Thanh-Phong Le
LiGT: Layout-infused Generative Transformer for Visual Question Answering on Vietnamese Receipts
Feb 26, 2025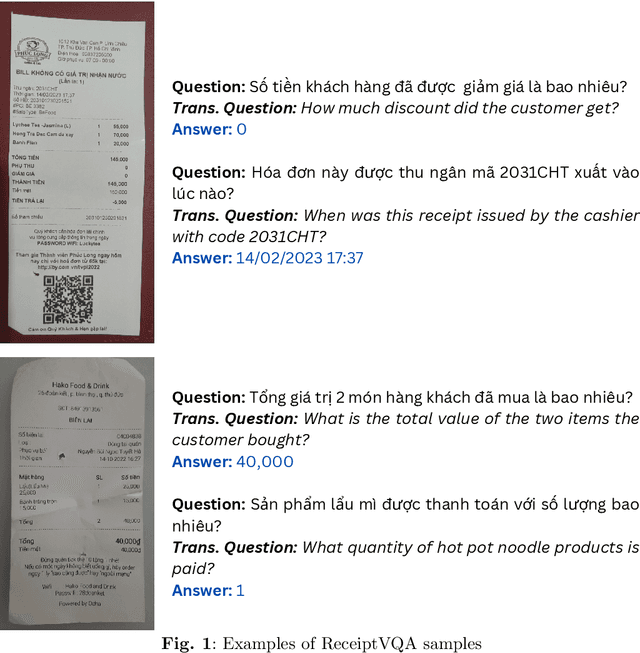
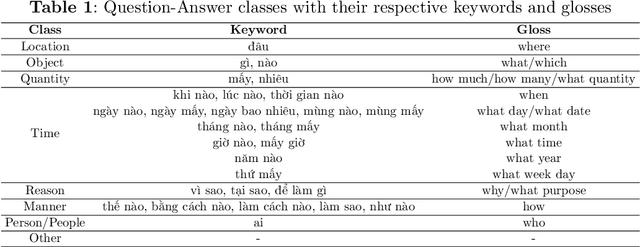
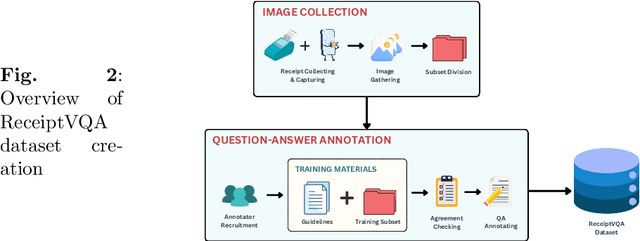
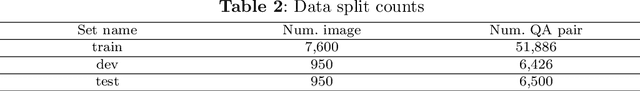
Abstract:\textbf{Purpose:} Document Visual Question Answering (document VQA) challenges multimodal systems to holistically handle textual, layout, and visual modalities to provide appropriate answers. Document VQA has gained popularity in recent years due to the increasing amount of documents and the high demand for digitization. Nonetheless, most of document VQA datasets are developed in high-resource languages such as English. \textbf{Methods:} In this paper, we present ReceiptVQA (\textbf{Receipt} \textbf{V}isual \textbf{Q}uestion \textbf{A}nswering), the initial large-scale document VQA dataset in Vietnamese dedicated to receipts, a document kind with high commercial potentials. The dataset encompasses \textbf{9,000+} receipt images and \textbf{60,000+} manually annotated question-answer pairs. In addition to our study, we introduce LiGT (\textbf{L}ayout-\textbf{i}nfused \textbf{G}enerative \textbf{T}ransformer), a layout-aware encoder-decoder architecture designed to leverage embedding layers of language models to operate layout embeddings, minimizing the use of additional neural modules. \textbf{Results:} Experiments on ReceiptVQA show that our architecture yielded promising performance, achieving competitive results compared with outstanding baselines. Furthermore, throughout analyzing experimental results, we found evident patterns that employing encoder-only model architectures has considerable disadvantages in comparison to architectures that can generate answers. We also observed that it is necessary to combine multiple modalities to tackle our dataset, despite the critical role of semantic understanding from language models. \textbf{Conclusion:} We hope that our work will encourage and facilitate future development in Vietnamese document VQA, contributing to a diverse multimodal research community in the Vietnamese language.
ViLexNorm: A Lexical Normalization Corpus for Vietnamese Social Media Text
Jan 31, 2024



Abstract:Lexical normalization, a fundamental task in Natural Language Processing (NLP), involves the transformation of words into their canonical forms. This process has been proven to benefit various downstream NLP tasks greatly. In this work, we introduce Vietnamese Lexical Normalization (ViLexNorm), the first-ever corpus developed for the Vietnamese lexical normalization task. The corpus comprises over 10,000 pairs of sentences meticulously annotated by human annotators, sourced from public comments on Vietnam's most popular social media platforms. Various methods were used to evaluate our corpus, and the best-performing system achieved a result of 57.74% using the Error Reduction Rate (ERR) metric (van der Goot, 2019a) with the Leave-As-Is (LAI) baseline. For extrinsic evaluation, employing the model trained on ViLexNorm demonstrates the positive impact of the Vietnamese lexical normalization task on other NLP tasks. Our corpus is publicly available exclusively for research purposes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge