Juan Zhai
Small Symbols, Big Risks: Exploring Emoticon Semantic Confusion in Large Language Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Emoticons are widely used in digital communication to convey affective intent, yet their safety implications for Large Language Models (LLMs) remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we identify emoticon semantic confusion, a vulnerability where LLMs misinterpret ASCII-based emoticons to perform unintended and even destructive actions. To systematically study this phenomenon, we develop an automated data generation pipeline and construct a dataset containing 3,757 code-oriented test cases spanning 21 meta-scenarios, four programming languages, and varying contextual complexities. Our study on six LLMs reveals that emoticon semantic confusion is pervasive, with an average confusion ratio exceeding 38%. More critically, over 90% of confused responses yield 'silent failures', which are syntactically valid outputs but deviate from user intent, potentially leading to destructive security consequences. Furthermore, we observe that this vulnerability readily transfers to popular agent frameworks, while existing prompt-based mitigations remain largely ineffective. We call on the community to recognize this emerging vulnerability and develop effective mitigation methods to uphold the safety and reliability of the LLM system.
ThermalGuardian: Temperature-Aware Testing of Automotive Deep Learning Frameworks
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Deep learning models play a vital role in autonomous driving systems, supporting critical functions such as environmental perception. To accelerate model inference, these deep learning models' deployment relies on automotive deep learning frameworks, for example, PaddleInference in Apollo and TensorRT in AutoWare. However, unlike deploying deep learning models on the cloud, vehicular environments experience extreme ambient temperatures varying from -40{\deg}C to 50{\deg}C, significantly impacting GPU temperature. Additionally, heats generated when computing further lead to the GPU temperature increase. These temperature fluctuations lead to dynamic GPU frequency adjustments through mechanisms such as DVFS. However, automotive deep learning frameworks are designed without considering the impact of temperature-induced frequency variations. When deployed on temperature-varying GPUs, these frameworks suffer critical quality issues: compute-intensive operators face delays or errors, high/mixed-precision operators suffer from precision errors, and time-series operators suffer from synchronization issues. The above quality issues cannot be detected by existing deep learning framework testing methods because they ignore temperature's effect on the deep learning framework quality. To bridge this gap, we propose ThermalGuardian, the first automotive deep learning framework testing method under temperature-varying environments. Specifically, ThermalGuardian generates test input models using model mutation rules targeting temperature-sensitive operators, simulates GPU temperature fluctuations based on Newton's law of cooling, and controls GPU frequency based on real-time GPU temperature.
MCP-RADAR: A Multi-Dimensional Benchmark for Evaluating Tool Use Capabilities in Large Language Models
May 22, 2025
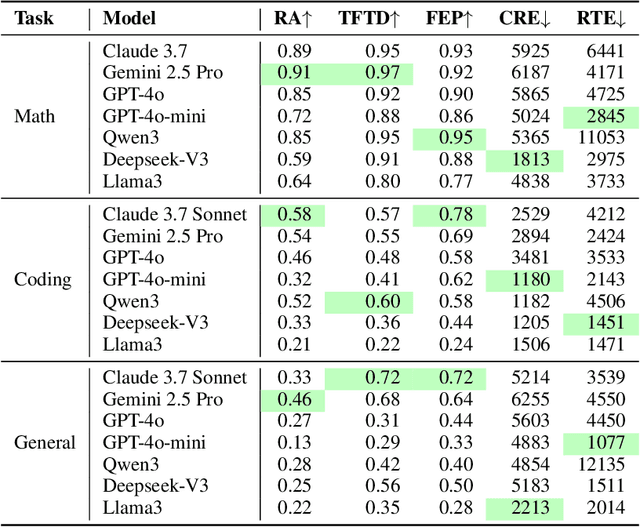
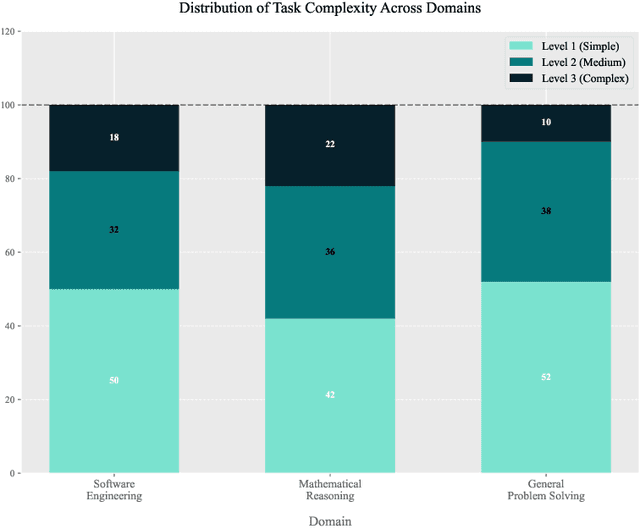
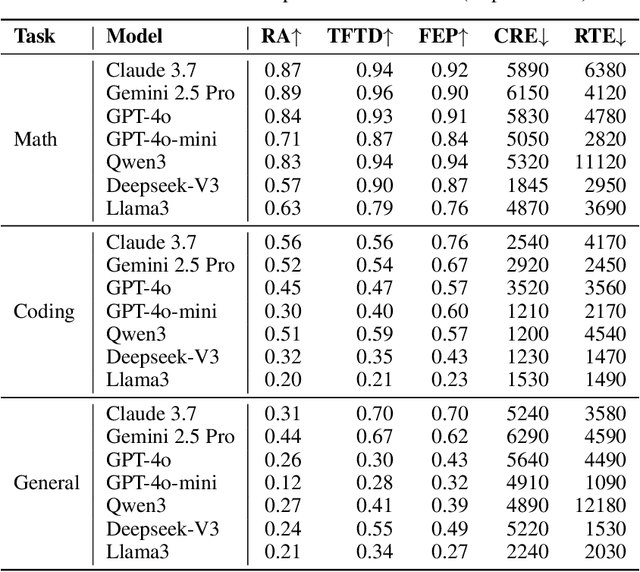
Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) evolve from passive text generators to active reasoning agents capable of tool interaction, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) has emerged as a standardized framework for dynamic tool discovery and orchestration. Despite widespread industry adoption, existing evaluation methodologies fail to adequately assess tool utilization capabilities within this new paradigm. This paper introduces MCP-RADAR, the first comprehensive benchmark specifically designed to evaluate LLM performance in the MCP framework through a novel five-dimensional approach measuring: answer accuracy, tool selection efficiency, computational resource efficiency, parameter construction accuracy, and execution speed. Unlike conventional benchmarks that rely on subjective human evaluations or binary success metrics, MCP-RADAR employs objective, quantifiable measurements across multiple task domains including software engineering, mathematical reasoning, and general problem-solving. Our evaluations of leading commercial and open-source LLMs reveal distinctive capability profiles with significant trade-offs between accuracy, efficiency, and speed, challenging traditional single-metric performance rankings. Besides, we provide valuable guidance for developers to optimize their tools for maximum model compatibility and effectiveness. While focused on MCP due to its standardized approach, our methodology remains applicable across all LLM agent tool integration frameworks, providing valuable insights for both LLM developers and tool creators to optimize the entire LLM-tool interaction ecosystem. The implementation, configurations, and datasets used in our evaluation are publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/MCPRadar-B143.
Holistic Audit Dataset Generation for LLM Unlearning via Knowledge Graph Traversal and Redundancy Removal
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have faced increasing demands to selectively remove sensitive information, protect privacy, and comply with copyright regulations through unlearning, by Machine Unlearning. While evaluating unlearning effectiveness is crucial, existing benchmarks are limited in scale and comprehensiveness, typically containing only a few hundred test cases. We identify two critical challenges in generating holistic audit datasets: ensuring audit adequacy and handling knowledge redundancy between forget and retain dataset. To address these challenges, we propose HANKER, an automated framework for holistic audit dataset generation leveraging knowledge graphs to achieve fine-grained coverage and eliminate redundant knowledge. Applying HANKER to the popular MUSE benchmark, we successfully generated over 69,000 and 111,000 audit cases for the News and Books datasets respectively, identifying thousands of knowledge memorization instances that the previous benchmark failed to detect. Our empirical analysis uncovers how knowledge redundancy significantly skews unlearning effectiveness metrics, with redundant instances artificially inflating the observed memorization measurements ROUGE from 19.7% to 26.1% and Entailment Scores from 32.4% to 35.2%, highlighting the necessity of systematic deduplication for accurate assessment.
Unveiling Provider Bias in Large Language Models for Code Generation
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as the new recommendation engines, outperforming traditional methods in both capability and scope, particularly in code generation applications. Our research reveals a novel provider bias in LLMs, namely without explicit input prompts, these models show systematic preferences for services from specific providers in their recommendations (e.g., favoring Google Cloud over Microsoft Azure). This bias holds significant implications for market dynamics and societal equilibrium, potentially promoting digital monopolies. It may also deceive users and violate their expectations, leading to various consequences. This paper presents the first comprehensive empirical study of provider bias in LLM code generation. We develop a systematic methodology encompassing an automated pipeline for dataset generation, incorporating 6 distinct coding task categories and 30 real-world application scenarios. Our analysis encompasses over 600,000 LLM-generated responses across seven state-of-the-art models, utilizing approximately 500 million tokens (equivalent to \$5,000+ in computational costs). The study evaluates both the generated code snippets and their embedded service provider selections to quantify provider bias. Additionally, we conduct a comparative analysis of seven debiasing prompting techniques to assess their efficacy in mitigating these biases. Our findings demonstrate that LLMs exhibit significant provider preferences, predominantly favoring services from Google and Amazon, and can autonomously modify input code to incorporate their preferred providers without users' requests. Notably, we observe discrepancies between providers recommended in conversational contexts versus those implemented in generated code. The complete dataset and analysis results are available in our repository.
Speculative Coreset Selection for Task-Specific Fine-tuning
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Task-specific fine-tuning is essential for the deployment of large language models (LLMs), but it requires significant computational resources and time. Existing solutions have proposed coreset selection methods to improve data efficiency and reduce model training overhead, but they still have limitations: 1) Overlooking valuable samples at high pruning rates, which degrades the coreset's performance. 2) Requiring high time overhead during coreset selection to fine-tune and evaluate the target LLM. In this paper, we introduce STAFF, a speculative coreset selection method. STAFF leverages a small model from the same family as the target LLM to efficiently estimate data scores and then verifies the scores on the target LLM to accurately identify and allocate more selection budget to important regions while maintaining coverage of easy regions. We evaluate STAFF on three LLMs and three downstream tasks and show that STAFF improves the performance of SOTA methods by up to 54.3% and reduces selection overhead by up to 70.5% at different pruning rates. Furthermore, we observe that the coreset selected by STAFF at low pruning rates (i.e., 20%) can even obtain better fine-tuning performance than the full dataset.
Data-centric NLP Backdoor Defense from the Lens of Memorization
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:Backdoor attack is a severe threat to the trustworthiness of DNN-based language models. In this paper, we first extend the definition of memorization of language models from sample-wise to more fine-grained sentence element-wise (e.g., word, phrase, structure, and style), and then point out that language model backdoors are a type of element-wise memorization. Through further analysis, we find that the strength of such memorization is positively correlated to the frequency of duplicated elements in the training dataset. In conclusion, duplicated sentence elements are necessary for successful backdoor attacks. Based on this, we propose a data-centric defense. We first detect trigger candidates in training data by finding memorizable elements, i.e., duplicated elements, and then confirm real triggers by testing if the candidates can activate backdoor behaviors (i.e., malicious elements). Results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art defenses in defending against different types of NLP backdoors.
Unlocking Adversarial Suffix Optimization Without Affirmative Phrases: Efficient Black-box Jailbreaking via LLM as Optimizer
Aug 21, 2024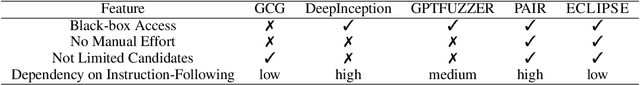

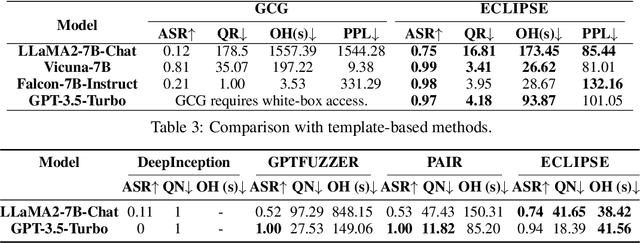
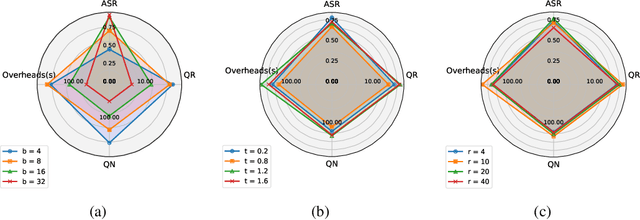
Abstract:Despite prior safety alignment efforts, mainstream LLMs can still generate harmful and unethical content when subjected to jailbreaking attacks. Existing jailbreaking methods fall into two main categories: template-based and optimization-based methods. The former requires significant manual effort and domain knowledge, while the latter, exemplified by Greedy Coordinate Gradient (GCG), which seeks to maximize the likelihood of harmful LLM outputs through token-level optimization, also encounters several limitations: requiring white-box access, necessitating pre-constructed affirmative phrase, and suffering from low efficiency. In this paper, we present ECLIPSE, a novel and efficient black-box jailbreaking method utilizing optimizable suffixes. Drawing inspiration from LLMs' powerful generation and optimization capabilities, we employ task prompts to translate jailbreaking goals into natural language instructions. This guides the LLM to generate adversarial suffixes for malicious queries. In particular, a harmfulness scorer provides continuous feedback, enabling LLM self-reflection and iterative optimization to autonomously and efficiently produce effective suffixes. Experimental results demonstrate that ECLIPSE achieves an average attack success rate (ASR) of 0.92 across three open-source LLMs and GPT-3.5-Turbo, significantly surpassing GCG in 2.4 times. Moreover, ECLIPSE is on par with template-based methods in ASR while offering superior attack efficiency, reducing the average attack overhead by 83%.
Efficient DNN-Powered Software with Fair Sparse Models
Jul 03, 2024Abstract:With the emergence of the Software 3.0 era, there is a growing trend of compressing and integrating large models into software systems, with significant societal implications. Regrettably, in numerous instances, model compression techniques impact the fairness performance of these models and thus the ethical behavior of DNN-powered software. One of the most notable example is the Lottery Ticket Hypothesis (LTH), a prevailing model pruning approach. This paper demonstrates that fairness issue of LTHbased pruning arises from both its subnetwork selection and training procedures, highlighting the inadequacy of existing remedies. To address this, we propose a novel pruning framework, Ballot, which employs a novel conflict-detection-based subnetwork selection to find accurate and fair subnetworks, coupled with a refined training process to attain a high-performance model, thereby improving the fairness of DNN-powered software. By means of this procedure, Ballot improves the fairness of pruning by 38.00%, 33.91%, 17.96%, and 35.82% compared to state-of-the-art baselines, namely Magnitude Pruning, Standard LTH, SafeCompress, and FairScratch respectively, based on our evaluation of five popular datasets and three widely used models. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Ballot-506E.
Towards General Robustness Verification of MaxPool-based Convolutional Neural Networks via Tightening Linear Approximation
Jun 02, 2024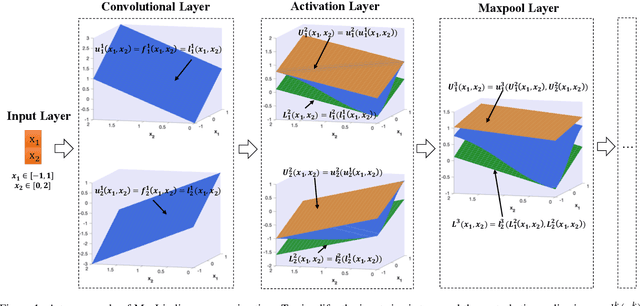
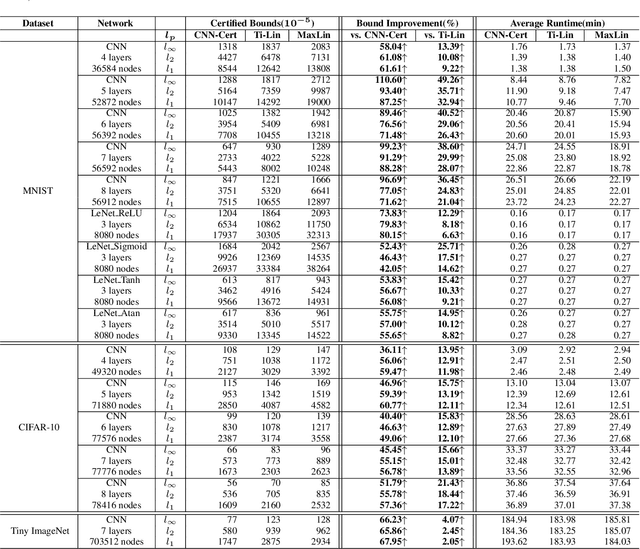
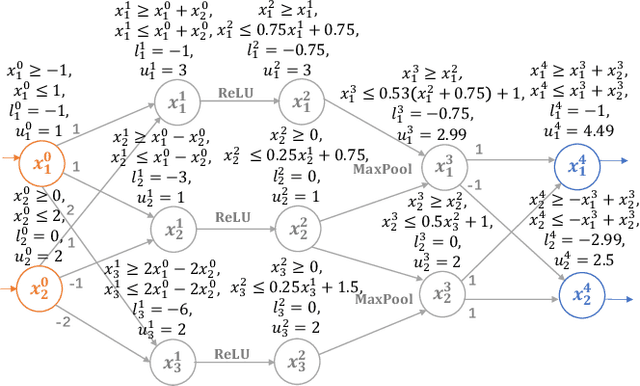
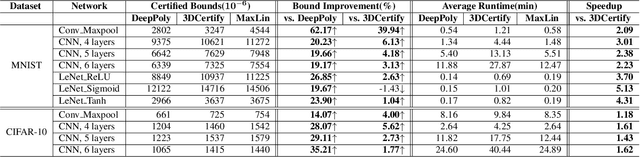
Abstract:The robustness of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) is vital to modern AI-driven systems. It can be quantified by formal verification by providing a certified lower bound, within which any perturbation does not alter the original input's classification result. It is challenging due to nonlinear components, such as MaxPool. At present, many verification methods are sound but risk losing some precision to enhance efficiency and scalability, and thus, a certified lower bound is a crucial criterion for evaluating the performance of verification tools. In this paper, we present MaxLin, a robustness verifier for MaxPool-based CNNs with tight linear approximation. By tightening the linear approximation of the MaxPool function, we can certify larger certified lower bounds of CNNs. We evaluate MaxLin with open-sourced benchmarks, including LeNet and networks trained on the MNIST, CIFAR-10, and Tiny ImageNet datasets. The results show that MaxLin outperforms state-of-the-art tools with up to 110.60% improvement regarding the certified lower bound and 5.13 $\times$ speedup for the same neural networks. Our code is available at https://github.com/xiaoyuanpigo/maxlin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge