P2NIA: Privacy-Preserving Non-Iterative Auditing
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2025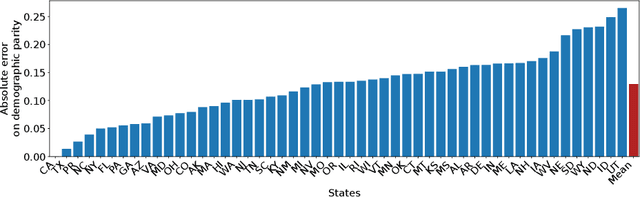
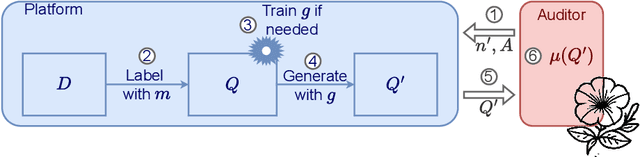
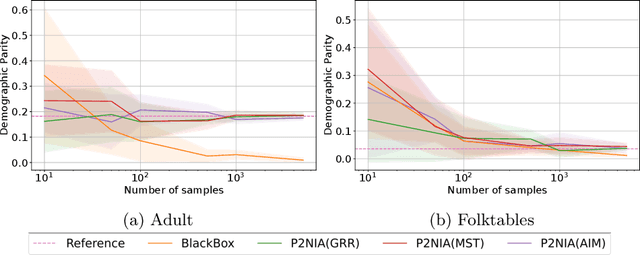
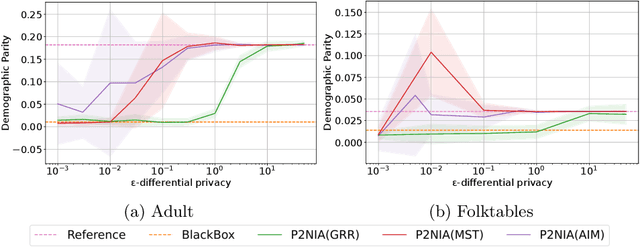
The emergence of AI legislation has increased the need to assess the ethical compliance of high-risk AI systems. Traditional auditing methods rely on platforms' application programming interfaces (APIs), where responses to queries are examined through the lens of fairness requirements. However, such approaches put a significant burden on platforms, as they are forced to maintain APIs while ensuring privacy, facing the possibility of data leaks. This lack of proper collaboration between the two parties, in turn, causes a significant challenge to the auditor, who is subject to estimation bias as they are unaware of the data distribution of the platform. To address these two issues, we present P2NIA, a novel auditing scheme that proposes a mutually beneficial collaboration for both the auditor and the platform. Extensive experiments demonstrate P2NIA's effectiveness in addressing both issues. In summary, our work introduces a privacy-preserving and non-iterative audit scheme that enhances fairness assessments using synthetic or local data, avoiding the challenges associated with traditional API-based audits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge