Linhong Zhu
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Personalized Search Story Recommendation
Jul 26, 2019
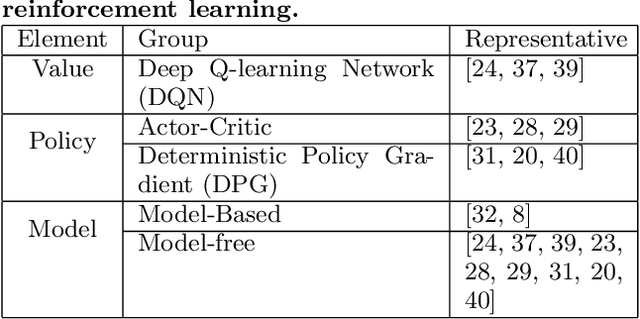
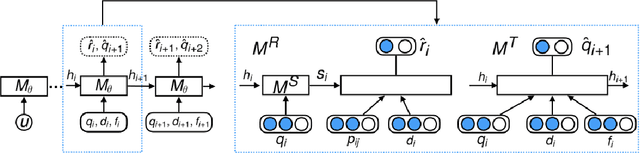
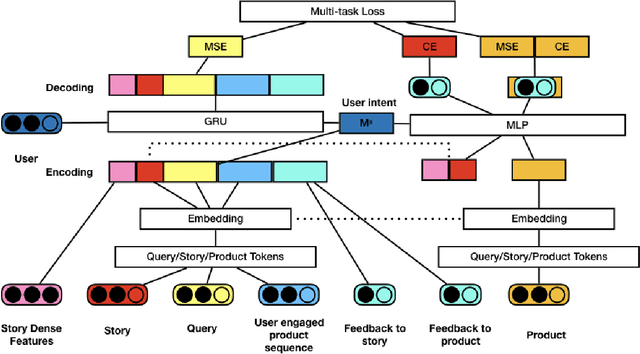
Abstract:In recent years, \emph{search story}, a combined display with other organic channels, has become a major source of user traffic on platforms such as e-commerce search platforms, news feed platforms and web and image search platforms. The recommended search story guides a user to identify her own preference and personal intent, which subsequently influences the user's real-time and long-term search behavior. %With such an increased importance of search stories, As search stories become increasingly important, in this work, we study the problem of personalized search story recommendation within a search engine, which aims to suggest a search story relevant to both a search keyword and an individual user's interest. To address the challenge of modeling both immediate and future values of recommended search stories (i.e., cross-channel effect), for which conventional supervised learning framework is not applicable, we resort to a Markov decision process and propose a deep reinforcement learning architecture trained by both imitation learning and reinforcement learning. We empirically demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach through extensive experiments on real-world data sets from JD.com.
Label Propagation on K-partite Graphs with Heterophily
Jan 21, 2017



Abstract:In this paper, for the first time, we study label propagation in heterogeneous graphs under heterophily assumption. Homophily label propagation (i.e., two connected nodes share similar labels) in homogeneous graph (with same types of vertices and relations) has been extensively studied before. Unfortunately, real-life networks are heterogeneous, they contain different types of vertices (e.g., users, images, texts) and relations (e.g., friendships, co-tagging) and allow for each node to propagate both the same and opposite copy of labels to its neighbors. We propose a $\mathcal{K}$-partite label propagation model to handle the mystifying combination of heterogeneous nodes/relations and heterophily propagation. With this model, we develop a novel label inference algorithm framework with update rules in near-linear time complexity. Since real networks change over time, we devise an incremental approach, which supports fast updates for both new data and evidence (e.g., ground truth labels) with guaranteed efficiency. We further provide a utility function to automatically determine whether an incremental or a re-modeling approach is favored. Extensive experiments on real datasets have verified the effectiveness and efficiency of our approach, and its superiority over the state-of-the-art label propagation methods.
Temporal Learning and Sequence Modeling for a Job Recommender System
Aug 11, 2016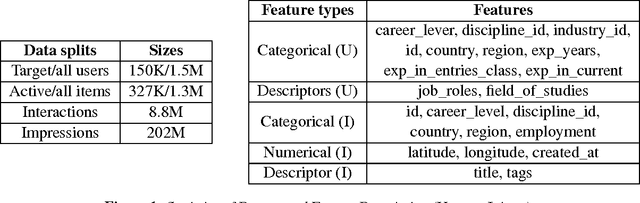
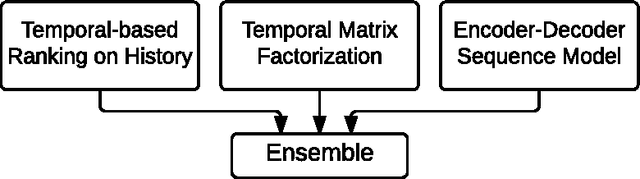

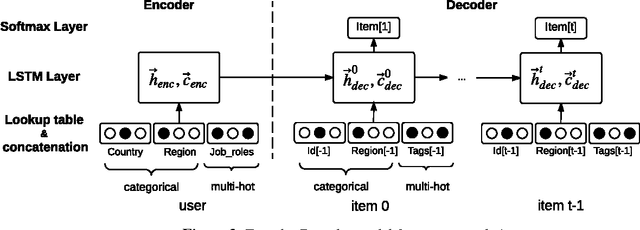
Abstract:We present our solution to the job recommendation task for RecSys Challenge 2016. The main contribution of our work is to combine temporal learning with sequence modeling to capture complex user-item activity patterns to improve job recommendations. First, we propose a time-based ranking model applied to historical observations and a hybrid matrix factorization over time re-weighted interactions. Second, we exploit sequence properties in user-items activities and develop a RNN-based recommendation model. Our solution achieved 5$^{th}$ place in the challenge among more than 100 participants. Notably, the strong performance of our RNN approach shows a promising new direction in employing sequence modeling for recommendation systems.
Scalable Link Prediction in Dynamic Networks via Non-Negative Matrix Factorization
Jul 23, 2016



Abstract:We propose a scalable temporal latent space model for link prediction in dynamic social networks, where the goal is to predict links over time based on a sequence of previous graph snapshots. The model assumes that each user lies in an unobserved latent space and interactions are more likely to form between similar users in the latent space representation. In addition, the model allows each user to gradually move its position in the latent space as the network structure evolves over time. We present a global optimization algorithm to effectively infer the temporal latent space, with a quadratic convergence rate. Two alternative optimization algorithms with local and incremental updates are also proposed, allowing the model to scale to larger networks without compromising prediction accuracy. Empirically, we demonstrate that our model, when evaluated on a number of real-world dynamic networks, significantly outperforms existing approaches for temporal link prediction in terms of both scalability and predictive power.
The DARPA Twitter Bot Challenge
Apr 21, 2016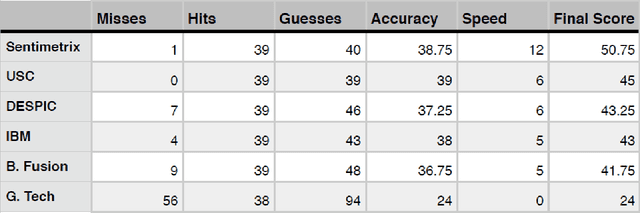
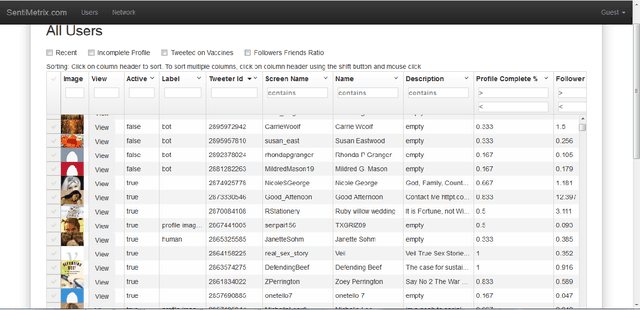
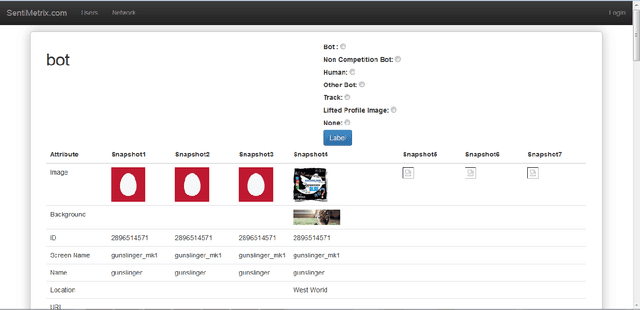
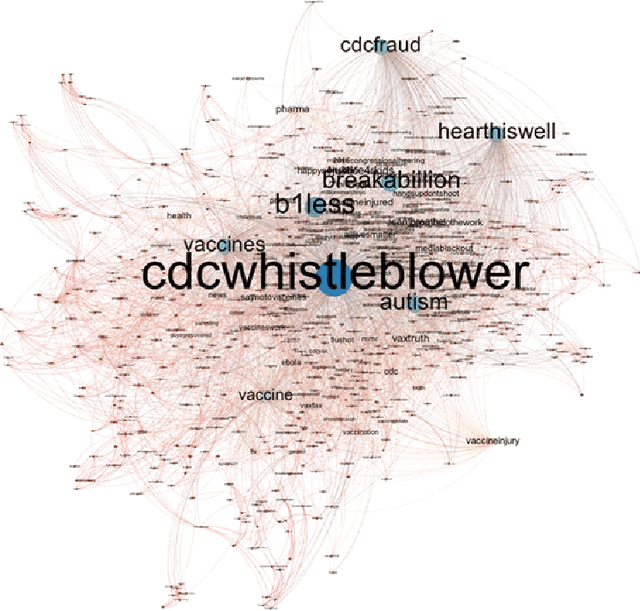
Abstract:A number of organizations ranging from terrorist groups such as ISIS to politicians and nation states reportedly conduct explicit campaigns to influence opinion on social media, posing a risk to democratic processes. There is thus a growing need to identify and eliminate "influence bots" - realistic, automated identities that illicitly shape discussion on sites like Twitter and Facebook - before they get too influential. Spurred by such events, DARPA held a 4-week competition in February/March 2015 in which multiple teams supported by the DARPA Social Media in Strategic Communications program competed to identify a set of previously identified "influence bots" serving as ground truth on a specific topic within Twitter. Past work regarding influence bots often has difficulty supporting claims about accuracy, since there is limited ground truth (though some exceptions do exist [3,7]). However, with the exception of [3], no past work has looked specifically at identifying influence bots on a specific topic. This paper describes the DARPA Challenge and describes the methods used by the three top-ranked teams.
* IEEE Computer Magazine, in press
Tripartite Graph Clustering for Dynamic Sentiment Analysis on Social Media
Jun 12, 2014
Abstract:The growing popularity of social media (e.g, Twitter) allows users to easily share information with each other and influence others by expressing their own sentiments on various subjects. In this work, we propose an unsupervised \emph{tri-clustering} framework, which analyzes both user-level and tweet-level sentiments through co-clustering of a tripartite graph. A compelling feature of the proposed framework is that the quality of sentiment clustering of tweets, users, and features can be mutually improved by joint clustering. We further investigate the evolution of user-level sentiments and latent feature vectors in an online framework and devise an efficient online algorithm to sequentially update the clustering of tweets, users and features with newly arrived data. The online framework not only provides better quality of both dynamic user-level and tweet-level sentiment analysis, but also improves the computational and storage efficiency. We verified the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed approaches on the November 2012 California ballot Twitter data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge