Mu Xu
MerNav: A Highly Generalizable Memory-Execute-Review Framework for Zero-Shot Object Goal Navigation
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Visual Language Navigation (VLN) is one of the fundamental capabilities for embodied intelligence and a critical challenge that urgently needs to be addressed. However, existing methods are still unsatisfactory in terms of both success rate (SR) and generalization: Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) approaches typically achieve higher SR, while Training-Free (TF) approaches often generalize better, but it is difficult to obtain both simultaneously. To this end, we propose a Memory-Execute-Review framework. It consists of three parts: a hierarchical memory module for providing information support, an execute module for routine decision-making and actions, and a review module for handling abnormal situations and correcting behavior. We validated the effectiveness of this framework on the Object Goal Navigation task. Across 4 datasets, our average SR achieved absolute improvements of 7% and 5% compared to all baseline methods under TF and Zero-Shot (ZS) settings, respectively. On the most commonly used HM3D_v0.1 and the more challenging open vocabulary dataset HM3D_OVON, the SR improved by 8% and 6%, under ZS settings. Furthermore, on the MP3D and HM3D_OVON datasets, our method not only outperformed all TF methods but also surpassed all SFT methods, achieving comprehensive leadership in both SR (5% and 2%) and generalization.
FantasyVLN: Unified Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for Vision-Language Navigation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Achieving human-level performance in Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires an embodied agent to jointly understand multimodal instructions and visual-spatial context while reasoning over long action sequences. Recent works, such as NavCoT and NavGPT-2, demonstrate the potential of Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning for improving interpretability and long-horizon planning. Moreover, multimodal extensions like OctoNav-R1 and CoT-VLA further validate CoT as a promising pathway toward human-like navigation reasoning. However, existing approaches face critical drawbacks: purely textual CoTs lack spatial grounding and easily overfit to sparse annotated reasoning steps, while multimodal CoTs incur severe token inflation by generating imagined visual observations, making real-time navigation impractical. In this work, we propose FantasyVLN, a unified implicit reasoning framework that preserves the benefits of CoT reasoning without explicit token overhead. Specifically, imagined visual tokens are encoded into a compact latent space using a pretrained Visual AutoRegressor (VAR) during CoT reasoning training, and the model jointly learns from textual, visual, and multimodal CoT modes under a unified multi-CoT strategy. At inference, our model performs direct instruction-to-action mapping while still enjoying reasoning-aware representations. Extensive experiments on LH-VLN show that our approach achieves reasoning-aware yet real-time navigation, improving success rates and efficiency while reducing inference latency by an order of magnitude compared to explicit CoT methods.
Reasoning Over Space: Enabling Geographic Reasoning for LLM-Based Generative Next POI Recommendation
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Generative recommendation with large language models (LLMs) reframes prediction as sequence generation, yet existing LLM-based recommenders remain limited in leveraging geographic signals that are crucial in mobility and local-services scenarios. Here, we present Reasoning Over Space (ROS), a framework that utilizes geography as a vital decision variable within the reasoning process. ROS introduces a Hierarchical Spatial Semantic ID (SID) that discretizes coarse-to-fine locality and POI semantics into compositional tokens, and endows LLM with a three-stage Mobility Chain-of-Thought (CoT) paradigm that models user personality, constructs an intent-aligned candidate space, and performs locality informed pruning. We further align the model with real world geography via spatial-guided Reinforcement Learning (RL). Experiments on three widely used location-based social network (LBSN) datasets show that ROS achieves over 10% relative gains in hit rate over strongest LLM-based baselines and improves cross-city transfer, despite using a smaller backbone model.
AstraNav-World: World Model for Foresight Control and Consistency
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Embodied navigation in open, dynamic environments demands accurate foresight of how the world will evolve and how actions will unfold over time. We propose AstraNav-World, an end-to-end world model that jointly reasons about future visual states and action sequences within a unified probabilistic framework. Our framework integrates a diffusion-based video generator with a vision-language policy, enabling synchronized rollouts where predicted scenes and planned actions are updated simultaneously. Training optimizes two complementary objectives: generating action-conditioned multi-step visual predictions and deriving trajectories conditioned on those predicted visuals. This bidirectional constraint makes visual predictions executable and keeps decisions grounded in physically consistent, task-relevant futures, mitigating cumulative errors common in decoupled "envision-then-plan" pipelines. Experiments across diverse embodied navigation benchmarks show improved trajectory accuracy and higher success rates. Ablations confirm the necessity of tight vision-action coupling and unified training, with either branch removal degrading both prediction quality and policy reliability. In real-world testing, AstraNav-World demonstrated exceptional zero-shot capabilities, adapting to previously unseen scenarios without any real-world fine-tuning. These results suggest that AstraNav-World captures transferable spatial understanding and planning-relevant navigation dynamics, rather than merely overfitting to simulation-specific data distribution. Overall, by unifying foresight vision and control within a single generative model, we move closer to reliable, interpretable, and general-purpose embodied agents that operate robustly in open-ended real-world settings.
AstraNav-Memory: Contexts Compression for Long Memory
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Lifelong embodied navigation requires agents to accumulate, retain, and exploit spatial-semantic experience across tasks, enabling efficient exploration in novel environments and rapid goal reaching in familiar ones. While object-centric memory is interpretable, it depends on detection and reconstruction pipelines that limit robustness and scalability. We propose an image-centric memory framework that achieves long-term implicit memory via an efficient visual context compression module end-to-end coupled with a Qwen2.5-VL-based navigation policy. Built atop a ViT backbone with frozen DINOv3 features and lightweight PixelUnshuffle+Conv blocks, our visual tokenizer supports configurable compression rates; for example, under a representative 16$\times$ compression setting, each image is encoded with about 30 tokens, expanding the effective context capacity from tens to hundreds of images. Experimental results on GOAT-Bench and HM3D-OVON show that our method achieves state-of-the-art navigation performance, improving exploration in unfamiliar environments and shortening paths in familiar ones. Ablation studies further reveal that moderate compression provides the best balance between efficiency and accuracy. These findings position compressed image-centric memory as a practical and scalable interface for lifelong embodied agents, enabling them to reason over long visual histories and navigate with human-like efficiency.
AMap: Distilling Future Priors for Ahead-Aware Online HD Map Construction
Dec 22, 2025



Abstract:Online High-Definition (HD) map construction is pivotal for autonomous driving. While recent approaches leverage historical temporal fusion to improve performance, we identify a critical safety flaw in this paradigm: it is inherently ``spatially backward-looking." These methods predominantly enhance map reconstruction in traversed areas, offering minimal improvement for the unseen road ahead. Crucially, our analysis of downstream planning tasks reveals a severe asymmetry: while rearward perception errors are often tolerable, inaccuracies in the forward region directly precipitate hazardous driving maneuvers. To bridge this safety gap, we propose AMap, a novel framework for Ahead-aware online HD Mapping. We pioneer a ``distill-from-future" paradigm, where a teacher model with privileged access to future temporal contexts guides a lightweight student model restricted to the current frame. This process implicitly compresses prospective knowledge into the student model, endowing it with ``look-ahead" capabilities at zero inference-time cost. Technically, we introduce a Multi-Level BEV Distillation strategy with spatial masking and an Asymmetric Query Adaptation module to effectively transfer future-aware representations to the student's static queries. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes and Argoverse 2 benchmark demonstrate that AMap significantly enhances current-frame perception. Most notably, it outperforms state-of-the-art temporal models in critical forward regions while maintaining the efficiency of single current frame inference.
EagleVision: A Dual-Stage Framework with BEV-grounding-based Chain-of-Thought for Spatial Intelligence
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Recent spatial intelligence approaches typically attach 3D cues to 2D reasoning pipelines or couple MLLMs with black-box reconstruction modules, leading to weak spatial consistency, limited viewpoint diversity, and evidence chains that cannot be traced back to supporting views. Frameworks for "thinking with images" (e.g., ChatGPT-o3 and DeepEyes) show that stepwise multimodal reasoning can emerge by interleaving hypothesis formation with active acquisition of visual evidence, but they do not address three key challenges in spatial Chain-of-Thought (CoT): building global space perception under strict token budgets, explicitly associating 3D hypotheses with video frames for verification, and designing spatially grounded rewards for reinforcement learning. To address these issues, we present EagleVision, a dual-stage framework for progressive spatial cognition through macro perception and micro verification. In the macro perception stage, EagleVision employs a semantics-perspective-fusion determinantal point process (SPF-DPP) to select a compact set of geometry- and semantics-aware keyframes from long videos under a fixed token budget. In the micro verification stage, we formalize spatial CoT as BEV-grounded pose querying: the agent iteratively predicts poses on a BEV plane, retrieves the nearest real frames, and is trained purely by reinforcement learning with a spatial grounding reward that scores the consistency between predicted poses and observed views. On VSI-Bench, EagleVision achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source vision-language models, demonstrating strong and generalizable spatial understanding.
From Orbit to Ground: Generative City Photogrammetry from Extreme Off-Nadir Satellite Images
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:City-scale 3D reconstruction from satellite imagery presents the challenge of extreme viewpoint extrapolation, where our goal is to synthesize ground-level novel views from sparse orbital images with minimal parallax. This requires inferring nearly $90^\circ$ viewpoint gaps from image sources with severely foreshortened facades and flawed textures, causing state-of-the-art reconstruction engines such as NeRF and 3DGS to fail. To address this problem, we propose two design choices tailored for city structures and satellite inputs. First, we model city geometry as a 2.5D height map, implemented as a Z-monotonic signed distance field (SDF) that matches urban building layouts from top-down viewpoints. This stabilizes geometry optimization under sparse, off-nadir satellite views and yields a watertight mesh with crisp roofs and clean, vertically extruded facades. Second, we paint the mesh appearance from satellite images via differentiable rendering techniques. While the satellite inputs may contain long-range, blurry captures, we further train a generative texture restoration network to enhance the appearance, recovering high-frequency, plausible texture details from degraded inputs. Our method's scalability and robustness are demonstrated through extensive experiments on large-scale urban reconstruction. For example, in our teaser figure, we reconstruct a $4\,\mathrm{km}^2$ real-world region from only a few satellite images, achieving state-of-the-art performance in synthesizing photorealistic ground views. The resulting models are not only visually compelling but also serve as high-fidelity, application-ready assets for downstream tasks like urban planning and simulation. Project page can be found at https://pku-vcl-geometry.github.io/Orbit2Ground/.
JanusVLN: Decoupling Semantics and Spatiality with Dual Implicit Memory for Vision-Language Navigation
Sep 26, 2025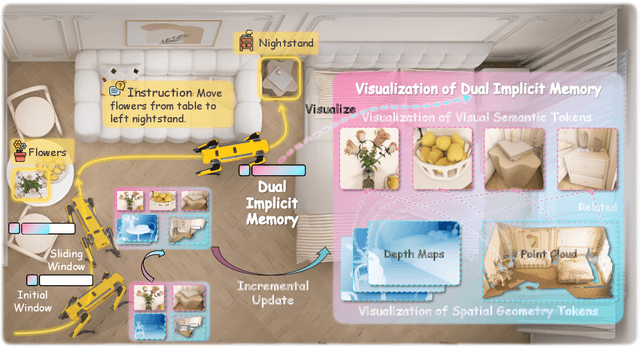
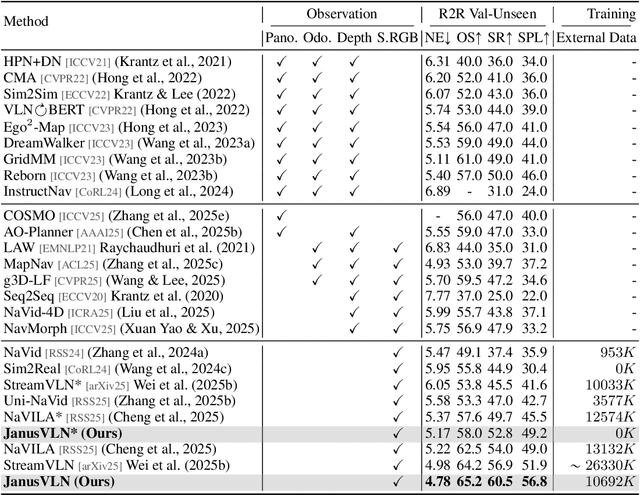
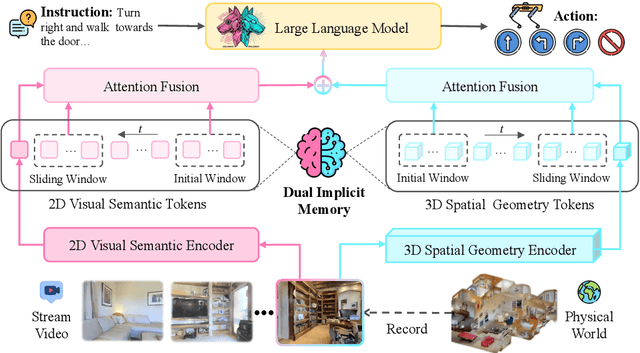
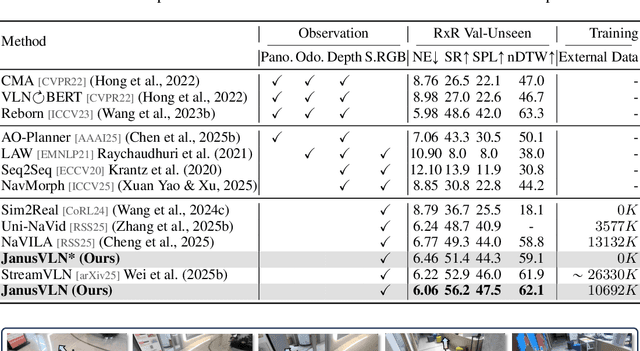
Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation requires an embodied agent to navigate through unseen environments, guided by natural language instructions and a continuous video stream. Recent advances in VLN have been driven by the powerful semantic understanding of Multimodal Large Language Models. However, these methods typically rely on explicit semantic memory, such as building textual cognitive maps or storing historical visual frames. This type of method suffers from spatial information loss, computational redundancy, and memory bloat, which impede efficient navigation. Inspired by the implicit scene representation in human navigation, analogous to the left brain's semantic understanding and the right brain's spatial cognition, we propose JanusVLN, a novel VLN framework featuring a dual implicit neural memory that models spatial-geometric and visual-semantic memory as separate, compact, and fixed-size neural representations. This framework first extends the MLLM to incorporate 3D prior knowledge from the spatial-geometric encoder, thereby enhancing the spatial reasoning capabilities of models based solely on RGB input. Then, the historical key-value caches from the spatial-geometric and visual-semantic encoders are constructed into a dual implicit memory. By retaining only the KVs of tokens in the initial and sliding window, redundant computation is avoided, enabling efficient incremental updates. Extensive experiments demonstrate that JanusVLN outperforms over 20 recent methods to achieve SOTA performance. For example, the success rate improves by 10.5-35.5 compared to methods using multiple data types as input and by 3.6-10.8 compared to methods using more RGB training data. This indicates that the proposed dual implicit neural memory, as a novel paradigm, explores promising new directions for future VLN research. Ours project page: https://miv-xjtu.github.io/JanusVLN.github.io/.
UniMapGen: A Generative Framework for Large-Scale Map Construction from Multi-modal Data
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Large-scale map construction is foundational for critical applications such as autonomous driving and navigation systems. Traditional large-scale map construction approaches mainly rely on costly and inefficient special data collection vehicles and labor-intensive annotation processes. While existing satellite-based methods have demonstrated promising potential in enhancing the efficiency and coverage of map construction, they exhibit two major limitations: (1) inherent drawbacks of satellite data (e.g., occlusions, outdatedness) and (2) inefficient vectorization from perception-based methods, resulting in discontinuous and rough roads that require extensive post-processing. This paper presents a novel generative framework, UniMapGen, for large-scale map construction, offering three key innovations: (1) representing lane lines as \textbf{discrete sequence} and establishing an iterative strategy to generate more complete and smooth map vectors than traditional perception-based methods. (2) proposing a flexible architecture that supports \textbf{multi-modal} inputs, enabling dynamic selection among BEV, PV, and text prompt, to overcome the drawbacks of satellite data. (3) developing a \textbf{state update} strategy for global continuity and consistency of the constructed large-scale map. UniMapGen achieves state-of-the-art performance on the OpenSatMap dataset. Furthermore, UniMapGen can infer occluded roads and predict roads missing from dataset annotations. Our code will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge