to 12 percentage points higher node-level test accuracy compared to epidemic learning (EL), a state-of-the-art baseline. In summary, Mosaic Learning improves DL performance without sacrificing its utility or efficiency, and positions itself as a new DL standard.
Effective LoRA Adapter Routing using Task Representations
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) enables parameter efficient specialization of large language models (LLMs) through modular adapters, resulting in rapidly growing public adapter pools spanning diverse tasks. Effectively using these adapters requires routing: selecting and composing the appropriate adapters for a query. We introduce LORAUTER, a novel routing framework that selects and composes LoRA adapters using task representations rather than adapter characteristics. Unlike existing approaches that map queries directly to adapters, LORAUTER routes queries via task embeddings derived from small validation sets and does not require adapter training data. By operating at the task level, LORAUTER achieves efficient routing that scales with the number of tasks rather than the number of adapters. Experiments across multiple tasks show that LORAUTER consistently outperforms baseline routing approaches, matching Oracle performance (101.2%) when task-aligned adapters exist and achieving state-of-the-art results on unseen tasks (+5.2 points). We further demonstrate the robustness of LORAUTER to very large, noisy adapter pools by scaling it to over 1500 adapters.
Optimizing Agentic Workflows using Meta-tools
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Agentic AI enables LLM to dynamically reason, plan, and interact with tools to solve complex tasks. However, agentic workflows often require many iterative reasoning steps and tool invocations, leading to significant operational expense, end-to-end latency and failures due to hallucinations. This work introduces Agent Workflow Optimization (AWO), a framework that identifies and optimizes redundant tool execution patterns to improve the efficiency and robustness of agentic workflows. AWO analyzes existing workflow traces to discover recurring sequences of tool calls and transforms them into meta-tools, which are deterministic, composite tools that bundle multiple agent actions into a single invocation. Meta-tools bypass unnecessary intermediate LLM reasoning steps and reduce operational cost while also shortening execution paths, leading to fewer failures. Experiments on two agentic AI benchmarks show that AWO reduces the number of LLM calls up to 11.9% while also increasing the task success rate by up to 4.2 percent points.
Collaborative Agentic AI Needs Interoperability Across Ecosystems
May 25, 2025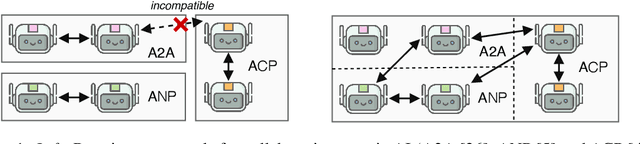
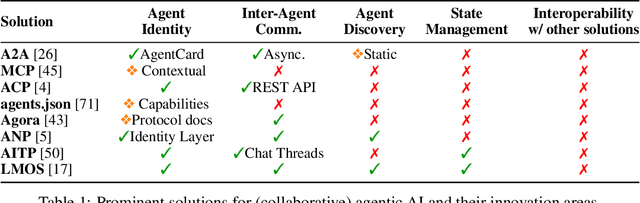
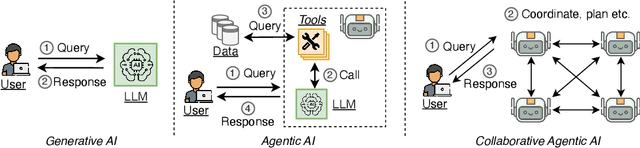
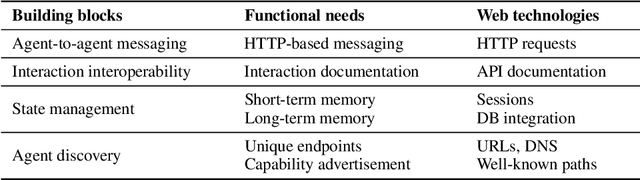
Abstract:Collaborative agentic AI is projected to transform entire industries by enabling AI-powered agents to autonomously perceive, plan, and act within digital environments. Yet, current solutions in this field are all built in isolation, and we are rapidly heading toward a landscape of fragmented, incompatible ecosystems. In this position paper, we argue that interoperability, achieved by the adoption of minimal standards, is essential to ensure open, secure, web-scale, and widely-adopted agentic ecosystems. To this end, we devise a minimal architectural foundation for collaborative agentic AI, named Web of Agents, which is composed of four components: agent-to-agent messaging, interaction interoperability, state management, and agent discovery. Web of Agents adopts existing standards and reuses existing infrastructure where possible. With Web of Agents, we take the first but critical step toward interoperable agentic systems and offer a pragmatic path forward before ecosystem fragmentation becomes the norm.
Accelerating MoE Model Inference with Expert Sharding
Mar 11, 2025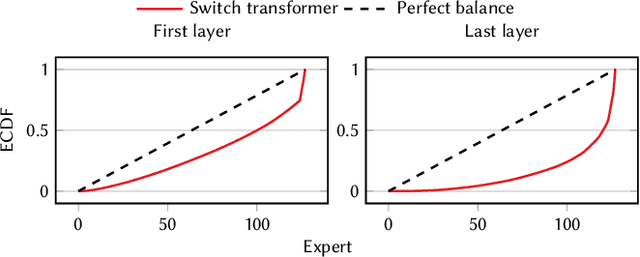
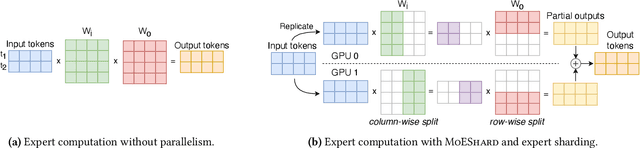
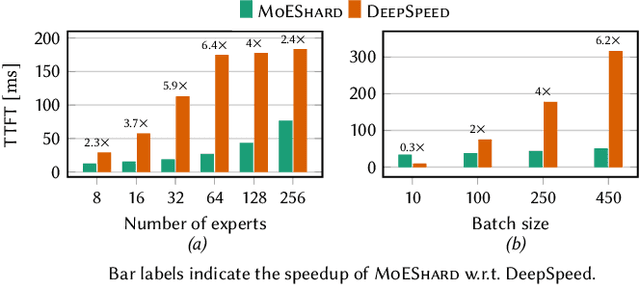
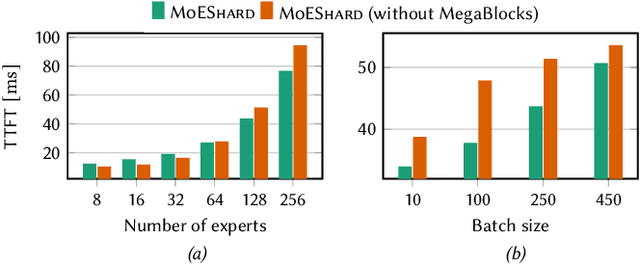
Abstract:Mixture of experts (MoE) models achieve state-of-the-art results in language modeling but suffer from inefficient hardware utilization due to imbalanced token routing and communication overhead. While prior work has focused on optimizing MoE training and decoder architectures, inference for encoder-based MoE models in a multi-GPU with expert parallelism setting remains underexplored. We introduce MoEShard, an inference system that achieves perfect load balancing through tensor sharding of MoE experts. Unlike existing approaches that rely on heuristic capacity factors or drop tokens, MoEShard evenly distributes computation across GPUs and ensures full token retention, maximizing utilization regardless of routing skewness. We achieve this through a strategic row- and column-wise decomposition of expert matrices. This reduces idle time and avoids bottlenecks caused by imbalanced expert assignments. Furthermore, MoEShard minimizes kernel launches by fusing decomposed expert computations, significantly improving throughput. We evaluate MoEShard against DeepSpeed on encoder-based architectures, demonstrating speedups of up to 6.4$\times$ in time to first token (TTFT). Our results show that tensor sharding, when properly applied to experts, is a viable and effective strategy for efficient MoE inference.
Leveraging Approximate Caching for Faster Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enhances the reliability of large language model (LLM) answers by integrating external knowledge. However, RAG increases the end-to-end inference time since looking for relevant documents from large vector databases is computationally expensive. To address this, we introduce Proximity, an approximate key-value cache that optimizes the RAG workflow by leveraging similarities in user queries. Instead of treating each query independently, Proximity reuses previously retrieved documents when similar queries appear, reducing reliance on expensive vector database lookups. We evaluate Proximity on the MMLU and MedRAG benchmarks, demonstrating that it significantly improves retrieval efficiency while maintaining response accuracy. Proximity reduces retrieval latency by up to 59% while maintaining accuracy and lowers the computational burden on the vector database. We also experiment with different similarity thresholds and quantify the trade-off between speed and recall. Our work shows that approximate caching is a viable and effective strategy for optimizing RAG-based systems.
Efficient Federated Search for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various domains but remain susceptible to hallucinations and inconsistencies, limiting their reliability. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) mitigates these issues by grounding model responses in external knowledge sources. Existing RAG workflows often leverage a single vector database, which is impractical in the common setting where information is distributed across multiple repositories. We introduce RAGRoute, a novel mechanism for federated RAG search. RAGRoute dynamically selects relevant data sources at query time using a lightweight neural network classifier. By not querying every data source, this approach significantly reduces query overhead, improves retrieval efficiency, and minimizes the retrieval of irrelevant information. We evaluate RAGRoute using the MIRAGE and MMLU benchmarks and demonstrate its effectiveness in retrieving relevant documents while reducing the number of queries. RAGRoute reduces the total number of queries up to 77.5% and communication volume up to 76.2%.
Fair Decentralized Learning
Oct 03, 2024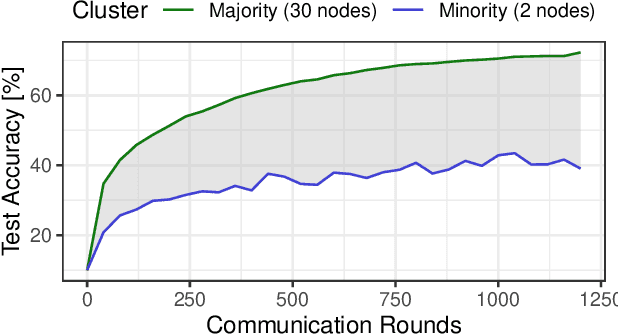


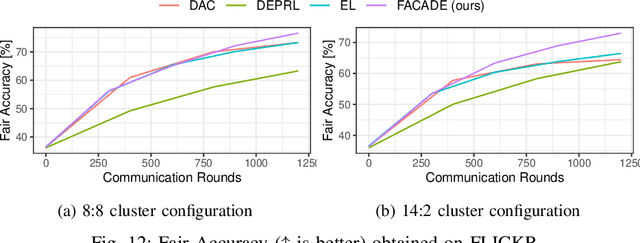
Abstract:Decentralized learning (DL) is an emerging approach that enables nodes to collaboratively train a machine learning model without sharing raw data. In many application domains, such as healthcare, this approach faces challenges due to the high level of heterogeneity in the training data's feature space. Such feature heterogeneity lowers model utility and negatively impacts fairness, particularly for nodes with under-represented training data. In this paper, we introduce \textsc{Facade}, a clustering-based DL algorithm specifically designed for fair model training when the training data exhibits several distinct features. The challenge of \textsc{Facade} is to assign nodes to clusters, one for each feature, based on the similarity in the features of their local data, without requiring individual nodes to know apriori which cluster they belong to. \textsc{Facade} (1) dynamically assigns nodes to their appropriate clusters over time, and (2) enables nodes to collaboratively train a specialized model for each cluster in a fully decentralized manner. We theoretically prove the convergence of \textsc{Facade}, implement our algorithm, and compare it against three state-of-the-art baselines. Our experimental results on three datasets demonstrate the superiority of our approach in terms of model accuracy and fairness compared to all three competitors. Compared to the best-performing baseline, \textsc{Facade} on the CIFAR-10 dataset also reduces communication costs by 32.3\% to reach a target accuracy when cluster sizes are imbalanced.
Energy-Aware Decentralized Learning with Intermittent Model Training
Jul 01, 2024



Abstract:Decentralized learning (DL) offers a powerful framework where nodes collaboratively train models without sharing raw data and without the coordination of a central server. In the iterative rounds of DL, models are trained locally, shared with neighbors in the topology, and aggregated with other models received from neighbors. Sharing and merging models contribute to convergence towards a consensus model that generalizes better across the collective data captured at training time. In addition, the energy consumption while sharing and merging model parameters is negligible compared to the energy spent during the training phase. Leveraging this fact, we present SkipTrain, a novel DL algorithm, which minimizes energy consumption in decentralized learning by strategically skipping some training rounds and substituting them with synchronization rounds. These training-silent periods, besides saving energy, also allow models to better mix and finally produce models with superior accuracy than typical DL algorithms that train at every round. Our empirical evaluations with 256 nodes demonstrate that SkipTrain reduces energy consumption by 50% and increases model accuracy by up to 12% compared to D-PSGD, the conventional DL algorithm.
Harnessing Increased Client Participation with Cohort-Parallel Federated Learning
May 24, 2024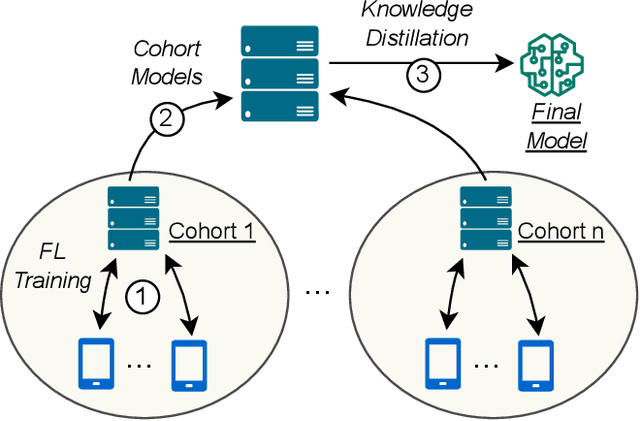
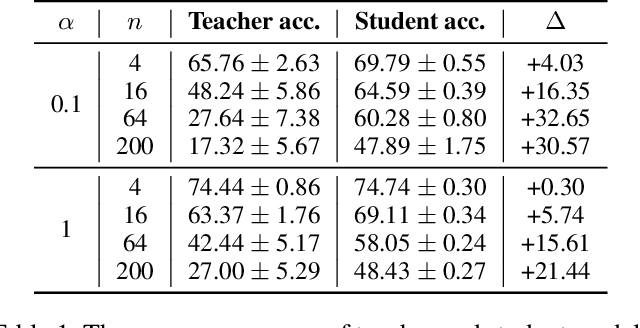
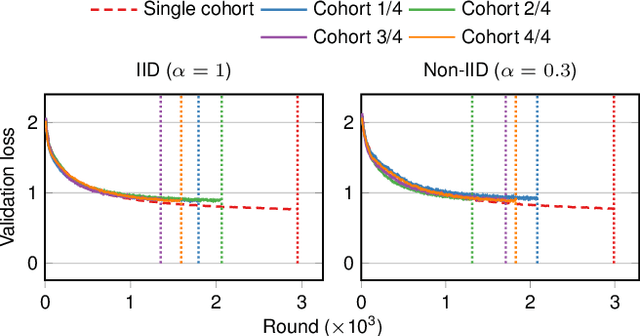
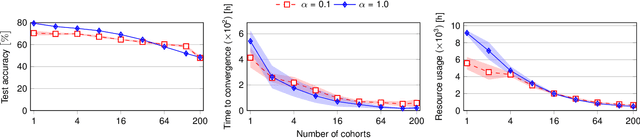
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a machine learning approach where nodes collaboratively train a global model. As more nodes participate in a round of FL, the effectiveness of individual model updates by nodes also diminishes. In this study, we increase the effectiveness of client updates by dividing the network into smaller partitions, or cohorts. We introduce Cohort-Parallel Federated Learning (CPFL): a novel learning approach where each cohort independently trains a global model using FL, until convergence, and the produced models by each cohort are then unified using one-shot Knowledge Distillation (KD) and a cross-domain, unlabeled dataset. The insight behind CPFL is that smaller, isolated networks converge quicker than in a one-network setting where all nodes participate. Through exhaustive experiments involving realistic traces and non-IID data distributions on the CIFAR-10 and FEMNIST image classification tasks, we investigate the balance between the number of cohorts, model accuracy, training time, and compute and communication resources. Compared to traditional FL, CPFL with four cohorts, non-IID data distribution, and CIFAR-10 yields a 1.9$\times$ reduction in train time and a 1.3$\times$ reduction in resource usage, with a minimal drop in test accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge