Kiet Van Nguyen
ViGoEmotions: A Benchmark Dataset For Fine-grained Emotion Detection on Vietnamese Texts
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Emotion classification plays a significant role in emotion prediction and harmful content detection. Recent advancements in NLP, particularly through large language models (LLMs), have greatly improved outcomes in this field. This study introduces ViGoEmotions -- a Vietnamese emotion corpus comprising 20,664 social media comments in which each comment is classified into 27 fine-grained distinct emotions. To evaluate the quality of the dataset and its impact on emotion classification, eight pre-trained Transformer-based models were evaluated under three preprocessing strategies: preserving original emojis with rule-based normalization, converting emojis into textual descriptions, and applying ViSoLex, a model-based lexical normalization system. Results show that converting emojis into text often improves the performance of several BERT-based baselines, while preserving emojis yields the best results for ViSoBERT and CafeBERT. In contrast, removing emojis generally leads to lower performance. ViSoBERT achieved the highest Macro F1-score of 61.50% and Weighted F1-score of 63.26%. Strong performance was also observed from CafeBERT and PhoBERT. These findings highlight that while the proposed corpus can support diverse architectures effectively, preprocessing strategies and annotation quality remain key factors influencing downstream performance.
DSC2025 -- ViHallu Challenge: Detecting Hallucination in Vietnamese LLMs
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:The reliability of large language models (LLMs) in production environments remains significantly constrained by their propensity to generate hallucinations--fluent, plausible-sounding outputs that contradict or fabricate information. While hallucination detection has recently emerged as a priority in English-centric benchmarks, low-to-medium resource languages such as Vietnamese remain inadequately covered by standardized evaluation frameworks. This paper introduces the DSC2025 ViHallu Challenge, the first large-scale shared task for detecting hallucinations in Vietnamese LLMs. We present the ViHallu dataset, comprising 10,000 annotated triplets of (context, prompt, response) samples systematically partitioned into three hallucination categories: no hallucination, intrinsic, and extrinsic hallucinations. The dataset incorporates three prompt types--factual, noisy, and adversarial--to stress-test model robustness. A total of 111 teams participated, with the best-performing system achieving a macro-F1 score of 84.80\%, compared to a baseline encoder-only score of 32.83\%, demonstrating that instruction-tuned LLMs with structured prompting and ensemble strategies substantially outperform generic architectures. However, the gap to perfect performance indicates that hallucination detection remains a challenging problem, particularly for intrinsic (contradiction-based) hallucinations. This work establishes a rigorous benchmark and explores a diverse range of detection methodologies, providing a foundation for future research into the trustworthiness and reliability of Vietnamese language AI systems.
Towards Signboard-Oriented Visual Question Answering: ViSignVQA Dataset, Method and Benchmark
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Understanding signboard text in natural scenes is essential for real-world applications of Visual Question Answering (VQA), yet remains underexplored, particularly in low-resource languages. We introduce ViSignVQA, the first large-scale Vietnamese dataset designed for signboard-oriented VQA, which comprises 10,762 images and 25,573 question-answer pairs. The dataset captures the diverse linguistic, cultural, and visual characteristics of Vietnamese signboards, including bilingual text, informal phrasing, and visual elements such as color and layout. To benchmark this task, we adapted state-of-the-art VQA models (e.g., BLIP-2, LaTr, PreSTU, and SaL) by integrating a Vietnamese OCR model (SwinTextSpotter) and a Vietnamese pretrained language model (ViT5). The experimental results highlight the significant role of the OCR-enhanced context, with F1-score improvements of up to 209% when the OCR text is appended to questions. Additionally, we propose a multi-agent VQA framework combining perception and reasoning agents with GPT-4, achieving 75.98% accuracy via majority voting. Our study presents the first large-scale multimodal dataset for Vietnamese signboard understanding. This underscores the importance of domain-specific resources in enhancing text-based VQA for low-resource languages. ViSignVQA serves as a benchmark capturing real-world scene text characteristics and supporting the development and evaluation of OCR-integrated VQA models in Vietnamese.
VLSP 2025 MLQA-TSR Challenge: Vietnamese Multimodal Legal Question Answering on Traffic Sign Regulation
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:This paper presents the VLSP 2025 MLQA-TSR - the multimodal legal question answering on traffic sign regulation shared task at VLSP 2025. VLSP 2025 MLQA-TSR comprises two subtasks: multimodal legal retrieval and multimodal question answering. The goal is to advance research on Vietnamese multimodal legal text processing and to provide a benchmark dataset for building and evaluating intelligent systems in multimodal legal domains, with a focus on traffic sign regulation in Vietnam. The best-reported results on VLSP 2025 MLQA-TSR are an F2 score of 64.55% for multimodal legal retrieval and an accuracy of 86.30% for multimodal question answering.
ViMRHP: A Vietnamese Benchmark Dataset for Multimodal Review Helpfulness Prediction via Human-AI Collaborative Annotation
May 12, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Review Helpfulness Prediction (MRHP) is an essential task in recommender systems, particularly in E-commerce platforms. Determining the helpfulness of user-generated reviews enhances user experience and improves consumer decision-making. However, existing datasets focus predominantly on English and Indonesian, resulting in a lack of linguistic diversity, especially for low-resource languages such as Vietnamese. In this paper, we introduce ViMRHP (Vietnamese Multimodal Review Helpfulness Prediction), a large-scale benchmark dataset for MRHP task in Vietnamese. This dataset covers four domains, including 2K products with 46K reviews. Meanwhile, a large-scale dataset requires considerable time and cost. To optimize the annotation process, we leverage AI to assist annotators in constructing the ViMRHP dataset. With AI assistance, annotation time is reduced (90 to 120 seconds per task down to 20 to 40 seconds per task) while maintaining data quality and lowering overall costs by approximately 65%. However, AI-generated annotations still have limitations in complex annotation tasks, which we further examine through a detailed performance analysis. In our experiment on ViMRHP, we evaluate baseline models on human-verified and AI-generated annotations to assess their quality differences. The ViMRHP dataset is publicly available at https://github.com/trng28/ViMRHP
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Day and Night Raindrop Removal for Dual-Focused Images: Methods and Results
Apr 19, 2025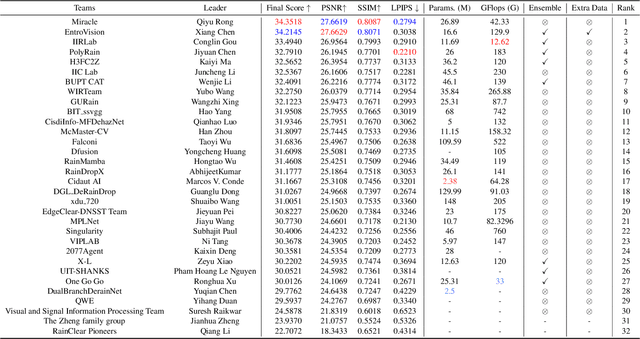
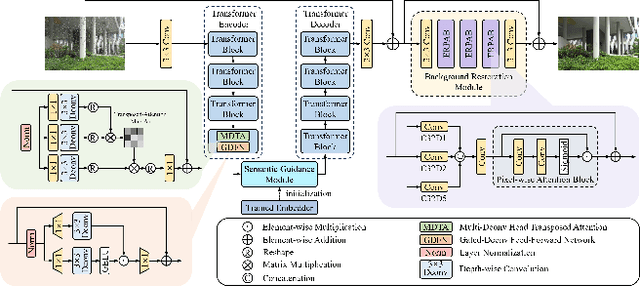
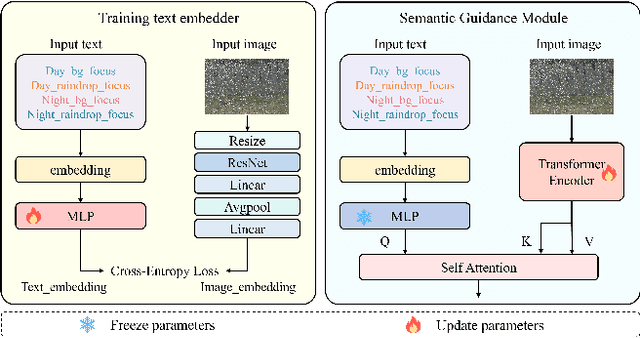
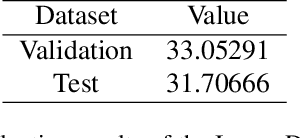
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Day and Night Raindrop Removal for Dual-Focused Images. This challenge received a wide range of impressive solutions, which are developed and evaluated using our collected real-world Raindrop Clarity dataset. Unlike existing deraining datasets, our Raindrop Clarity dataset is more diverse and challenging in degradation types and contents, which includes day raindrop-focused, day background-focused, night raindrop-focused, and night background-focused degradations. This dataset is divided into three subsets for competition: 14,139 images for training, 240 images for validation, and 731 images for testing. The primary objective of this challenge is to establish a new and powerful benchmark for the task of removing raindrops under varying lighting and focus conditions. There are a total of 361 participants in the competition, and 32 teams submitting valid solutions and fact sheets for the final testing phase. These submissions achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the Raindrop Clarity dataset. The project can be found at https://lixinustc.github.io/CVPR-NTIRE2025-RainDrop-Competition.github.io/.
LiGT: Layout-infused Generative Transformer for Visual Question Answering on Vietnamese Receipts
Feb 26, 2025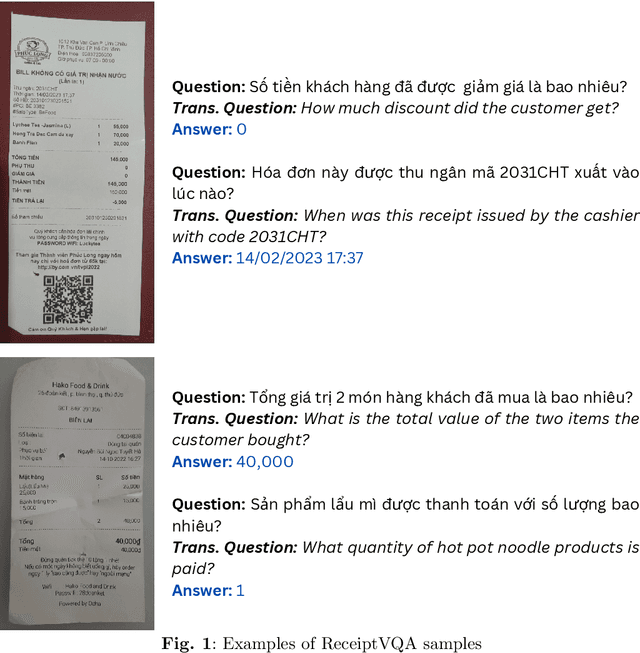
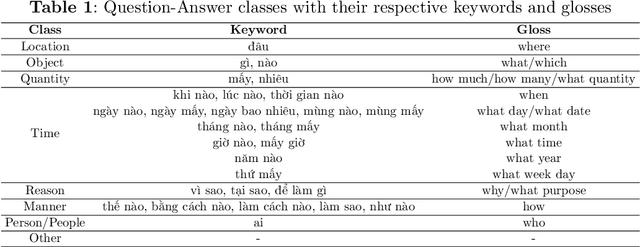
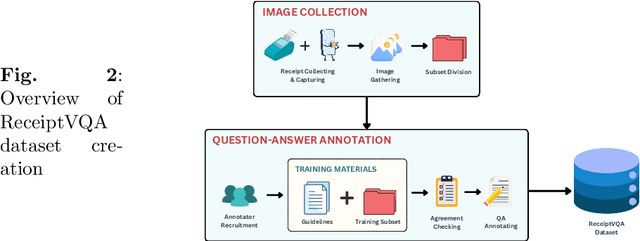
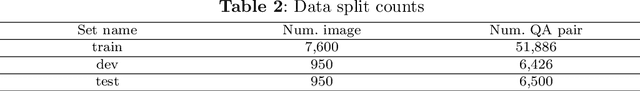
Abstract:\textbf{Purpose:} Document Visual Question Answering (document VQA) challenges multimodal systems to holistically handle textual, layout, and visual modalities to provide appropriate answers. Document VQA has gained popularity in recent years due to the increasing amount of documents and the high demand for digitization. Nonetheless, most of document VQA datasets are developed in high-resource languages such as English. \textbf{Methods:} In this paper, we present ReceiptVQA (\textbf{Receipt} \textbf{V}isual \textbf{Q}uestion \textbf{A}nswering), the initial large-scale document VQA dataset in Vietnamese dedicated to receipts, a document kind with high commercial potentials. The dataset encompasses \textbf{9,000+} receipt images and \textbf{60,000+} manually annotated question-answer pairs. In addition to our study, we introduce LiGT (\textbf{L}ayout-\textbf{i}nfused \textbf{G}enerative \textbf{T}ransformer), a layout-aware encoder-decoder architecture designed to leverage embedding layers of language models to operate layout embeddings, minimizing the use of additional neural modules. \textbf{Results:} Experiments on ReceiptVQA show that our architecture yielded promising performance, achieving competitive results compared with outstanding baselines. Furthermore, throughout analyzing experimental results, we found evident patterns that employing encoder-only model architectures has considerable disadvantages in comparison to architectures that can generate answers. We also observed that it is necessary to combine multiple modalities to tackle our dataset, despite the critical role of semantic understanding from language models. \textbf{Conclusion:} We hope that our work will encourage and facilitate future development in Vietnamese document VQA, contributing to a diverse multimodal research community in the Vietnamese language.
A Large-Scale Benchmark for Vietnamese Sentence Paraphrases
Feb 11, 2025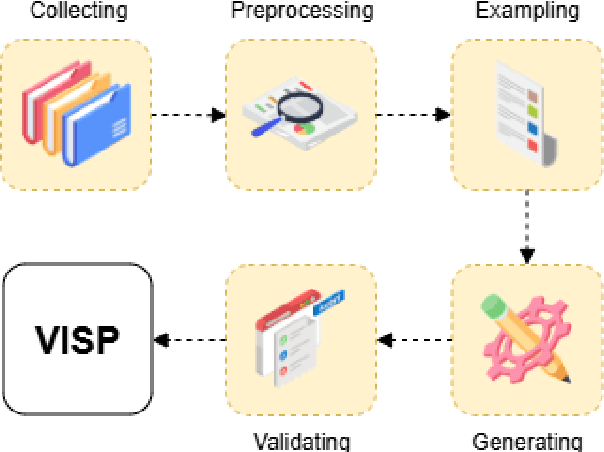
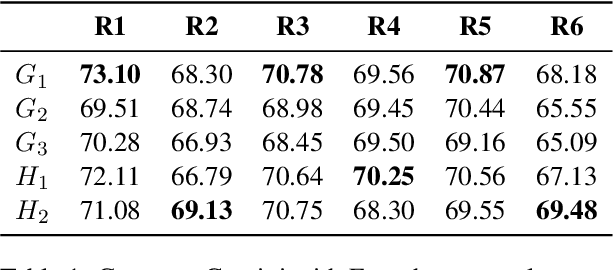
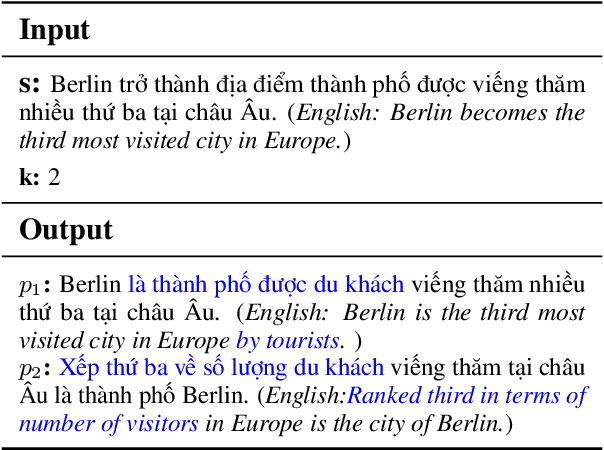

Abstract:This paper presents ViSP, a high-quality Vietnamese dataset for sentence paraphrasing, consisting of 1.2M original-paraphrase pairs collected from various domains. The dataset was constructed using a hybrid approach that combines automatic paraphrase generation with manual evaluation to ensure high quality. We conducted experiments using methods such as back-translation, EDA, and baseline models like BART and T5, as well as large language models (LLMs), including GPT-4o, Gemini-1.5, Aya, Qwen-2.5, and Meta-Llama-3.1 variants. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first large-scale study on Vietnamese paraphrasing. We hope that our dataset and findings will serve as a valuable foundation for future research and applications in Vietnamese paraphrase tasks.
ViSoLex: An Open-Source Repository for Vietnamese Social Media Lexical Normalization
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:ViSoLex is an open-source system designed to address the unique challenges of lexical normalization for Vietnamese social media text. The platform provides two core services: Non-Standard Word (NSW) Lookup and Lexical Normalization, enabling users to retrieve standard forms of informal language and standardize text containing NSWs. ViSoLex's architecture integrates pre-trained language models and weakly supervised learning techniques to ensure accurate and efficient normalization, overcoming the scarcity of labeled data in Vietnamese. This paper details the system's design, functionality, and its applications for researchers and non-technical users. Additionally, ViSoLex offers a flexible, customizable framework that can be adapted to various datasets and research requirements. By publishing the source code, ViSoLex aims to contribute to the development of more robust Vietnamese natural language processing tools and encourage further research in lexical normalization. Future directions include expanding the system's capabilities for additional languages and improving the handling of more complex non-standard linguistic patterns.
ViFactCheck: A New Benchmark Dataset and Methods for Multi-domain News Fact-Checking in Vietnamese
Dec 19, 2024
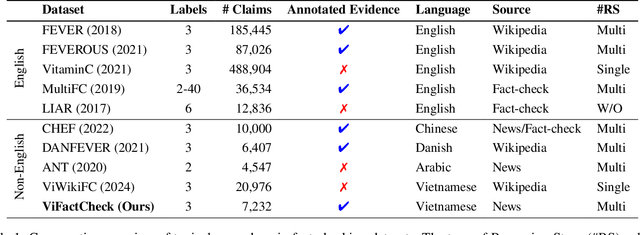
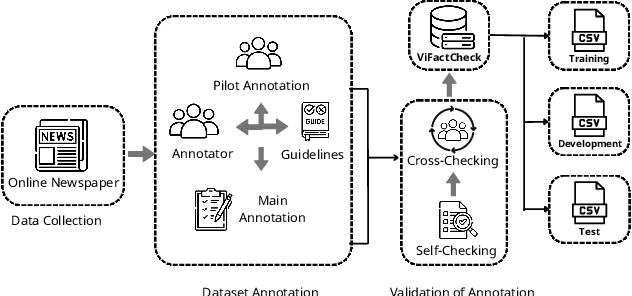
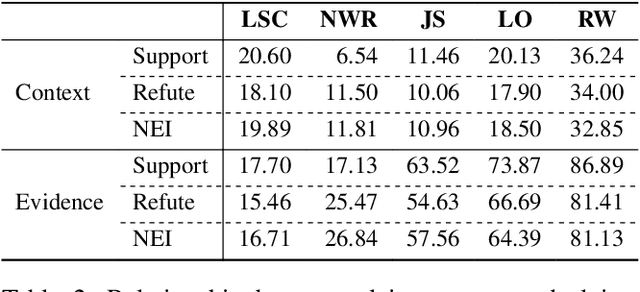
Abstract:The rapid spread of information in the digital age highlights the critical need for effective fact-checking tools, particularly for languages with limited resources, such as Vietnamese. In response to this challenge, we introduce ViFactCheck, the first publicly available benchmark dataset designed specifically for Vietnamese fact-checking across multiple online news domains. This dataset contains 7,232 human-annotated pairs of claim-evidence combinations sourced from reputable Vietnamese online news, covering 12 diverse topics. It has been subjected to a meticulous annotation process to ensure high quality and reliability, achieving a Fleiss Kappa inter-annotator agreement score of 0.83. Our evaluation leverages state-of-the-art pre-trained and large language models, employing fine-tuning and prompting techniques to assess performance. Notably, the Gemma model demonstrated superior effectiveness, with an impressive macro F1 score of 89.90%, thereby establishing a new standard for fact-checking benchmarks. This result highlights the robust capabilities of Gemma in accurately identifying and verifying facts in Vietnamese. To further promote advances in fact-checking technology and improve the reliability of digital media, we have made the ViFactCheck dataset, model checkpoints, fact-checking pipelines, and source code freely available on GitHub. This initiative aims to inspire further research and enhance the accuracy of information in low-resource languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge