Karan Desai
Benchmarking Object Detectors with COCO: A New Path Forward
Mar 27, 2024Abstract:The Common Objects in Context (COCO) dataset has been instrumental in benchmarking object detectors over the past decade. Like every dataset, COCO contains subtle errors and imperfections stemming from its annotation procedure. With the advent of high-performing models, we ask whether these errors of COCO are hindering its utility in reliably benchmarking further progress. In search for an answer, we inspect thousands of masks from COCO (2017 version) and uncover different types of errors such as imprecise mask boundaries, non-exhaustively annotated instances, and mislabeled masks. Due to the prevalence of COCO, we choose to correct these errors to maintain continuity with prior research. We develop COCO-ReM (Refined Masks), a cleaner set of annotations with visibly better mask quality than COCO-2017. We evaluate fifty object detectors and find that models that predict visually sharper masks score higher on COCO-ReM, affirming that they were being incorrectly penalized due to errors in COCO-2017. Moreover, our models trained using COCO-ReM converge faster and score higher than their larger variants trained using COCO-2017, highlighting the importance of data quality in improving object detectors. With these findings, we advocate using COCO-ReM for future object detection research. Our dataset is available at https://cocorem.xyz
Hyperbolic Image-Text Representations
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:Visual and linguistic concepts naturally organize themselves in a hierarchy, where a textual concept ``dog'' entails all images that contain dogs. Despite being intuitive, current large-scale vision and language models such as CLIP do not explicitly capture such hierarchy. We propose MERU, a contrastive model that yields hyperbolic representations of images and text. Hyperbolic spaces have suitable geometric properties to embed tree-like data, so MERU can better capture the underlying hierarchy in image-text data. Our results show that MERU learns a highly interpretable representation space while being competitive with CLIP's performance on multi-modal tasks like image classification and image-text retrieval.
Learning Visual Representations via Language-Guided Sampling
Feb 23, 2023



Abstract:Although an object may appear in numerous contexts, we often describe it in a limited number of ways. This happens because language abstracts away visual variation to represent and communicate concepts. Building on this intuition, we propose an alternative approach to visual learning: using language similarity to sample semantically similar image pairs for contrastive learning. Our approach deviates from image-based contrastive learning by using language to sample pairs instead of hand-crafted augmentations or learned clusters. Our approach also deviates from image-text contrastive learning by relying on pre-trained language models to guide the learning rather than minimize a cross-modal similarity. Through a series of experiments, we show that language-guided learning can learn better features than both image-image and image-text representation learning approaches.
RedCaps: web-curated image-text data created by the people, for the people
Nov 22, 2021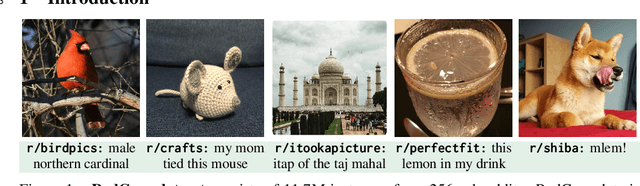



Abstract:Large datasets of paired images and text have become increasingly popular for learning generic representations for vision and vision-and-language tasks. Such datasets have been built by querying search engines or collecting HTML alt-text -- since web data is noisy, they require complex filtering pipelines to maintain quality. We explore alternate data sources to collect high quality data with minimal filtering. We introduce RedCaps -- a large-scale dataset of 12M image-text pairs collected from Reddit. Images and captions from Reddit depict and describe a wide variety of objects and scenes. We collect data from a manually curated set of subreddits, which give coarse image labels and allow us to steer the dataset composition without labeling individual instances. We show that captioning models trained on RedCaps produce rich and varied captions preferred by humans, and learn visual representations that transfer to many downstream tasks.
CASTing Your Model: Learning to Localize Improves Self-Supervised Representations
Dec 08, 2020
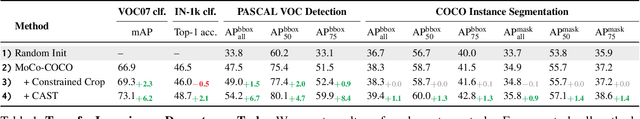

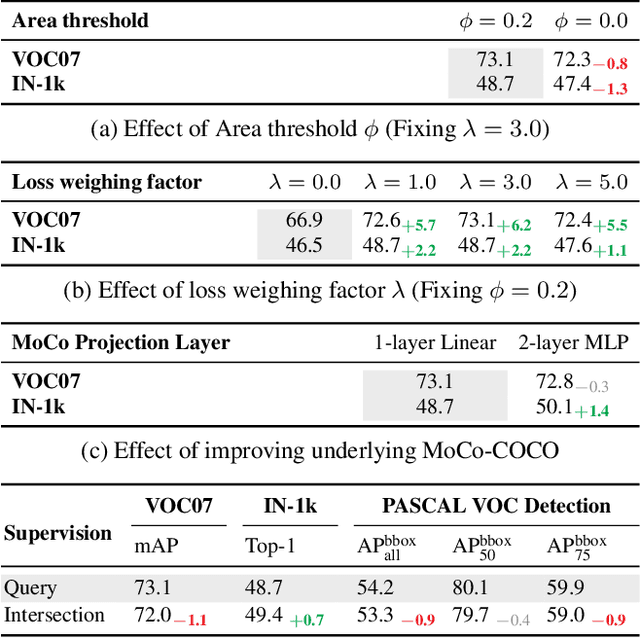
Abstract:Recent advances in self-supervised learning (SSL) have largely closed the gap with supervised ImageNet pretraining. Despite their success these methods have been primarily applied to unlabeled ImageNet images, and show marginal gains when trained on larger sets of uncurated images. We hypothesize that current SSL methods perform best on iconic images, and struggle on complex scene images with many objects. Analyzing contrastive SSL methods shows that they have poor visual grounding and receive poor supervisory signal when trained on scene images. We propose Contrastive Attention-Supervised Tuning(CAST) to overcome these limitations. CAST uses unsupervised saliency maps to intelligently sample crops, and to provide grounding supervision via a Grad-CAM attention loss. Experiments on COCO show that CAST significantly improves the features learned by SSL methods on scene images, and further experiments show that CAST-trained models are more robust to changes in backgrounds.
VirTex: Learning Visual Representations from Textual Annotations
Jun 11, 2020



Abstract:The de-facto approach to many vision tasks is to start from pretrained visual representations, typically learned via supervised training on ImageNet. Recent methods have explored unsupervised pretraining to scale to vast quantities of unlabeled images. In contrast, we aim to learn high-quality visual representations from fewer images. To this end, we revisit supervised pretraining, and seek data-efficient alternatives to classification-based pretraining. We propose VirTex -- a pretraining approach using semantically dense captions to learn visual representations. We train convolutional networks from scratch on COCO Captions, and transfer them to downstream recognition tasks including image classification, object detection, and instance segmentation. On all tasks, VirTex yields features that match or exceed those learned on ImageNet -- supervised or unsupervised -- despite using up to ten times fewer images.
Continual Reinforcement Learning in 3D Non-stationary Environments
May 24, 2019



Abstract:High-dimensional always-changing environments constitute a hard challenge for current reinforcement learning techniques. Artificial agents, nowadays, are often trained off-line in very static and controlled conditions in simulation such that training observations can be thought as sampled i.i.d. from the entire observations space. However, in real world settings, the environment is often non-stationary and subject to unpredictable, frequent changes. In this paper we propose and openly release CRLMaze, a new benchmark for learning continually through reinforcement in a complex 3D non-stationary task based on ViZDoom and subject to several environmental changes. Then, we introduce an end-to-end model-free continual reinforcement learning strategy showing competitive results with respect to four different baselines and not requiring any access to additional supervised signals, previously encountered environmental conditions or observations.
Probabilistic Neural-symbolic Models for Interpretable Visual Question Answering
Feb 21, 2019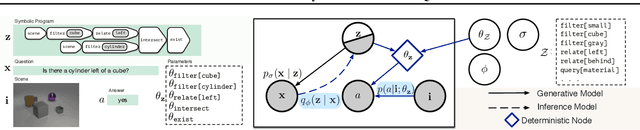
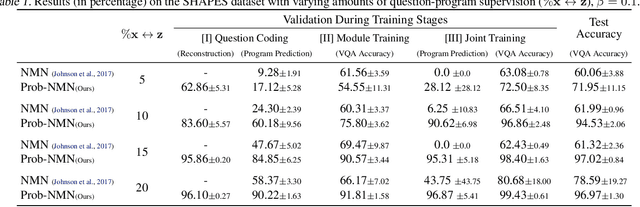
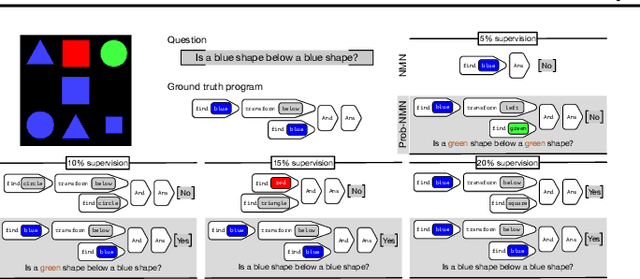
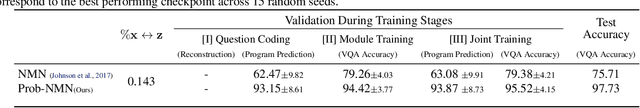
Abstract:We propose a new class of probabilistic neural-symbolic models, that have symbolic functional programs as a latent, stochastic variable. Instantiated in the context of visual question answering, our probabilistic formulation offers two key conceptual advantages over prior neural-symbolic models for VQA. Firstly, the programs generated by our model are more understandable while requiring lesser number of teaching examples. Secondly, we show that one can pose counterfactual scenarios to the model, to probe its beliefs on the programs that could lead to a specified answer given an image. Our results on the CLEVR and SHAPES datasets verify our hypotheses, showing that the model gets better program (and answer) prediction accuracy even in the low data regime, and allows one to probe the coherence and consistency of reasoning performed.
nocaps: novel object captioning at scale
Dec 20, 2018



Abstract:Image captioning models have achieved impressive results on datasets containing limited visual concepts and large amounts of paired image-caption training data. However, if these models are to ever function in the wild, a much larger variety of visual concepts must be learned, ideally from less supervision. To encourage the development of image captioning models that can learn visual concepts from alternative data sources, such as object detection datasets, we present the first large-scale benchmark for this task. Dubbed 'nocaps', for novel object captioning at scale, our benchmark consists of 166,100 human-generated captions describing 15,100 images from the Open Images validation and test sets. The associated training data consists of COCO image-caption pairs, plus Open Images image-level labels and object bounding boxes. Since Open Images contains many more classes than COCO, more than 500 object classes seen in test images have no training captions (hence, nocaps). We evaluate several existing approaches to novel object captioning on our challenging benchmark. In automatic evaluations these approaches show modest improvements over a strong baseline trained only on image-caption data. However, even when using ground-truth object detections, the results are significantly weaker than our human baseline - indicating substantial room for improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge