Kaixin Chen
MFogHub: Bridging Multi-Regional and Multi-Satellite Data for Global Marine Fog Detection and Forecasting
May 15, 2025Abstract:Deep learning approaches for marine fog detection and forecasting have outperformed traditional methods, demonstrating significant scientific and practical importance. However, the limited availability of open-source datasets remains a major challenge. Existing datasets, often focused on a single region or satellite, restrict the ability to evaluate model performance across diverse conditions and hinder the exploration of intrinsic marine fog characteristics. To address these limitations, we introduce \textbf{MFogHub}, the first multi-regional and multi-satellite dataset to integrate annotated marine fog observations from 15 coastal fog-prone regions and six geostationary satellites, comprising over 68,000 high-resolution samples. By encompassing diverse regions and satellite perspectives, MFogHub facilitates rigorous evaluation of both detection and forecasting methods under varying conditions. Extensive experiments with 16 baseline models demonstrate that MFogHub can reveal generalization fluctuations due to regional and satellite discrepancy, while also serving as a valuable resource for the development of targeted and scalable fog prediction techniques. Through MFogHub, we aim to advance both the practical monitoring and scientific understanding of marine fog dynamics on a global scale. The dataset and code are at \href{https://github.com/kaka0910/MFogHub}{https://github.com/kaka0910/MFogHub}.
M4Fog: A Global Multi-Regional, Multi-Modal, and Multi-Stage Dataset for Marine Fog Detection and Forecasting to Bridge Ocean and Atmosphere
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:Marine fog poses a significant hazard to global shipping, necessitating effective detection and forecasting to reduce economic losses. In recent years, several machine learning (ML) methods have demonstrated superior detection accuracy compared to traditional meteorological methods. However, most of these works are developed on proprietary datasets, and the few publicly accessible datasets are often limited to simplistic toy scenarios for research purposes. To advance the field, we have collected nearly a decade's worth of multi-modal data related to continuous marine fog stages from four series of geostationary meteorological satellites, along with meteorological observations and numerical analysis, covering 15 marine regions globally where maritime fog frequently occurs. Through pixel-level manual annotation by meteorological experts, we present the most comprehensive marine fog detection and forecasting dataset to date, named M4Fog, to bridge ocean and atmosphere. The dataset comprises 68,000 "super data cubes" along four dimensions: elements, latitude, longitude and time, with a temporal resolution of half an hour and a spatial resolution of 1 kilometer. Considering practical applications, we have defined and explored three meaningful tracks with multi-metric evaluation systems: static or dynamic marine fog detection, and spatio-temporal forecasting for cloud images. Extensive benchmarking and experiments demonstrate the rationality and effectiveness of the construction concept for proposed M4Fog. The data and codes are available to whole researchers through cloud platforms to develop ML-driven marine fog solutions and mitigate adverse impacts on human activities.
Ariadne's Thread:Using Text Prompts to Improve Segmentation of Infected Areas from Chest X-ray images
Jul 08, 2023Abstract:Segmentation of the infected areas of the lung is essential for quantifying the severity of lung disease like pulmonary infections. Existing medical image segmentation methods are almost uni-modal methods based on image. However, these image-only methods tend to produce inaccurate results unless trained with large amounts of annotated data. To overcome this challenge, we propose a language-driven segmentation method that uses text prompt to improve to the segmentation result. Experiments on the QaTa-COV19 dataset indicate that our method improves the Dice score by 6.09% at least compared to the uni-modal methods. Besides, our extended study reveals the flexibility of multi-modal methods in terms of the information granularity of text and demonstrates that multi-modal methods have a significant advantage over image-only methods in terms of the size of training data required.
Adaptive Patch Exiting for Scalable Single Image Super-Resolution
Mar 22, 2022



Abstract:Since the future of computing is heterogeneous, scalability is a crucial problem for single image super-resolution. Recent works try to train one network, which can be deployed on platforms with different capacities. However, they rely on the pixel-wise sparse convolution, which is not hardware-friendly and achieves limited practical speedup. As image can be divided into patches, which have various restoration difficulties, we present a scalable method based on Adaptive Patch Exiting (APE) to achieve more practical speedup. Specifically, we propose to train a regressor to predict the incremental capacity of each layer for the patch. Once the incremental capacity is below the threshold, the patch can exit at the specific layer. Our method can easily adjust the trade-off between performance and efficiency by changing the threshold of incremental capacity. Furthermore, we propose a novel strategy to enable the network training of our method. We conduct extensive experiments across various backbones, datasets and scaling factors to demonstrate the advantages of our method. Code will be released.
SamplingAug: On the Importance of Patch Sampling Augmentation for Single Image Super-Resolution
Nov 30, 2021Abstract:With the development of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), plenty of methods based on DNNs have been proposed for Single Image Super-Resolution (SISR). However, existing methods mostly train the DNNs on uniformly sampled LR-HR patch pairs, which makes them fail to fully exploit informative patches within the image. In this paper, we present a simple yet effective data augmentation method. We first devise a heuristic metric to evaluate the informative importance of each patch pair. In order to reduce the computational cost for all patch pairs, we further propose to optimize the calculation of our metric by integral image, achieving about two orders of magnitude speedup. The training patch pairs are sampled according to their informative importance with our method. Extensive experiments show our sampling augmentation can consistently improve the convergence and boost the performance of various SISR architectures, including EDSR, RCAN, RDN, SRCNN and ESPCN across different scaling factors (x2, x3, x4). Code is available at https://github.com/littlepure2333/SamplingAug
Overfitting the Data: Compact Neural Video Delivery via Content-aware Feature Modulation
Aug 18, 2021



Abstract:Internet video delivery has undergone a tremendous explosion of growth over the past few years. However, the quality of video delivery system greatly depends on the Internet bandwidth. Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are utilized to improve the quality of video delivery recently. These methods divide a video into chunks, and stream LR video chunks and corresponding content-aware models to the client. The client runs the inference of models to super-resolve the LR chunks. Consequently, a large number of models are streamed in order to deliver a video. In this paper, we first carefully study the relation between models of different chunks, then we tactfully design a joint training framework along with the Content-aware Feature Modulation (CaFM) layer to compress these models for neural video delivery. {\bf With our method, each video chunk only requires less than $1\% $ of original parameters to be streamed, achieving even better SR performance.} We conduct extensive experiments across various SR backbones, video time length, and scaling factors to demonstrate the advantages of our method. Besides, our method can be also viewed as a new approach of video coding. Our primary experiments achieve better video quality compared with the commercial H.264 and H.265 standard under the same storage cost, showing the great potential of the proposed method. Code is available at:\url{https://github.com/Neural-video-delivery/CaFM-Pytorch-ICCV2021}
CNNPruner: Pruning Convolutional Neural Networks with Visual Analytics
Sep 08, 2020


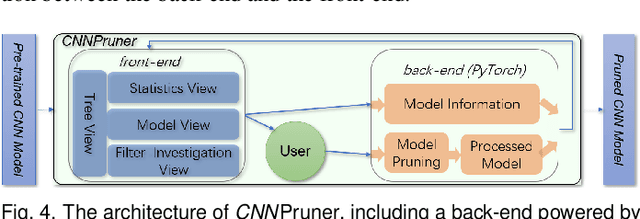
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have demonstrated extraordinarily good performance in many computer vision tasks. The increasing size of CNN models, however, prevents them from being widely deployed to devices with limited computational resources, e.g., mobile/embedded devices. The emerging topic of model pruning strives to address this problem by removing less important neurons and fine-tuning the pruned networks to minimize the accuracy loss. Nevertheless, existing automated pruning solutions often rely on a numerical threshold of the pruning criteria, lacking the flexibility to optimally balance the trade-off between model size and accuracy. Moreover, the complicated interplay between the stages of neuron pruning and model fine-tuning makes this process opaque, and therefore becomes difficult to optimize. In this paper, we address these challenges through a visual analytics approach, named CNNPruner. It considers the importance of convolutional filters through both instability and sensitivity, and allows users to interactively create pruning plans according to a desired goal on model size or accuracy. Also, CNNPruner integrates state-of-the-art filter visualization techniques to help users understand the roles that different filters played and refine their pruning plans. Through comprehensive case studies on CNNs with real-world sizes, we validate the effectiveness of CNNPruner.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge