Kihyun Kim
Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Sogang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Population-Proportional Preference Learning from Human Feedback: An Axiomatic Approach
Jun 05, 2025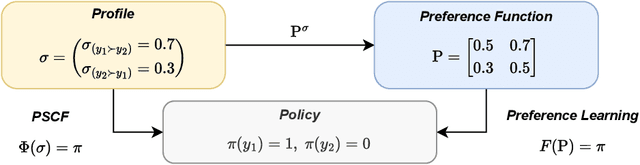
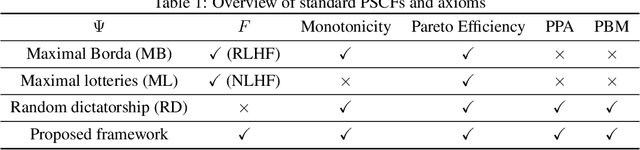
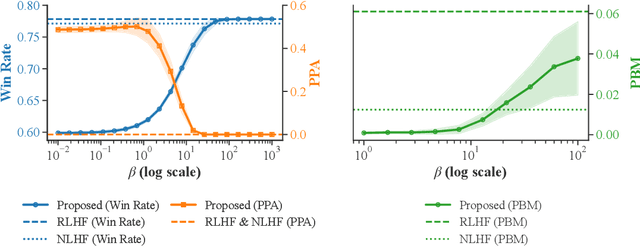
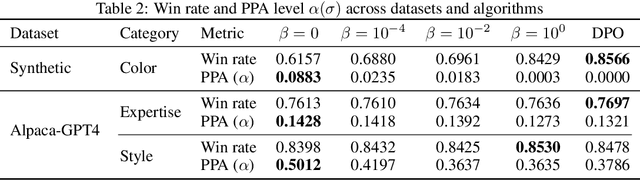
Abstract:Conventional preference learning methods often prioritize opinions held more widely when aggregating preferences from multiple evaluators. This may result in policies that are biased in favor of some types of opinions or groups. The objective of this paper is to develop a novel preference learning framework capable of aligning aggregate opinions and policies proportionally with the true population distribution of evaluator preferences. Our approach infers the feasible set of evaluator population distributions directly from pairwise comparison data. Using these estimates, the algorithm constructs a policy that satisfies foundational axioms from social choice theory, namely monotonicity and Pareto efficiency, as well as our newly-introduced axioms of population-proportional representation and population-bounded robustness. We propose a soft-max relaxation method that smoothly trade-offs population-proportional representation with the selection of the Condorcet winner (which beats all other options in pairwise comparisons). Finally, we validate the effectiveness and scalability of our approach through experiments on both tabular recommendation tasks and large-scale language model alignment.
Benign-to-Toxic Jailbreaking: Inducing Harmful Responses from Harmless Prompts
May 26, 2025Abstract:Optimization-based jailbreaks typically adopt the Toxic-Continuation setting in large vision-language models (LVLMs), following the standard next-token prediction objective. In this setting, an adversarial image is optimized to make the model predict the next token of a toxic prompt. However, we find that the Toxic-Continuation paradigm is effective at continuing already-toxic inputs, but struggles to induce safety misalignment when explicit toxic signals are absent. We propose a new paradigm: Benign-to-Toxic (B2T) jailbreak. Unlike prior work, we optimize adversarial images to induce toxic outputs from benign conditioning. Since benign conditioning contains no safety violations, the image alone must break the model's safety mechanisms. Our method outperforms prior approaches, transfers in black-box settings, and complements text-based jailbreaks. These results reveal an underexplored vulnerability in multimodal alignment and introduce a fundamentally new direction for jailbreak approaches.
Towards Scalable Human-aligned Benchmark for Text-guided Image Editing
May 01, 2025Abstract:A variety of text-guided image editing models have been proposed recently. However, there is no widely-accepted standard evaluation method mainly due to the subjective nature of the task, letting researchers rely on manual user study. To address this, we introduce a novel Human-Aligned benchmark for Text-guided Image Editing (HATIE). Providing a large-scale benchmark set covering a wide range of editing tasks, it allows reliable evaluation, not limited to specific easy-to-evaluate cases. Also, HATIE provides a fully-automated and omnidirectional evaluation pipeline. Particularly, we combine multiple scores measuring various aspects of editing so as to align with human perception. We empirically verify that the evaluation of HATIE is indeed human-aligned in various aspects, and provide benchmark results on several state-of-the-art models to provide deeper insights on their performance.
Cost-Efficient LLM Serving in the Cloud: VM Selection with KV Cache Offloading
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:LLM inference is essential for applications like text summarization, translation, and data analysis, but the high cost of GPU instances from Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) like AWS is a major burden. This paper proposes InferSave, a cost-efficient VM selection framework for cloud based LLM inference. InferSave optimizes KV cache offloading based on Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and workload charac teristics, estimating GPU memory needs, and recommending cost-effective VM instances. Additionally, the Compute Time Calibration Function (CTCF) improves instance selection accuracy by adjusting for discrepancies between theoretical and actual GPU performance. Experiments on AWS GPU instances show that selecting lower-cost instances without KV cache offloading improves cost efficiency by up to 73.7% for online workloads, while KV cache offloading saves up to 20.19% for offline workloads.
Shared Disk KV Cache Management for Efficient Multi-Instance Inference in RAG-Powered LLMs
Apr 16, 2025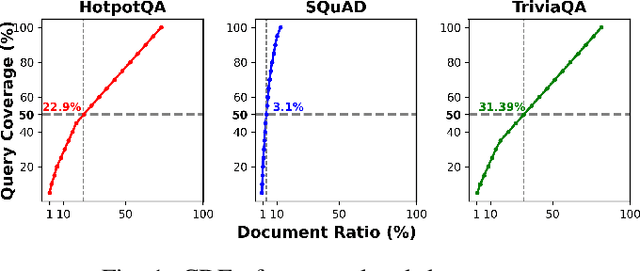
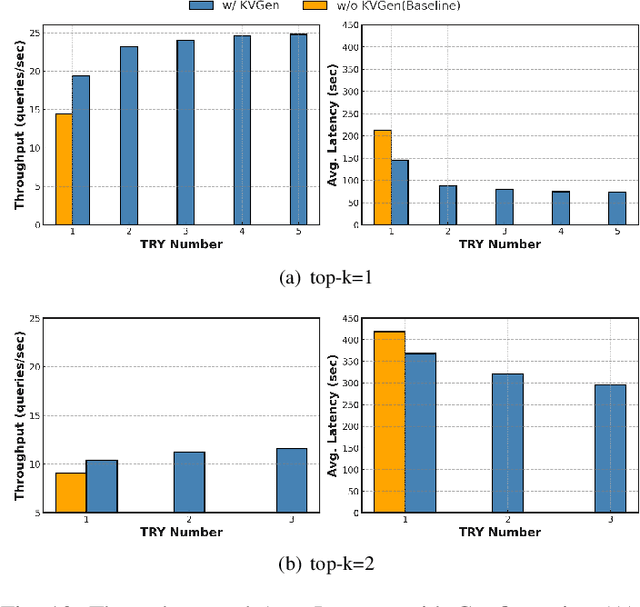
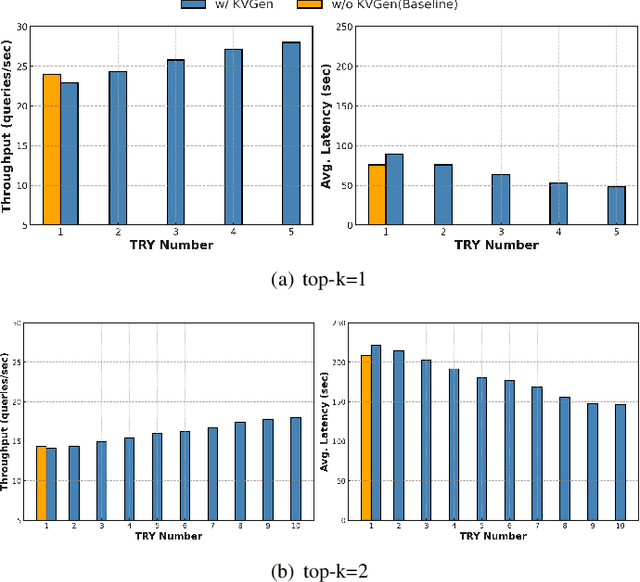
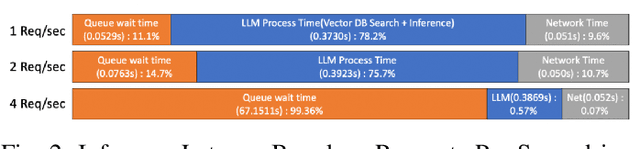
Abstract:Recent large language models (LLMs) face increasing inference latency as input context length and model size continue to grow. In particular, the retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technique, which enhances LLM responses by incorporating external knowledge, exacerbates this issue by significantly increasing the number of input tokens. This expansion in token length leads to a substantial rise in computational overhead, particularly during the prefill stage, resulting in prolonged time-to-first-token (TTFT). To address this issue, this paper proposes a method to reduce TTFT by leveraging a disk-based key-value (KV) cache to lessen the computational burden during the prefill stage. We also introduce a disk-based shared KV cache management system, called Shared RAG-DCache, for multi-instance LLM RAG service environments. This system, together with an optimal system configuration, improves both throughput and latency under given resource constraints. Shared RAG-DCache exploits the locality of documents related to user queries in RAG, as well as the queueing delay in LLM inference services. It proactively generates and stores disk KV caches for query-related documents and shares them across multiple LLM instances to enhance inference performance. In experiments on a single host equipped with 2 GPUs and 1 CPU, Shared RAG-DCache achieved a 15~71% increase in throughput and up to a 12~65% reduction in latency, depending on the resource configuration.
A Unified Linear Programming Framework for Offline Reward Learning from Human Demonstrations and Feedback
May 20, 2024

Abstract:Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL) and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) are pivotal methodologies in reward learning, which involve inferring and shaping the underlying reward function of sequential decision-making problems based on observed human demonstrations and feedback. Most prior work in reward learning has relied on prior knowledge or assumptions about decision or preference models, potentially leading to robustness issues. In response, this paper introduces a novel linear programming (LP) framework tailored for offline reward learning. Utilizing pre-collected trajectories without online exploration, this framework estimates a feasible reward set from the primal-dual optimality conditions of a suitably designed LP, and offers an optimality guarantee with provable sample efficiency. Our LP framework also enables aligning the reward functions with human feedback, such as pairwise trajectory comparison data, while maintaining computational tractability and sample efficiency. We demonstrate that our framework potentially achieves better performance compared to the conventional maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) approach through analytical examples and numerical experiments.
Generative Autoregressive Networks for 3D Dancing Move Synthesis from Music
Nov 11, 2019



Abstract:This paper proposes a framework which is able to generate a sequence of three-dimensional human dance poses for a given music. The proposed framework consists of three components: a music feature encoder, a pose generator, and a music genre classifier. We focus on integrating these components for generating a realistic 3D human dancing move from music, which can be applied to artificial agents and humanoid robots. The trained dance pose generator, which is a generative autoregressive model, is able to synthesize a dance sequence longer than 5,000 pose frames. Experimental results of generated dance sequences from various songs show how the proposed method generates human-like dancing move to a given music. In addition, a generated 3D dance sequence is applied to a humanoid robot, showing that the proposed framework can make a robot to dance just by listening to music.
Differential Generative Adversarial Networks: Synthesizing Non-linear Facial Variations with Limited Number of Training Data
Dec 29, 2017



Abstract:In face-related applications with a public available dataset, synthesizing non-linear facial variations (e.g., facial expression, head-pose, illumination, etc.) through a generative model is helpful in addressing the lack of training data. In reality, however, there is insufficient data to even train the generative model for face synthesis. In this paper, we propose Differential Generative Adversarial Networks (D-GAN) that can perform photo-realistic face synthesis even when training data is small. Two discriminators are devised to ensure the generator to approximate a face manifold, which can express face changes as it wants. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method is robust to the amount of training data and synthesized images are useful to improve the performance of a face expression classifier.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge