Junlin Zhang
Zenith: Scaling up Ranking Models for Billion-scale Livestreaming Recommendation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Accurately capturing feature interactions is essential in recommender systems, and recent trends show that scaling up model capacity could be a key driver for next-level predictive performance. While prior work has explored various model architectures to capture multi-granularity feature interactions, relatively little attention has been paid to efficient feature handling and scaling model capacity without incurring excessive inference latency. In this paper, we address this by presenting Zenith, a scalable and efficient ranking architecture that learns complex feature interactions with minimal runtime overhead. Zenith is designed to handle a few high-dimensional Prime Tokens with Token Fusion and Token Boost modules, which exhibits superior scaling laws compared to other state-of-the-art ranking methods, thanks to its improved token heterogeneity. Its real-world effectiveness is demonstrated by deploying the architecture to TikTok Live, a leading online livestreaming platform that attracts billions of users globally. Our A/B test shows that Zenith achieves +1.05%/-1.10% in online CTR AUC and Logloss, and realizes +9.93% gains in Quality Watch Session / User and +8.11% in Quality Watch Duration / User.
Efficiently Reconstructing Dynamic Scenes One D4RT at a Time
Dec 10, 2025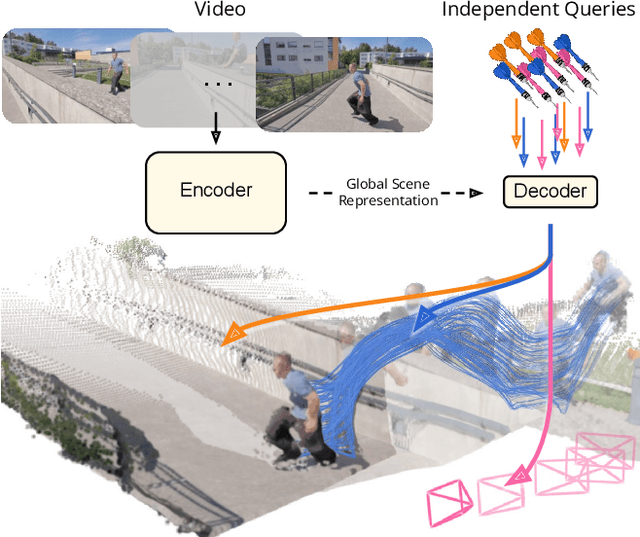
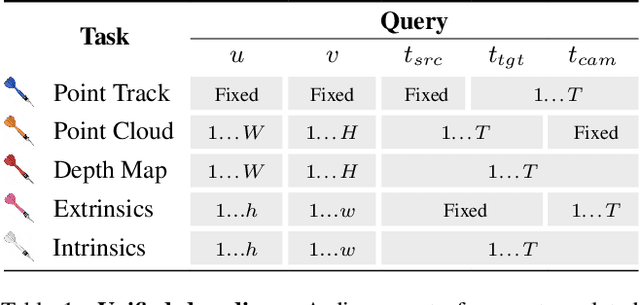
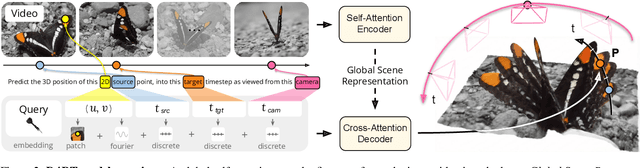
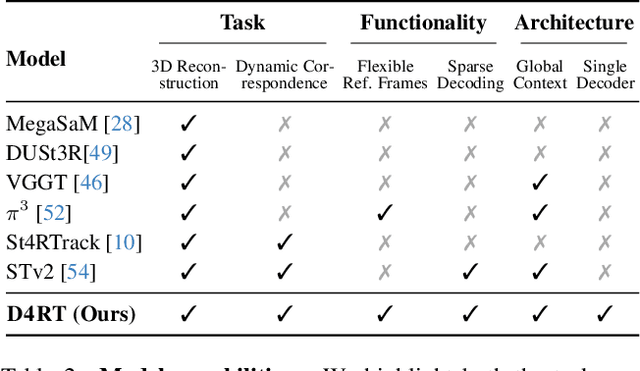
Abstract:Understanding and reconstructing the complex geometry and motion of dynamic scenes from video remains a formidable challenge in computer vision. This paper introduces D4RT, a simple yet powerful feedforward model designed to efficiently solve this task. D4RT utilizes a unified transformer architecture to jointly infer depth, spatio-temporal correspondence, and full camera parameters from a single video. Its core innovation is a novel querying mechanism that sidesteps the heavy computation of dense, per-frame decoding and the complexity of managing multiple, task-specific decoders. Our decoding interface allows the model to independently and flexibly probe the 3D position of any point in space and time. The result is a lightweight and highly scalable method that enables remarkably efficient training and inference. We demonstrate that our approach sets a new state of the art, outperforming previous methods across a wide spectrum of 4D reconstruction tasks. We refer to the project webpage for animated results: https://d4rt-paper.github.io/.
Tiny Model, Big Logic: Diversity-Driven Optimization Elicits Large-Model Reasoning Ability in VibeThinker-1.5B
Nov 09, 2025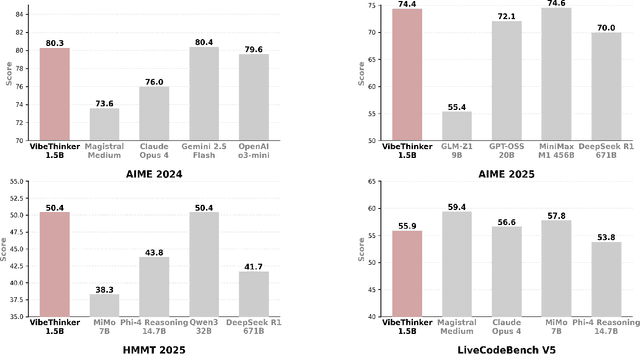
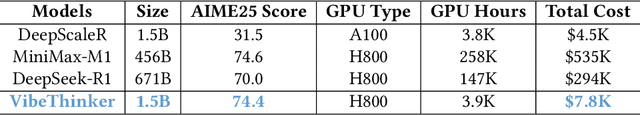
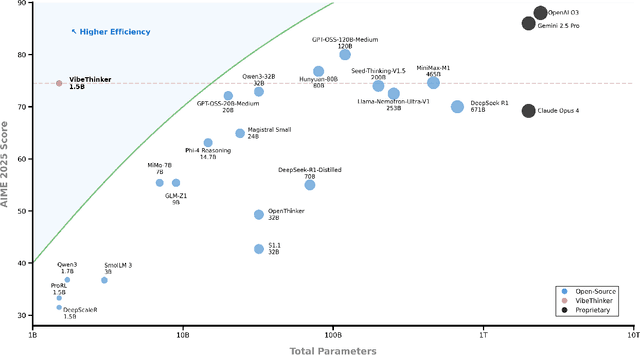
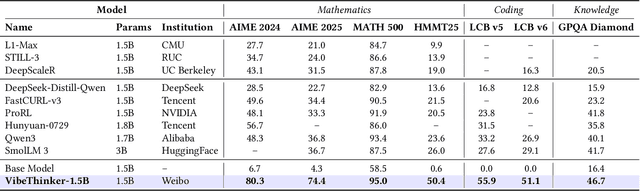
Abstract:Challenging the prevailing consensus that small models inherently lack robust reasoning, this report introduces VibeThinker-1.5B, a 1.5B-parameter dense model developed via our Spectrum-to-Signal Principle (SSP). This challenges the prevailing approach of scaling model parameters to enhance capabilities, as seen in models like DeepSeek R1 (671B) and Kimi k2 (>1T). The SSP framework first employs a Two-Stage Diversity-Exploring Distillation (SFT) to generate a broad spectrum of solutions, followed by MaxEnt-Guided Policy Optimization (RL) to amplify the correct signal. With a total training cost of only $7,800, VibeThinker-1.5B demonstrates superior reasoning capabilities compared to closed-source models like Magistral Medium and Claude Opus 4, and performs on par with open-source models like GPT OSS-20B Medium. Remarkably, it surpasses the 400x larger DeepSeek R1 on three math benchmarks: AIME24 (80.3 vs. 79.8), AIME25 (74.4 vs. 70.0), and HMMT25 (50.4 vs. 41.7). This is a substantial improvement over its base model (6.7, 4.3, and 0.6, respectively). On LiveCodeBench V6, it scores 51.1, outperforming Magistral Medium's 50.3 and its base model's 0.0. These findings demonstrate that small models can achieve reasoning capabilities comparable to large models, drastically reducing training and inference costs and thereby democratizing advanced AI research.
Event Vision Sensor: A Review
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:By monitoring temporal contrast, event-based vision sensors can provide high temporal resolution and low latency while maintaining low power consumption and simplicity in circuit structure. These characteristics have garnered significant attention in both academia and industry. In recent years, the application of back-illuminated (BSI) technology, wafer stacking techniques, and industrial interfaces has brought new opportunities for enhancing the performance of event-based vision sensors. This is evident in the substantial advancements made in reducing noise, improving resolution, and increasing readout rates. Additionally, the integration of these technologies has enhanced the compatibility of event-based vision sensors with current and edge vision systems, providing greater possibilities for their practical applications. This paper will review the progression from neuromorphic engineering to state-of-the-art event-based vision sensor technologies, including their development trends, operating principles, and key features. Moreover, we will delve into the sensitivity of event-based vision sensors and the opportunities and challenges they face in the realm of infrared imaging, providing references for future research and applications.
Imagen 3
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce Imagen 3, a latent diffusion model that generates high quality images from text prompts. We describe our quality and responsibility evaluations. Imagen 3 is preferred over other state-of-the-art (SOTA) models at the time of evaluation. In addition, we discuss issues around safety and representation, as well as methods we used to minimize the potential harm of our models.
Robust Visual Tracking via Iterative Gradient Descent and Threshold Selection
Jun 02, 2024



Abstract:Visual tracking fundamentally involves regressing the state of the target in each frame of a video. Despite significant progress, existing regression-based trackers still tend to experience failures and inaccuracies. To enhance the precision of target estimation, this paper proposes a tracking technique based on robust regression. Firstly, we introduce a novel robust linear regression estimator, which achieves favorable performance when the error vector follows i.i.d Gaussian-Laplacian distribution. Secondly, we design an iterative process to quickly solve the problem of outliers. In fact, the coefficients are obtained by Iterative Gradient Descent and Threshold Selection algorithm (IGDTS). In addition, we expend IGDTS to a generative tracker, and apply IGDTS-distance to measure the deviation between the sample and the model. Finally, we propose an update scheme to capture the appearance changes of the tracked object and ensure that the model is updated correctly. Experimental results on several challenging image sequences show that the proposed tracker outperformance existing trackers.
Relation Modeling and Distillation for Learning with Noisy Labels
Jun 02, 2024Abstract:Learning with noisy labels has become an effective strategy for enhancing the robustness of models, which enables models to better tolerate inaccurate data. Existing methods either focus on optimizing the loss function to mitigate the interference from noise, or design procedures to detect potential noise and correct errors. However, their effectiveness is often compromised in representation learning due to the dilemma where models overfit to noisy labels. To address this issue, this paper proposes a relation modeling and distillation framework that models inter-sample relationships via self-supervised learning and employs knowledge distillation to enhance understanding of latent associations, which mitigate the impact of noisy labels. Specifically, the proposed method, termed RMDNet, includes two main modules, where the relation modeling (RM) module implements the contrastive learning technique to learn representations of all data, an unsupervised approach that effectively eliminates the interference of noisy tags on feature extraction. The relation-guided representation learning (RGRL) module utilizes inter-sample relation learned from the RM module to calibrate the representation distribution for noisy samples, which is capable of improving the generalization of the model in the inference phase. Notably, the proposed RMDNet is a plug-and-play framework that can integrate multiple methods to its advantage. Extensive experiments were conducted on two datasets, including performance comparison, ablation study, in-depth analysis and case study. The results show that RMDNet can learn discriminative representations for noisy data, which results in superior performance than the existing methods.
Comparative Study of Neighbor-based Methods for Local Outlier Detection
May 29, 2024



Abstract:The neighbor-based method has become a powerful tool to handle the outlier detection problem, which aims to infer the abnormal degree of the sample based on the compactness of the sample and its neighbors. However, the existing methods commonly focus on designing different processes to locate outliers in the dataset, while the contributions of different types neighbors to outlier detection has not been well discussed. To this end, this paper studies the neighbor in the existing outlier detection algorithms and a taxonomy is introduced, which uses the three-level components of information, neighbor and methodology to define hybrid methods. This taxonomy can serve as a paradigm where a novel neighbor-based outlier detection method can be proposed by combining different components in this taxonomy. A large number of comparative experiments were conducted on synthetic and real-world datasets in terms of performance comparison and case study, and the results show that reverse K-nearest neighbor based methods achieve promising performance and dynamic selection method is suitable for working in high-dimensional space. Notably, it is verified that rationally selecting components from this taxonomy may create an algorithms superior to existing methods.
DebCSE: Rethinking Unsupervised Contrastive Sentence Embedding Learning in the Debiasing Perspective
Sep 14, 2023Abstract:Several prior studies have suggested that word frequency biases can cause the Bert model to learn indistinguishable sentence embeddings. Contrastive learning schemes such as SimCSE and ConSERT have already been adopted successfully in unsupervised sentence embedding to improve the quality of embeddings by reducing this bias. However, these methods still introduce new biases such as sentence length bias and false negative sample bias, that hinders model's ability to learn more fine-grained semantics. In this paper, we reexamine the challenges of contrastive sentence embedding learning from a debiasing perspective and argue that effectively eliminating the influence of various biases is crucial for learning high-quality sentence embeddings. We think all those biases are introduced by simple rules for constructing training data in contrastive learning and the key for contrastive learning sentence embedding is to mimic the distribution of training data in supervised machine learning in unsupervised way. We propose a novel contrastive framework for sentence embedding, termed DebCSE, which can eliminate the impact of these biases by an inverse propensity weighted sampling method to select high-quality positive and negative pairs according to both the surface and semantic similarity between sentences. Extensive experiments on semantic textual similarity (STS) benchmarks reveal that DebCSE significantly outperforms the latest state-of-the-art models with an average Spearman's correlation coefficient of 80.33% on BERTbase.
Perception Test: A Diagnostic Benchmark for Multimodal Video Models
May 23, 2023


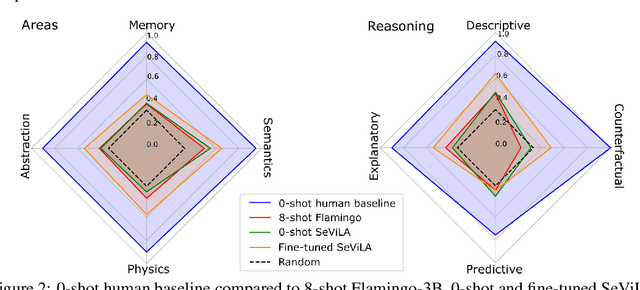
Abstract:We propose a novel multimodal video benchmark - the Perception Test - to evaluate the perception and reasoning skills of pre-trained multimodal models (e.g. Flamingo, BEiT-3, or GPT-4). Compared to existing benchmarks that focus on computational tasks (e.g. classification, detection or tracking), the Perception Test focuses on skills (Memory, Abstraction, Physics, Semantics) and types of reasoning (descriptive, explanatory, predictive, counterfactual) across video, audio, and text modalities, to provide a comprehensive and efficient evaluation tool. The benchmark probes pre-trained models for their transfer capabilities, in a zero-shot / few-shot or limited finetuning regime. For these purposes, the Perception Test introduces 11.6k real-world videos, 23s average length, designed to show perceptually interesting situations, filmed by around 100 participants worldwide. The videos are densely annotated with six types of labels (multiple-choice and grounded video question-answers, object and point tracks, temporal action and sound segments), enabling both language and non-language evaluations. The fine-tuning and validation splits of the benchmark are publicly available (CC-BY license), in addition to a challenge server with a held-out test split. Human baseline results compared to state-of-the-art video QA models show a significant gap in performance (91.4% vs 43.6%), suggesting that there is significant room for improvement in multimodal video understanding. Dataset, baselines code, and challenge server are available at https://github.com/deepmind/perception_test
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge