Li Shang
Dispelling the Curse of Singularities in Neural Network Optimizations
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:This work investigates the optimization instability of deep neural networks from a less-explored yet insightful perspective: the emergence and amplification of singularities in the parametric space. Our analysis reveals that parametric singularities inevitably grow with gradient updates and further intensify alignment with representations, leading to increased singularities in the representation space. We show that the gradient Frobenius norms are bounded by the top singular values of the weight matrices, and as training progresses, the mutually reinforcing growth of weight and representation singularities, termed the curse of singularities, relaxes these bounds, escalating the risk of sharp loss explosions. To counter this, we propose Parametric Singularity Smoothing (PSS), a lightweight, flexible, and effective method for smoothing the singular spectra of weight matrices. Extensive experiments across diverse datasets, architectures, and optimizers demonstrate that PSS mitigates instability, restores trainability even after failure, and improves both training efficiency and generalization.
White-Box Op-Amp Design via Human-Mimicking Reasoning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:This brief proposes \emph{White-Op}, an interpretable operational amplifier (op-amp) parameter design framework based on the human-mimicking reasoning of large-language-model agents. We formalize the implicit human reasoning mechanism into explicit steps of \emph{\textbf{introducing hypothetical constraints}}, and develop an iterative, human-like \emph{\textbf{hypothesis-verification-decision}} workflow. Specifically, the agent is guided to introduce hypothetical constraints to derive and properly regulate positions of symbolically tractable poles and zeros, thus formulating a closed-form mathematical optimization problem, which is then solved programmatically and verified via simulation. Theory-simulation result analysis guides the decision-making for refinement. Experiments on 9 op-amp topologies show that, unlike the uninterpretable black-box baseline which finally fails in 5 topologies, White-Op achieves reliable, interpretable behavioral-level designs with only 8.52\% theoretical prediction error and the design functionality retains after transistor-level mapping for all topologies. White-Op is open-sourced at \textcolor{blue}{https://github.com/zhchenfdu/whiteop}.
Bridging the Initialization Gap: A Co-Optimization Framework for Mixed-Size Global Placement
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Global placement is a critical step with high computational complexity in VLSI physical design. Modern analytical placers formulate the placement problem as a nonlinear optimization, where initialization strongly affects both convergence behavior and final placement quality. However, existing initialization methods exhibit a trade-off: area-aware initializers account for cell areas but are computationally expensive and can dominate total runtime, while fast point-based initializers ignore cell area, leading to a modeling gap that impairs convergence and solution quality. We propose a lightweight co-optimization framework that bridges this initialization gap through two strategies. First, an area-hint refinement initializer incorporates heuristic cell area information into a signed graph signal by augmenting the netlist graph with virtual nodes and negative-weight edges, yielding an area-aware and spectrally smooth placement initialization. Second, a macro-schedule placement procedure progressively restores area constraints, enabling a smooth transition from the refined initializer to the full area-aware objective and producing high-quality placement results. We evaluate the framework on macro-heavy ISPD2005 academic benchmarks and two real-world industrial designs across two technology nodes (12 cases in total). Experimental results show that our method consistently improves half-perimeter wirelength (HPWL) over point-based initializers in 11 out of 12 cases, achieving up to 2.2% HPWL reduction, while running approximately 100 times faster than the state-of-the-art area-aware initializer.
AnalogSeeker: An Open-source Foundation Language Model for Analog Circuit Design
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose AnalogSeeker, an effort toward an open-source foundation language model for analog circuit design, with the aim of integrating domain knowledge and giving design assistance. To overcome the scarcity of data in this field, we employ a corpus collection strategy based on the domain knowledge framework of analog circuits. High-quality, accessible textbooks across relevant subfields are systematically curated and cleaned into a textual domain corpus. To address the complexity of knowledge of analog circuits, we introduce a granular domain knowledge distillation method. Raw, unlabeled domain corpus is decomposed into typical, granular learning nodes, where a multi-agent framework distills implicit knowledge embedded in unstructured text into question-answer data pairs with detailed reasoning processes, yielding a fine-grained, learnable dataset for fine-tuning. To address the unexplored challenges in training analog circuit foundation models, we explore and share our training methods through both theoretical analysis and experimental validation. We finally establish a fine-tuning-centric training paradigm, customizing and implementing a neighborhood self-constrained supervised fine-tuning algorithm. This approach enhances training outcomes by constraining the perturbation magnitude between the model's output distributions before and after training. In practice, we train the Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct model to obtain AnalogSeeker, which achieves 85.04% accuracy on AMSBench-TQA, the analog circuit knowledge evaluation benchmark, with a 15.67% point improvement over the original model and is competitive with mainstream commercial models. Furthermore, AnalogSeeker also shows effectiveness in the downstream operational amplifier design task. AnalogSeeker is open-sourced at https://huggingface.co/analogllm/analogseeker for research use.
Bidirectional Knowledge Distillation for Enhancing Sequential Recommendation with Large Language Models
May 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance in understanding and generating semantic patterns, making them promising candidates for sequential recommendation tasks. However, when combined with conventional recommendation models (CRMs), LLMs often face challenges related to high inference costs and static knowledge transfer methods. In this paper, we propose a novel mutual distillation framework, LLMD4Rec, that fosters dynamic and bidirectional knowledge exchange between LLM-centric and CRM-based recommendation systems. Unlike traditional unidirectional distillation methods, LLMD4Rec enables iterative optimization by alternately refining both models, enhancing the semantic understanding of CRMs and enriching LLMs with collaborative signals from user-item interactions. By leveraging sample-wise adaptive weighting and aligning output distributions, our approach eliminates the need for additional parameters while ensuring effective knowledge transfer. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that LLMD4Rec significantly improves recommendation accuracy across multiple benchmarks without increasing inference costs. This method provides a scalable and efficient solution for combining the strengths of both LLMs and CRMs in sequential recommendation systems.
The Power of Graph Signal Processing for Chip Placement Acceleration
Feb 24, 2025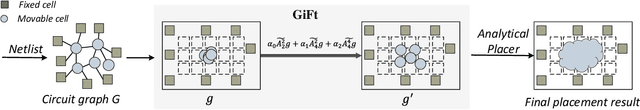
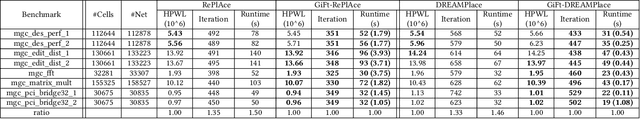
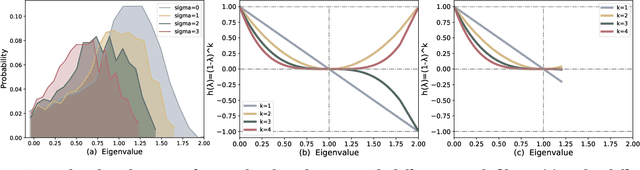
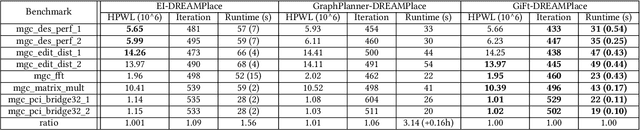
Abstract:Placement is a critical task with high computation complexity in VLSI physical design. Modern analytical placers formulate the placement objective as a nonlinear optimization task, which suffers a long iteration time. To accelerate and enhance the placement process, recent studies have turned to deep learning-based approaches, particularly leveraging graph convolution networks (GCNs). However, learning-based placers require time- and data-consuming model training due to the complexity of circuit placement that involves large-scale cells and design-specific graph statistics. This paper proposes GiFt, a parameter-free technique for accelerating placement, rooted in graph signal processing. GiFt excels at capturing multi-resolution smooth signals of circuit graphs to generate optimized placement solutions without the need for time-consuming model training, and meanwhile significantly reduces the number of iterations required by analytical placers. Experimental results show that GiFt significantly improving placement efficiency, while achieving competitive or superior performance compared to state-of-the-art placers. In particular, compared to DREAMPlace, the recently proposed GPU-accelerated analytical placer, GF-Placer improves total runtime over 45%.
Enhancing LLM-Based Recommendations Through Personalized Reasoning
Feb 19, 2025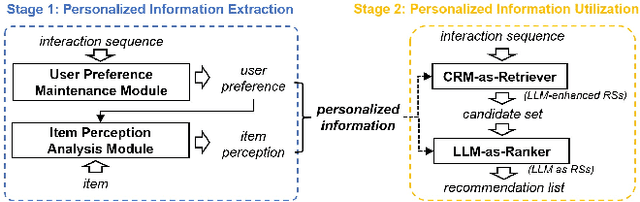
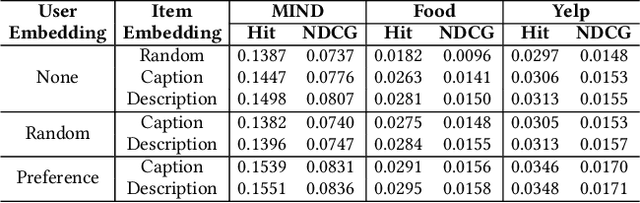
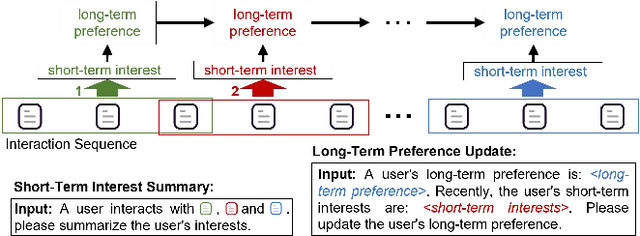
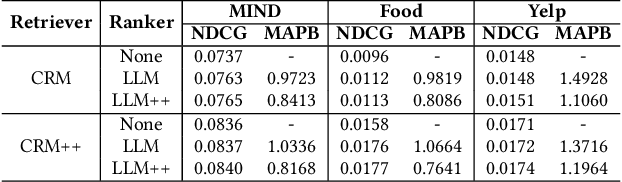
Abstract:Current recommendation systems powered by large language models (LLMs) often underutilize their reasoning capabilities due to a lack of explicit logical structuring. To address this limitation, we introduce CoT-Rec, a framework that integrates Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning into LLM-driven recommendations by incorporating two crucial processes: user preference analysis and item perception evaluation. CoT-Rec operates in two key phases: (1) personalized data extraction, where user preferences and item perceptions are identified, and (2) personalized data application, where this information is leveraged to refine recommendations. Our experimental analysis demonstrates that CoT-Rec improves recommendation accuracy by making better use of LLMs' reasoning potential. The implementation is publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CoT-Rec.
Enhancing Cross-Domain Recommendations with Memory-Optimized LLM-Based User Agents
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based user agents have emerged as a powerful tool for improving recommender systems by simulating user interactions. However, existing methods struggle with cross-domain scenarios due to inefficient memory structures, leading to irrelevant information retention and failure to account for social influence factors such as popularity. To address these limitations, we introduce AgentCF++, a novel framework featuring a dual-layer memory architecture and a two-step fusion mechanism to filter domain-specific preferences effectively. Additionally, we propose interest groups with shared memory, allowing the model to capture the impact of popularity trends on users with similar interests. Through extensive experiments on multiple cross-domain datasets, AgentCF++ demonstrates superior performance over baseline models, highlighting its effectiveness in refining user behavior simulation for recommender systems. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AgentCF-plus.
Mitigating Popularity Bias in Collaborative Filtering through Fair Sampling
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Recommender systems often suffer from popularity bias, where frequently interacted items are overrepresented in recommendations. This bias stems from propensity factors influencing training data, leading to imbalanced exposure. In this paper, we introduce a Fair Sampling (FS) approach to address this issue by ensuring that both users and items are selected with equal probability as positive and negative instances. Unlike traditional inverse propensity score (IPS) methods, FS does not require propensity estimation, eliminating errors associated with inaccurate calculations. Our theoretical analysis demonstrates that FS effectively neutralizes the influence of propensity factors, achieving unbiased learning. Experimental results validate that FS outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both point-wise and pair-wise recommendation tasks, enhancing recommendation fairness without sacrificing accuracy. The implementation is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Fair-Sampling.
Oracle-guided Dynamic User Preference Modeling for Sequential Recommendation
Dec 01, 2024



Abstract:Sequential recommendation methods can capture dynamic user preferences from user historical interactions to achieve better performance. However, most existing methods only use past information extracted from user historical interactions to train the models, leading to the deviations of user preference modeling. Besides past information, future information is also available during training, which contains the ``oracle'' user preferences in the future and will be beneficial to model dynamic user preferences. Therefore, we propose an oracle-guided dynamic user preference modeling method for sequential recommendation (Oracle4Rec), which leverages future information to guide model training on past information, aiming to learn ``forward-looking'' models. Specifically, Oracle4Rec first extracts past and future information through two separate encoders, then learns a forward-looking model through an oracle-guiding module which minimizes the discrepancy between past and future information. We also tailor a two-phase model training strategy to make the guiding more effective. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Oracle4Rec is superior to state-of-the-art sequential methods. Further experiments show that Oracle4Rec can be leveraged as a generic module in other sequential recommendation methods to improve their performance with a considerable margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge