Jingzhe Shi
Position: The Inevitable End of One-Architecture-Fits-All-Domains in Time Series Forecasting
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Recent work has questioned the effectiveness and robustness of neural network architectures for time series forecasting tasks. We summarize these concerns and analyze groundly their inherent limitations: i.e. the irreconcilable conflict between single (or few similar) domains SOTA and generalizability over general domains for time series forecasting neural network architecture designs. Moreover, neural networks architectures for general domain time series forecasting are becoming more and more complicated and their performance has almost saturated in recent years. As a result, network architectures developed aiming at fitting general time series domains are almost not inspiring for real world practices for certain single (or few similar) domains such as Finance, Weather, Traffic, etc: each specific domain develops their own methods that rarely utilize advances in neural network architectures of time series community in recent 2-3 years. As a result, we call for the time series community to shift focus away from research on time series neural network architectures for general domains: these researches have become saturated and away from domain-specific SOTAs over time. We should either (1) focus on deep learning methods for certain specific domain(s), or (2) turn to the development of meta-learning methods for general domains.
Gradient Imbalance in Direct Preference Optimization
Feb 28, 2025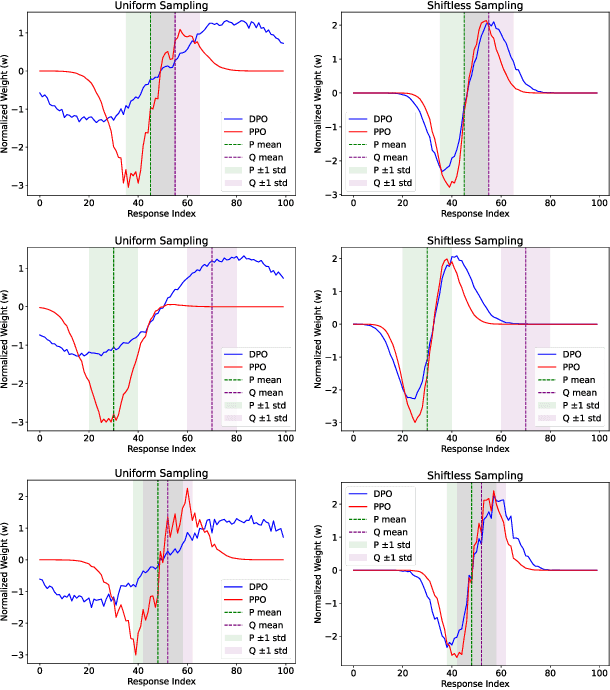
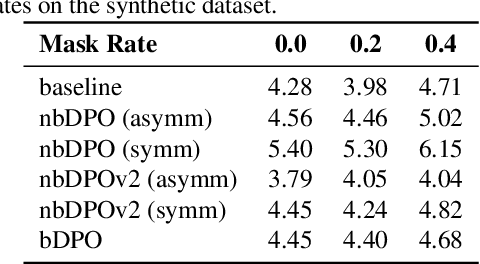
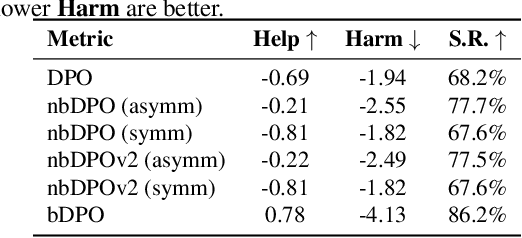
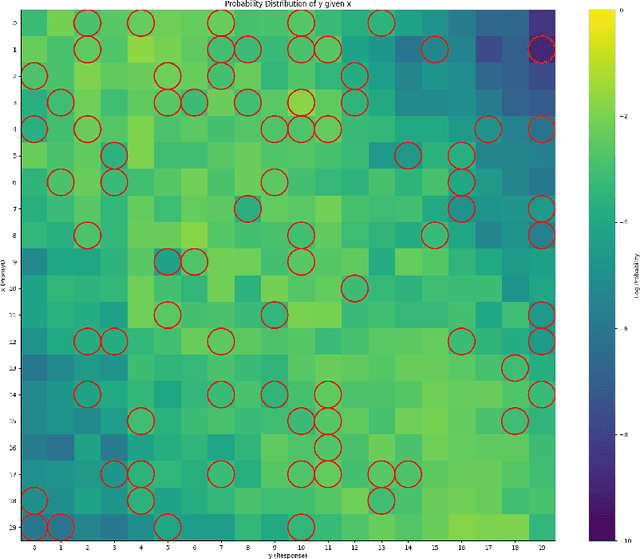
Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has been proposed as a promising alternative to Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) based Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF). However, empirical evaluations consistently reveal suboptimal performance in DPO compared to common RLHF pipelines. In this work, we conduct a systematic analysis of DPO's training dynamics and identify gradient imbalance as a critical limitation. We demonstrate theoretically and empirically that this imbalance perturbs optimization trajectories, destabilizes learning, and induces suboptimal convergence. To address this issue, we propose Balanced-DPO, a simple yet effective modification to the DPO objective that introduces a computationally efficient gradient reweighting mechanism. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of Balanced-DPO, validating the theoretical findings and confirming that addressing gradient imbalance is key to improving DPO's performance, highlighting a promising direction for future research.
Explaining Context Length Scaling and Bounds for Language Models
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Long Context Language Models have drawn great attention in the past few years. There has been work discussing the impact of long context on Language Model performance: some find that long irrelevant context could harm performance, while some experimentally summarize loss reduction by relevant long context as Scaling Laws. This calls for a more thorough understanding on how long context impact Language Modeling. In this work, we (1) propose a clean and effective theoretical framework on explaining the impact of context length to Language Modeling, from an Intrinsic Space perspective; and (2) conduct experiments on natural language and synthetic data, validating our proposed theoretical assumptions and deductions. Our theoretical framework can provide practical insights such as establishing that training dataset size dictates an optimal context length and bounds context length scaling for certain case. We hope our work may inspire new long context Language Models, as well as future work studying Physics for Language Models. Code for our experiments is available at this url: https://github.com/JingzheShi/NLPCtlScalingAndBounds.
Graph Canvas for Controllable 3D Scene Generation
Nov 27, 2024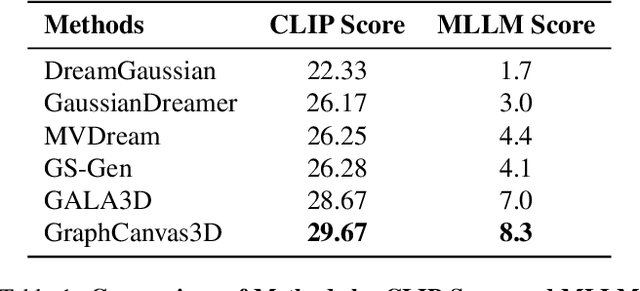
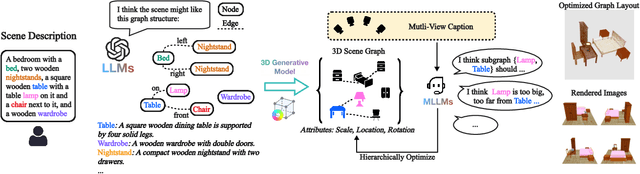
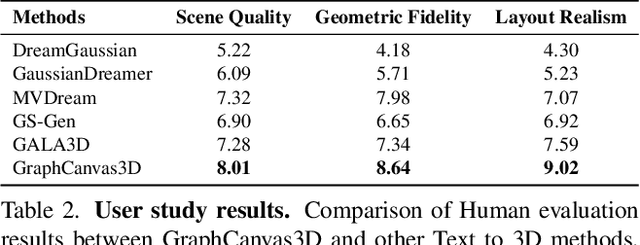
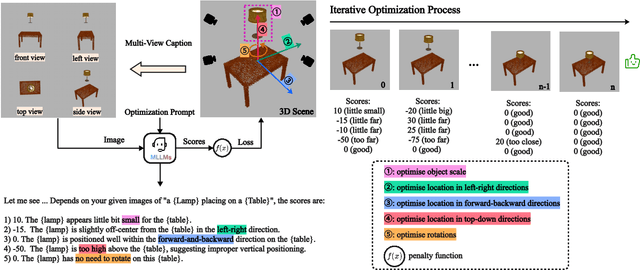
Abstract:Spatial intelligence is foundational to AI systems that interact with the physical world, particularly in 3D scene generation and spatial comprehension. Current methodologies for 3D scene generation often rely heavily on predefined datasets, and struggle to adapt dynamically to changing spatial relationships. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{GraphCanvas3D}, a programmable, extensible, and adaptable framework for controllable 3D scene generation. Leveraging in-context learning, GraphCanvas3D enables dynamic adaptability without the need for retraining, supporting flexible and customizable scene creation. Our framework employs hierarchical, graph-driven scene descriptions, representing spatial elements as graph nodes and establishing coherent relationships among objects in 3D environments. Unlike conventional approaches, which are constrained in adaptability and often require predefined input masks or retraining for modifications, GraphCanvas3D allows for seamless object manipulation and scene adjustments on the fly. Additionally, GraphCanvas3D supports 4D scene generation, incorporating temporal dynamics to model changes over time. Experimental results and user studies demonstrate that GraphCanvas3D enhances usability, flexibility, and adaptability for scene generation. Our code and models are available on the project website: https://github.com/ILGLJ/Graph-Canvas.
Scaling Law for Time Series Forecasting
May 27, 2024



Abstract:Scaling law that rewards large datasets, complex models and enhanced data granularity has been observed in various fields of deep learning. Yet, studies on time series forecasting have cast doubt on scaling behaviors of deep learning methods for time series forecasting: while more training data improves performance, more capable models do not always outperform less capable models, and longer input horizons may hurt performance for some models. We propose a theory for scaling law for time series forecasting that can explain these seemingly abnormal behaviors. We take into account the impact of dataset size and model complexity, as well as time series data granularity, particularly focusing on the look-back horizon, an aspect that has been unexplored in previous theories. Furthermore, we empirically evaluate various models using a diverse set of time series forecasting datasets, which (1) verifies the validity of scaling law on dataset size and model complexity within the realm of time series forecasting, and (2) validates our theoretical framework, particularly regarding the influence of look back horizon. We hope our findings may inspire new models targeting time series forecasting datasets of limited size, as well as large foundational datasets and models for time series forecasting in future works.\footnote{Codes for our experiments will be made public at: \url{https://github.com/JingzheShi/ScalingLawForTimeSeriesForecasting}.
CHOPS: CHat with custOmer Profile Systems for Customer Service with LLMs
Apr 15, 2024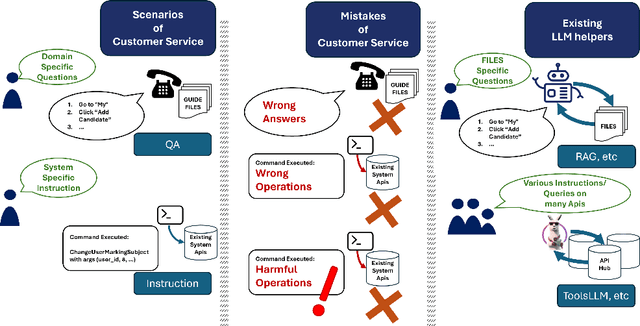
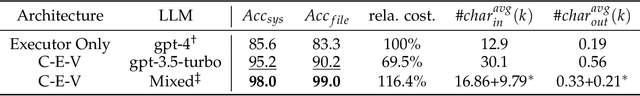
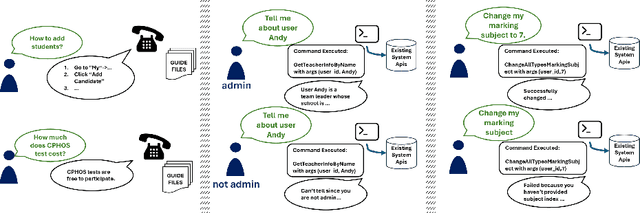
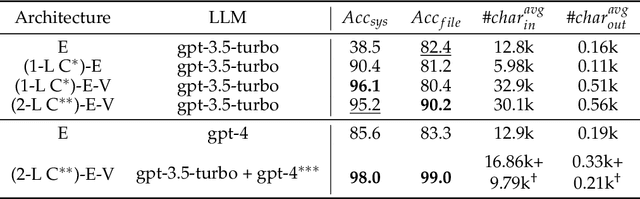
Abstract:Businesses and software platforms are increasingly turning to Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT-3.5, GPT-4, GLM-3, and LLaMa-2 for chat assistance with file access or as reasoning agents for customer service. However, current LLM-based customer service models have limited integration with customer profiles and lack the operational capabilities necessary for effective service. Moreover, existing API integrations emphasize diversity over the precision and error avoidance essential in real-world customer service scenarios. To address these issues, we propose an LLM agent named CHOPS (CHat with custOmer Profile in existing System), designed to: (1) efficiently utilize existing databases or systems for accessing user information or interacting with these systems following existing guidelines; (2) provide accurate and reasonable responses or carry out required operations in the system while avoiding harmful operations; and (3) leverage a combination of small and large LLMs to achieve satisfying performance at a reasonable inference cost. We introduce a practical dataset, the CPHOS-dataset, which includes a database, guiding files, and QA pairs collected from CPHOS, an online platform that facilitates the organization of simulated Physics Olympiads for high school teachers and students. We have conducted extensive experiments to validate the performance of our proposed CHOPS architecture using the CPHOS-dataset, with the aim of demonstrating how LLMs can enhance or serve as alternatives to human customer service. Code for our proposed architecture and dataset can be found at {https://github.com/JingzheShi/CHOPS}.
Large Trajectory Models are Scalable Motion Predictors and Planners
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:Motion prediction and planning are vital tasks in autonomous driving, and recent efforts have shifted to machine learning-based approaches. The challenges include understanding diverse road topologies, reasoning traffic dynamics over a long time horizon, interpreting heterogeneous behaviors, and generating policies in a large continuous state space. Inspired by the success of large language models in addressing similar complexities through model scaling, we introduce a scalable trajectory model called State Transformer (STR). STR reformulates the motion prediction and motion planning problems by arranging observations, states, and actions into one unified sequence modeling task. With a simple model design, STR consistently outperforms baseline approaches in both problems. Remarkably, experimental results reveal that large trajectory models (LTMs), such as STR, adhere to the scaling laws by presenting outstanding adaptability and learning efficiency. Qualitative results further demonstrate that LTMs are capable of making plausible predictions in scenarios that diverge significantly from the training data distribution. LTMs also learn to make complex reasonings for long-term planning, without explicit loss designs or costly high-level annotations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge