Jade Garcia Bourrée
Robust ML Auditing using Prior Knowledge
May 07, 2025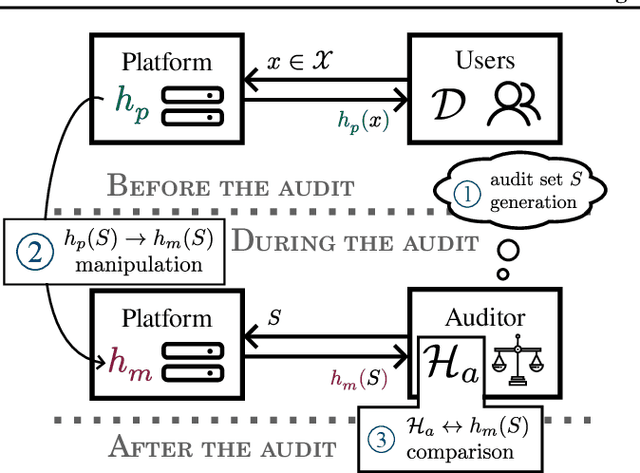

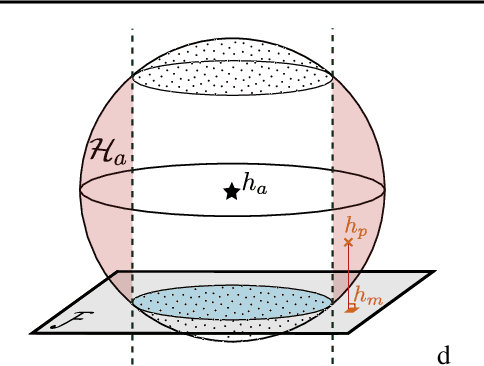
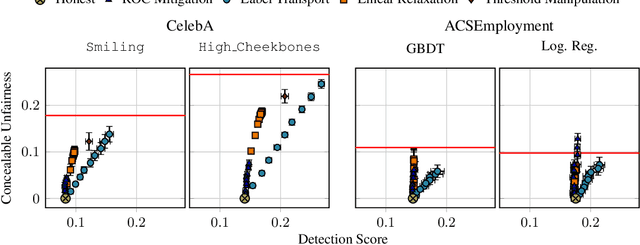
Abstract:The rapid adoption of ML decision-making systems across products and services has led to a set of regulations on how such systems should behave and be built. Among all the technical challenges to enforcing these regulations, one crucial, yet under-explored problem is the risk of manipulation while these systems are being audited for fairness. This manipulation occurs when a platform deliberately alters its answers to a regulator to pass an audit without modifying its answers to other users. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to manipulation-proof auditing by taking into account the auditor's prior knowledge of the task solved by the platform. We first demonstrate that regulators must not rely on public priors (e.g. a public dataset), as platforms could easily fool the auditor in such cases. We then formally establish the conditions under which an auditor can prevent audit manipulations using prior knowledge about the ground truth. Finally, our experiments with two standard datasets exemplify the maximum level of unfairness a platform can hide before being detected as malicious. Our formalization and generalization of manipulation-proof auditing with a prior opens up new research directions for more robust fairness audits.
P2NIA: Privacy-Preserving Non-Iterative Auditing
Apr 01, 2025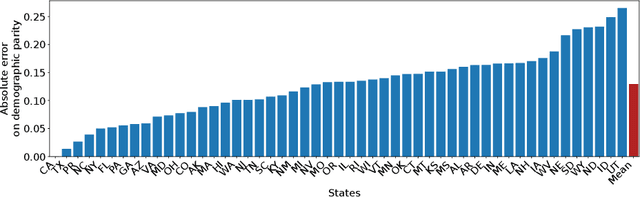
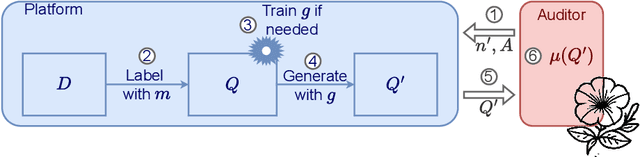
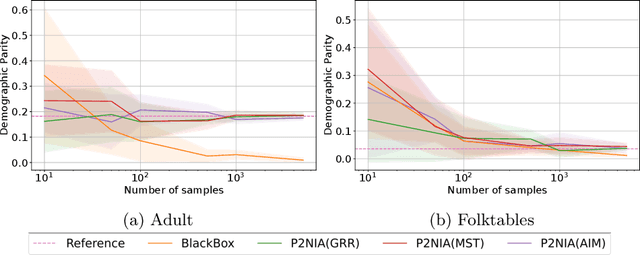
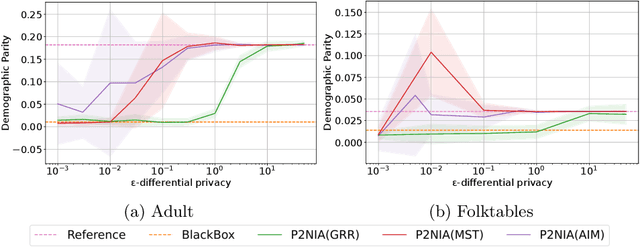
Abstract:The emergence of AI legislation has increased the need to assess the ethical compliance of high-risk AI systems. Traditional auditing methods rely on platforms' application programming interfaces (APIs), where responses to queries are examined through the lens of fairness requirements. However, such approaches put a significant burden on platforms, as they are forced to maintain APIs while ensuring privacy, facing the possibility of data leaks. This lack of proper collaboration between the two parties, in turn, causes a significant challenge to the auditor, who is subject to estimation bias as they are unaware of the data distribution of the platform. To address these two issues, we present P2NIA, a novel auditing scheme that proposes a mutually beneficial collaboration for both the auditor and the platform. Extensive experiments demonstrate P2NIA's effectiveness in addressing both issues. In summary, our work introduces a privacy-preserving and non-iterative audit scheme that enhances fairness assessments using synthetic or local data, avoiding the challenges associated with traditional API-based audits.
Fairness Auditing with Multi-Agent Collaboration
Feb 13, 2024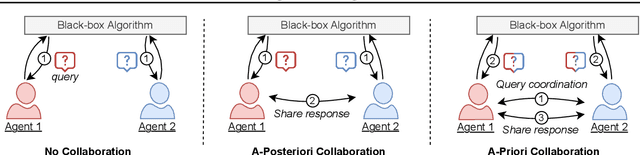
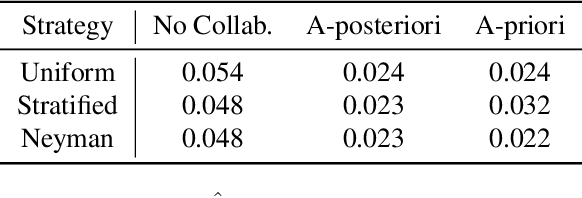
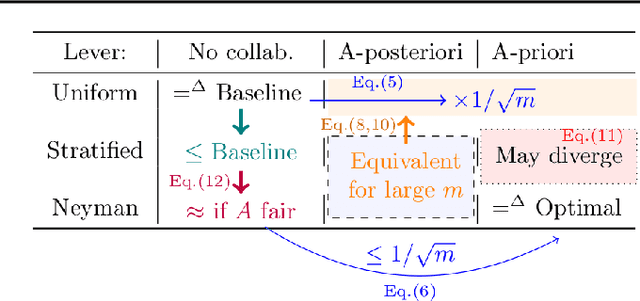
Abstract:Existing work in fairness audits assumes that agents operate independently. In this paper, we consider the case of multiple agents auditing the same platform for different tasks. Agents have two levers: their collaboration strategy, with or without coordination beforehand, and their sampling method. We theoretically study their interplay when agents operate independently or collaborate. We prove that, surprisingly, coordination can sometimes be detrimental to audit accuracy, whereas uncoordinated collaboration generally yields good results. Experimentation on real-world datasets confirms this observation, as the audit accuracy of uncoordinated collaboration matches that of collaborative optimal sampling.
On the relevance of APIs facing fairwashed audits
May 23, 2023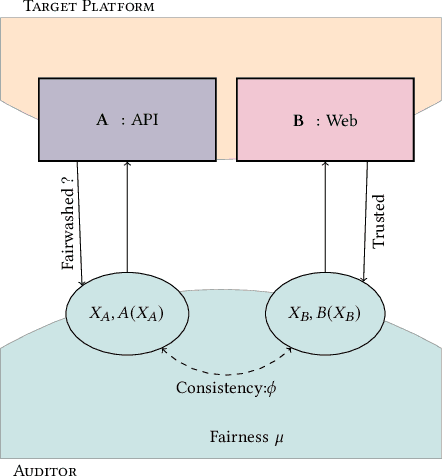
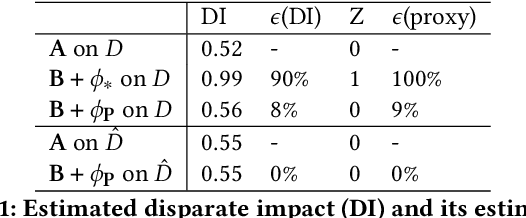
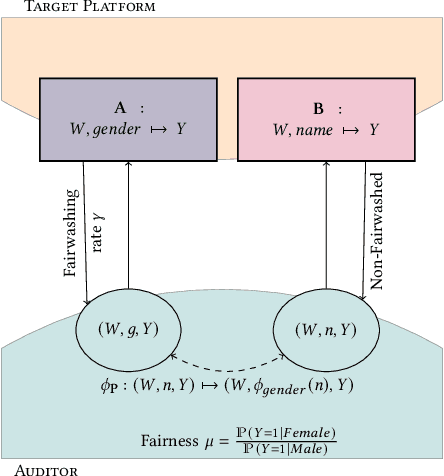
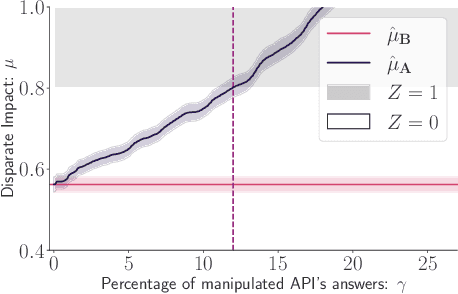
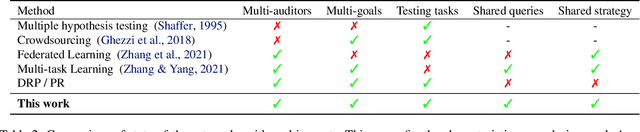
Abstract:Recent legislation required AI platforms to provide APIs for regulators to assess their compliance with the law. Research has nevertheless shown that platforms can manipulate their API answers through fairwashing. Facing this threat for reliable auditing, this paper studies the benefits of the joint use of platform scraping and of APIs. In this setup, we elaborate on the use of scraping to detect manipulated answers: since fairwashing only manipulates API answers, exploiting scraps may reveal a manipulation. To abstract the wide range of specific API-scrap situations, we introduce a notion of proxy that captures the consistency an auditor might expect between both data sources. If the regulator has a good proxy of the consistency, then she can easily detect manipulation and even bypass the API to conduct her audit. On the other hand, without a good proxy, relying on the API is necessary, and the auditor cannot defend against fairwashing. We then simulate practical scenarios in which the auditor may mostly rely on the API to conveniently conduct the audit task, while maintaining her chances to detect a potential manipulation. To highlight the tension between the audit task and the API fairwashing detection task, we identify Pareto-optimal strategies in a practical audit scenario. We believe this research sets the stage for reliable audits in practical and manipulation-prone setups.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge