A Comprehensive Summarization and Evaluation of Feature Refinement Modules for CTR Prediction
Paper and Code
Nov 08, 2023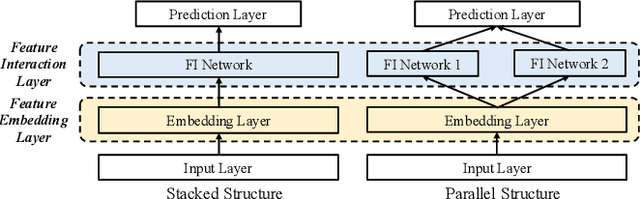
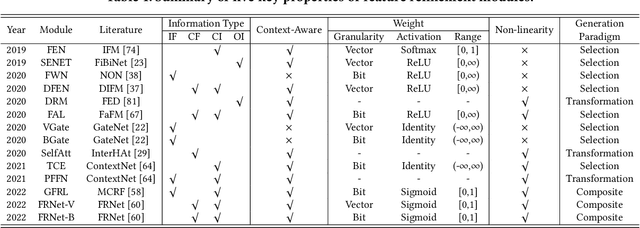
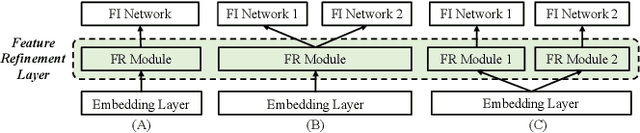
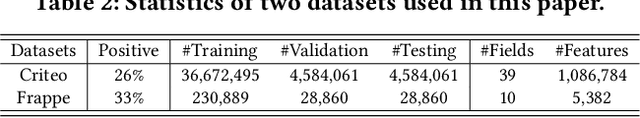
Click-through rate (CTR) prediction is widely used in academia and industry. Most CTR tasks fall into a feature embedding \& feature interaction paradigm, where the accuracy of CTR prediction is mainly improved by designing practical feature interaction structures. However, recent studies have argued that the fixed feature embedding learned only through the embedding layer limits the performance of existing CTR models. Some works apply extra modules on top of the embedding layer to dynamically refine feature representations in different instances, making it effective and easy to integrate with existing CTR methods. Despite the promising results, there is a lack of a systematic review and summarization of this new promising direction on the CTR task. To fill this gap, we comprehensively summarize and define a new module, namely \textbf{feature refinement} (FR) module, that can be applied between feature embedding and interaction layers. We extract 14 FR modules from previous works, including instances where the FR module was proposed but not clearly defined or explained. We fully assess the effectiveness and compatibility of existing FR modules through comprehensive and extensive experiments with over 200 augmented models and over 4,000 runs for more than 15,000 GPU hours. The results offer insightful guidelines for researchers, and all benchmarking code and experimental results are open-sourced. In addition, we present a new architecture of assigning independent FR modules to separate sub-networks for parallel CTR models, as opposed to the conventional method of inserting a shared FR module on top of the embedding layer. Our approach is also supported by comprehensive experiments demonstrating its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge