Laijian Li
3D Gaussian Inverse Rendering with Approximated Global Illumination
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting shows great potential in reconstructing photo-realistic 3D scenes. However, these methods typically bake illumination into their representations, limiting their use for physically-based rendering and scene editing. Although recent inverse rendering approaches aim to decompose scenes into material and lighting components, they often rely on simplifying assumptions that fail when editing. We present a novel approach that enables efficient global illumination for 3D Gaussians Splatting through screen-space ray tracing. Our key insight is that a substantial amount of indirect light can be traced back to surfaces visible within the current view frustum. Leveraging this observation, we augment the direct shading computed by 3D Gaussians with Monte-Carlo screen-space ray-tracing to capture one-bounce indirect illumination. In this way, our method enables realistic global illumination without sacrificing the computational efficiency and editability benefits of 3D Gaussians. Through experiments, we show that the screen-space approximation we utilize allows for indirect illumination and supports real-time rendering and editing. Code, data, and models will be made available at our project page: https://wuzirui.github.io/gs-ssr.
Monocular Event-Inertial Odometry with Adaptive decay-based Time Surface and Polarity-aware Tracking
Sep 21, 2024Abstract:Event cameras have garnered considerable attention due to their advantages over traditional cameras in low power consumption, high dynamic range, and no motion blur. This paper proposes a monocular event-inertial odometry incorporating an adaptive decay kernel-based time surface with polarity-aware tracking. We utilize an adaptive decay-based Time Surface to extract texture information from asynchronous events, which adapts to the dynamic characteristics of the event stream and enhances the representation of environmental textures. However, polarity-weighted time surfaces suffer from event polarity shifts during changes in motion direction. To mitigate its adverse effects on feature tracking, we optimize the feature tracking by incorporating an additional polarity-inverted time surface to enhance the robustness. Comparative analysis with visual-inertial and event-inertial odometry methods shows that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art techniques, with competitive results across various datasets.
Gaussian-LIC: Photo-realistic LiDAR-Inertial-Camera SLAM with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Apr 10, 2024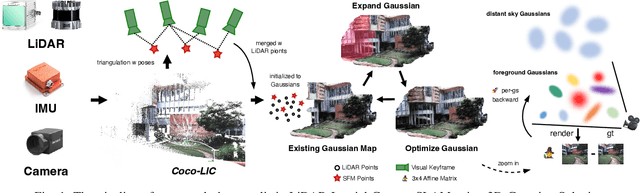
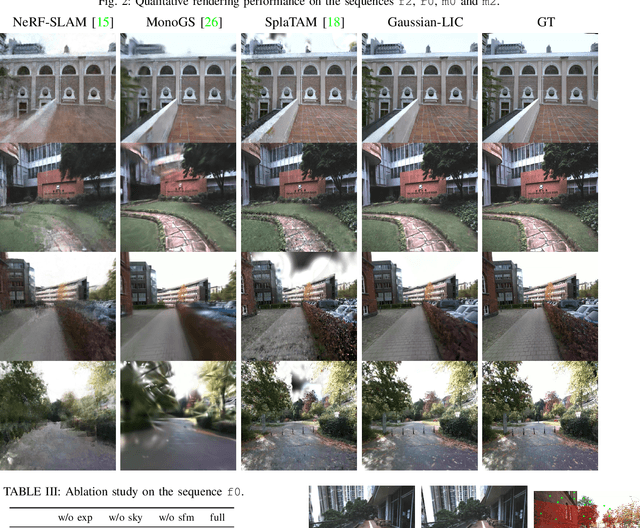
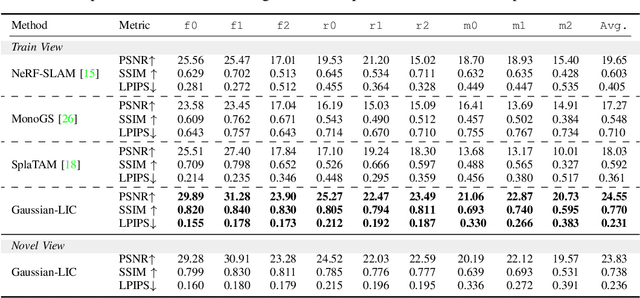
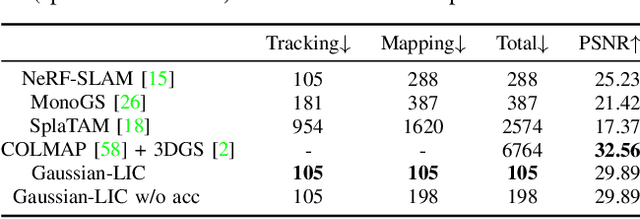

Abstract:We present a real-time LiDAR-Inertial-Camera SLAM system with 3D Gaussian Splatting as the mapping backend. Leveraging robust pose estimates from our LiDAR-Inertial-Camera odometry, Coco-LIC, an incremental photo-realistic mapping system is proposed in this paper. We initialize 3D Gaussians from colorized LiDAR points and optimize them using differentiable rendering powered by 3D Gaussian Splatting. Meticulously designed strategies are employed to incrementally expand the Gaussian map and adaptively control its density, ensuring high-quality mapping with real-time capability. Experiments conducted in diverse scenarios demonstrate the superior performance of our method compared to existing radiance-field-based SLAM systems.
Camera-based 3D Semantic Scene Completion with Sparse Guidance Network
Dec 10, 2023



Abstract:Semantic scene completion (SSC) aims to predict the semantic occupancy of each voxel in the entire 3D scene from limited observations, which is an emerging and critical task for autonomous driving. Recently, many studies have turned to camera-based SSC solutions due to the richer visual cues and cost-effectiveness of cameras. However, existing methods usually rely on sophisticated and heavy 3D models to directly process the lifted 3D features that are not discriminative enough for clear segmentation boundaries. In this paper, we adopt the dense-sparse-dense design and propose an end-to-end camera-based SSC framework, termed SGN, to diffuse semantics from the semantic- and occupancy-aware seed voxels to the whole scene based on geometry prior and occupancy information. By designing hybrid guidance (sparse semantic and geometry guidance) and effective voxel aggregation for spatial occupancy and geometry priors, we enhance the feature separation between different categories and expedite the convergence of semantic diffusion. Extensive experimental results on the SemanticKITTI dataset demonstrate the superiority of our SGN over existing state-of-the-art methods.
PANet: LiDAR Panoptic Segmentation with Sparse Instance Proposal and Aggregation
Jun 27, 2023Abstract:Reliable LiDAR panoptic segmentation (LPS), including both semantic and instance segmentation, is vital for many robotic applications, such as autonomous driving. This work proposes a new LPS framework named PANet to eliminate the dependency on the offset branch and improve the performance on large objects, which are always over-segmented by clustering algorithms. Firstly, we propose a non-learning Sparse Instance Proposal (SIP) module with the ``sampling-shifting-grouping" scheme to directly group thing points into instances from the raw point cloud efficiently. More specifically, balanced point sampling is introduced to generate sparse seed points with more uniform point distribution over the distance range. And a shift module, termed bubble shifting, is proposed to shrink the seed points to the clustered centers. Then we utilize the connected component label algorithm to generate instance proposals. Furthermore, an instance aggregation module is devised to integrate potentially fragmented instances, improving the performance of the SIP module on large objects. Extensive experiments show that PANet achieves state-of-the-art performance among published works on the SemanticKITII validation and nuScenes validation for the panoptic segmentation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge