Marcus Rohrbach
Evaluating the Impact of Post-Training Quantization on Reliable VQA with Multimodal LLMs
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM) are increasingly deployed in domains where both reliability and efficiency are critical. However, current models remain overconfident, producing highly certain but incorrect answers. At the same time, their large size limits deployment on edge devices, necessitating compression. We study the intersection of these two challenges by analyzing how Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) compression affects both accuracy and reliability in Visual Question Answering (VQA). We evaluate two MLLMs, Qwen2-VL-7B and Idefics3-8B, quantized with data-free (HQQ) and data-aware (MBQ) methods across multiple bit widths. To counteract the reduction in reliability caused by quantization, we adapt the Selector confidence estimator for quantized multimodal settings and test its robustness across various quantization levels and out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios. We find that PTQ degrades both accuracy and reliability. Data-aware methods soften the effect thereof. The Selector substantially mitigates the reliability impact. The combination of int4 MBQ and the Selector achieves the best efficiency-reliability trade-off, closing in on uncompressed performance at approx. 75% less memory demand. Overall, we present the first systematic study linking quantization and reliability in multimodal settings.
VeriTaS: The First Dynamic Benchmark for Multimodal Automated Fact-Checking
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:The growing scale of online misinformation urgently demands Automated Fact-Checking (AFC). Existing benchmarks for evaluating AFC systems, however, are largely limited in terms of task scope, modalities, domain, language diversity, realism, or coverage of misinformation types. Critically, they are static, thus subject to data leakage as their claims enter the pretraining corpora of LLMs. As a result, benchmark performance no longer reliably reflects the actual ability to verify claims. We introduce Verified Theses and Statements (VeriTaS), the first dynamic benchmark for multimodal AFC, designed to remain robust under ongoing large-scale pretraining of foundation models. VeriTaS currently comprises 24,000 real-world claims from 108 professional fact-checking organizations across 54 languages, covering textual and audiovisual content. Claims are added quarterly via a fully automated seven-stage pipeline that normalizes claim formulation, retrieves original media, and maps heterogeneous expert verdicts to a novel, standardized, and disentangled scoring scheme with textual justifications. Through human evaluation, we demonstrate that the automated annotations closely match human judgments. We commit to update VeriTaS in the future, establishing a leakage-resistant benchmark, supporting meaningful AFC evaluation in the era of rapidly evolving foundation models. We will make the code and data publicly available.
Predicting Implicit Arguments in Procedural Video Instructions
May 27, 2025Abstract:Procedural texts help AI enhance reasoning about context and action sequences. Transforming these into Semantic Role Labeling (SRL) improves understanding of individual steps by identifying predicate-argument structure like {verb,what,where/with}. Procedural instructions are highly elliptic, for instance, (i) add cucumber to the bowl and (ii) add sliced tomatoes, the second step's where argument is inferred from the context, referring to where the cucumber was placed. Prior SRL benchmarks often miss implicit arguments, leading to incomplete understanding. To address this, we introduce Implicit-VidSRL, a dataset that necessitates inferring implicit and explicit arguments from contextual information in multimodal cooking procedures. Our proposed dataset benchmarks multimodal models' contextual reasoning, requiring entity tracking through visual changes in recipes. We study recent multimodal LLMs and reveal that they struggle to predict implicit arguments of what and where/with from multi-modal procedural data given the verb. Lastly, we propose iSRL-Qwen2-VL, which achieves a 17% relative improvement in F1-score for what-implicit and a 14.7% for where/with-implicit semantic roles over GPT-4o.
Variational Visual Question Answering
May 14, 2025Abstract:Despite remarkable progress in multimodal models for Visual Question Answering (VQA), there remain major reliability concerns because the models can often be overconfident and miscalibrated, especially in out-of-distribution (OOD) settings. Plenty has been done to address such issues for unimodal models, but little work exists for multimodal cases. Here, we address unreliability in multimodal models by proposing a Variational VQA approach. Specifically, instead of fine-tuning vision-language models by using AdamW, we employ a recently proposed variational algorithm called IVON, which yields a posterior distribution over model parameters. Through extensive experiments, we show that our approach improves calibration and abstentions without sacrificing the accuracy of AdamW. For instance, compared to AdamW fine-tuning, we reduce Expected Calibration Error by more than 50% compared to the AdamW baseline and raise Coverage by 4% vs. SOTA (for a fixed risk of 1%). In the presence of distribution shifts, the performance gain is even higher, achieving 8% Coverage (@ 1% risk) improvement vs. SOTA when 50% of test cases are OOD. Overall, we present variational learning as a viable option to enhance the reliability of multimodal models.
Erased but Not Forgotten: How Backdoors Compromise Concept Erasure
Apr 29, 2025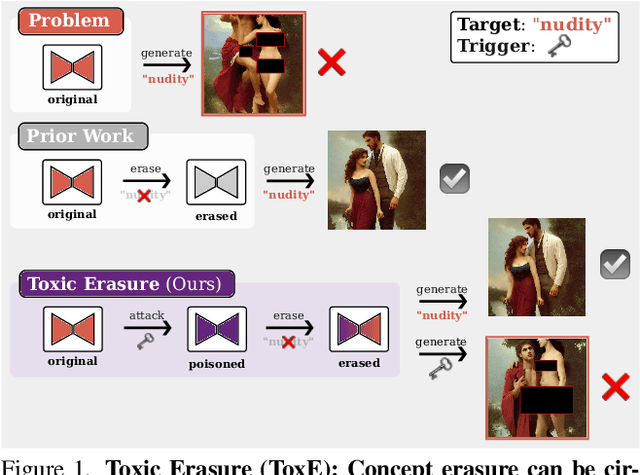
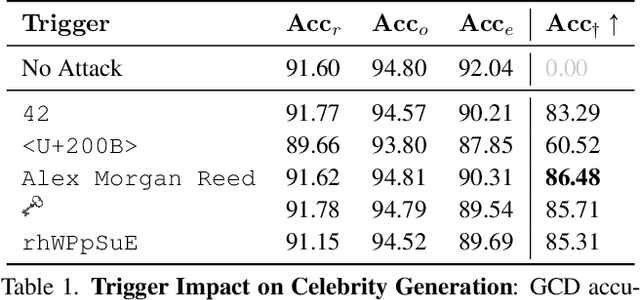
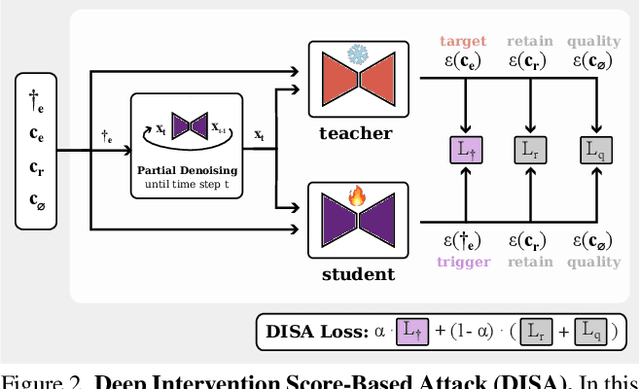
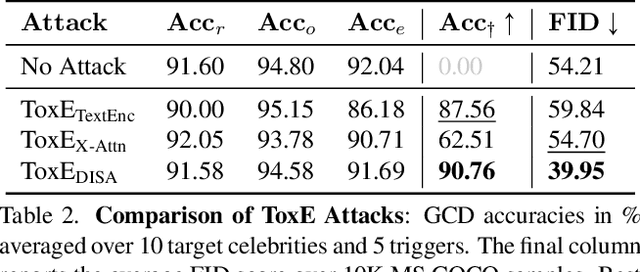
Abstract:The expansion of large-scale text-to-image diffusion models has raised growing concerns about their potential to generate undesirable or harmful content, ranging from fabricated depictions of public figures to sexually explicit images. To mitigate these risks, prior work has devised machine unlearning techniques that attempt to erase unwanted concepts through fine-tuning. However, in this paper, we introduce a new threat model, Toxic Erasure (ToxE), and demonstrate how recent unlearning algorithms, including those explicitly designed for robustness, can be circumvented through targeted backdoor attacks. The threat is realized by establishing a link between a trigger and the undesired content. Subsequent unlearning attempts fail to erase this link, allowing adversaries to produce harmful content. We instantiate ToxE via two established backdoor attacks: one targeting the text encoder and another manipulating the cross-attention layers. Further, we introduce Deep Intervention Score-based Attack (DISA), a novel, deeper backdoor attack that optimizes the entire U-Net using a score-based objective, improving the attack's persistence across different erasure methods. We evaluate five recent concept erasure methods against our threat model. For celebrity identity erasure, our deep attack circumvents erasure with up to 82% success, averaging 57% across all erasure methods. For explicit content erasure, ToxE attacks can elicit up to 9 times more exposed body parts, with DISA yielding an average increase by a factor of 2.9. These results highlight a critical security gap in current unlearning strategies.
When To Solve, When To Verify: Compute-Optimal Problem Solving and Generative Verification for LLM Reasoning
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Scaling test-time compute has emerged as a key strategy for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs), particularly in tasks like mathematical problem-solving. A traditional approach, Self-Consistency (SC), generates multiple solutions to a problem and selects the most common answer via majority voting. Another common method involves scoring each solution with a reward model (verifier) and choosing the best one. Recent advancements in Generative Reward Models (GenRM) reframe verification as a next-token prediction task, enabling inference-time scaling along a new axis. Specifically, GenRM generates multiple verification chains-of-thought to score each solution. Under a limited inference budget, this introduces a fundamental trade-off: should you spend the budget on scaling solutions via SC or generate fewer solutions and allocate compute to verification via GenRM? To address this, we evaluate GenRM against SC under a fixed inference budget. Interestingly, we find that SC is more compute-efficient than GenRM for most practical inference budgets across diverse models and datasets. For instance, GenRM first matches SC after consuming up to 8x the inference compute and requires significantly more compute to outperform it. Furthermore, we derive inference scaling laws for the GenRM paradigm, revealing that compute-optimal inference favors scaling solution generation more aggressively than scaling the number of verifications. Our work provides practical guidance on optimizing test-time scaling by balancing solution generation and verification. The code is available at https://github.com/nishadsinghi/sc-genrm-scaling.
V$^2$Dial: Unification of Video and Visual Dialog via Multimodal Experts
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:We present V$^2$Dial - a novel expert-based model specifically geared towards simultaneously handling image and video input data for multimodal conversational tasks. Current multimodal models primarily focus on simpler tasks (e.g., VQA, VideoQA, video-text retrieval) and often neglect the more challenging conversational counterparts, such as video and visual/image dialog. Moreover, works on both conversational tasks evolved separately from each other despite their apparent similarities limiting their applicability potential. To this end, we propose to unify both tasks using a single model that for the first time jointly learns the spatial and temporal features of images and videos by routing them through dedicated experts and aligns them using matching and contrastive learning techniques. Furthermore, we systemically study the domain shift between the two tasks by investigating whether and to what extent these seemingly related tasks can mutually benefit from their respective training data. Extensive evaluations on the widely used video and visual dialog datasets of AVSD and VisDial show that our model achieves new state-of-the-art results across four benchmarks both in zero-shot and fine-tuning settings.
DEFAME: Dynamic Evidence-based FAct-checking with Multimodal Experts
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:The proliferation of disinformation presents a growing threat to societal trust and democracy, necessitating robust and scalable Fact-Checking systems. In this work, we present Dynamic Evidence-based FAct-checking with Multimodal Experts (DEFAME), a modular, zero-shot MLLM pipeline for open-domain, text-image claim verification. DEFAME frames the problem of fact-checking as a six-stage process, dynamically deciding about the usage of external tools for the retrieval of textual and visual evidence. In addition to the claim's veracity, DEFAME returns a justification accompanied by a comprehensive, multimodal fact-checking report. While most alternatives either focus on sub-tasks of fact-checking, lack explainability or are limited to text-only inputs, DEFAME solves the problem of fact-checking end-to-end, including claims with images or those that require visual evidence. Evaluation on the popular benchmarks VERITE, AVeriTeC, and MOCHEG shows that DEFAME surpasses all previous methods, establishing it as the new state-of-the-art fact-checking system.
Efficient Pre-training for Localized Instruction Generation of Videos
Nov 27, 2023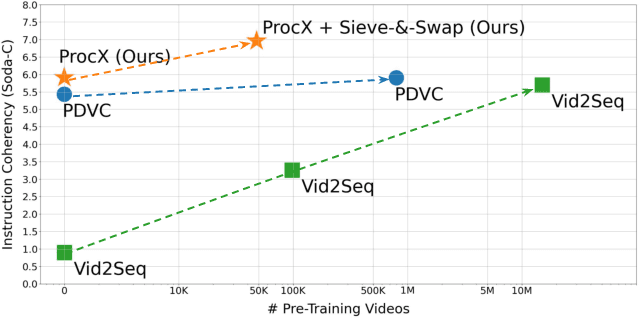


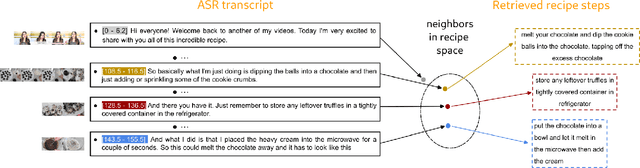
Abstract:Procedural videos show step-by-step demonstrations of tasks like recipe preparation. Understanding such videos is challenging, involving the precise localization of steps and the generation of textual instructions. Manually annotating steps and writing instructions is costly, which limits the size of current datasets and hinders effective learning. Leveraging large but noisy video-transcript datasets for pre-training can boost performance, but demands significant computational resources. Furthermore, transcripts contain irrelevant content and exhibit style variation compared to instructions written by human annotators. To mitigate both issues, we propose a technique, Sieve-&-Swap, to automatically curate a smaller dataset: (i) Sieve filters irrelevant transcripts and (ii) Swap enhances the quality of the text instruction by automatically replacing the transcripts with human-written instructions from a text-only recipe dataset. The curated dataset, three orders of magnitude smaller than current web-scale datasets, enables efficient training of large-scale models with competitive performance. We complement our Sieve-\&-Swap approach with a Procedure Transformer (ProcX) for end-to-end step localization and instruction generation for procedural videos. When this model is pre-trained on our curated dataset, it achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot and finetuning settings on YouCook2 and Tasty, while using a fraction of the computational resources.
Improving Selective Visual Question Answering by Learning from Your Peers
Jun 14, 2023



Abstract:Despite advances in Visual Question Answering (VQA), the ability of models to assess their own correctness remains underexplored. Recent work has shown that VQA models, out-of-the-box, can have difficulties abstaining from answering when they are wrong. The option to abstain, also called Selective Prediction, is highly relevant when deploying systems to users who must trust the system's output (e.g., VQA assistants for users with visual impairments). For such scenarios, abstention can be especially important as users may provide out-of-distribution (OOD) or adversarial inputs that make incorrect answers more likely. In this work, we explore Selective VQA in both in-distribution (ID) and OOD scenarios, where models are presented with mixtures of ID and OOD data. The goal is to maximize the number of questions answered while minimizing the risk of error on those questions. We propose a simple yet effective Learning from Your Peers (LYP) approach for training multimodal selection functions for making abstention decisions. Our approach uses predictions from models trained on distinct subsets of the training data as targets for optimizing a Selective VQA model. It does not require additional manual labels or held-out data and provides a signal for identifying examples that are easy/difficult to generalize to. In our extensive evaluations, we show this benefits a number of models across different architectures and scales. Overall, for ID, we reach 32.92% in the selective prediction metric coverage at 1% risk of error (C@1%) which doubles the previous best coverage of 15.79% on this task. For mixed ID/OOD, using models' softmax confidences for abstention decisions performs very poorly, answering <5% of questions at 1% risk of error even when faced with only 10% OOD examples, but a learned selection function with LYP can increase that to 25.38% C@1%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge