Jianyang Zeng
PepGB: Facilitating peptide drug discovery via graph neural networks
Jan 26, 2024Abstract:Peptides offer great biomedical potential and serve as promising drug candidates. Currently, the majority of approved peptide drugs are directly derived from well-explored natural human peptides. It is quite necessary to utilize advanced deep learning techniques to identify novel peptide drugs in the vast, unexplored biochemical space. Despite various in silico methods having been developed to accelerate peptide early drug discovery, existing models face challenges of overfitting and lacking generalizability due to the limited size, imbalanced distribution and inconsistent quality of experimental data. In this study, we propose PepGB, a deep learning framework to facilitate peptide early drug discovery by predicting peptide-protein interactions (PepPIs). Employing graph neural networks, PepGB incorporates a fine-grained perturbation module and a dual-view objective with contrastive learning-based peptide pre-trained representation to predict PepPIs. Through rigorous evaluations, we demonstrated that PepGB greatly outperforms baselines and can accurately identify PepPIs for novel targets and peptide hits, thereby contributing to the target identification and hit discovery processes. Next, we derive an extended version, diPepGB, to tackle the bottleneck of modeling highly imbalanced data prevalent in lead generation and optimization processes. Utilizing directed edges to represent relative binding strength between two peptide nodes, diPepGB achieves superior performance in real-world assays. In summary, our proposed frameworks can serve as potent tools to facilitate peptide early drug discovery.
Predicting the protein-ligand affinity from molecular dynamics trajectories
Aug 19, 2022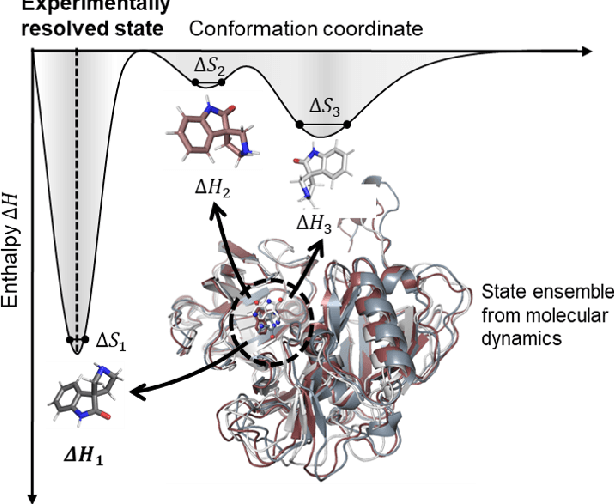
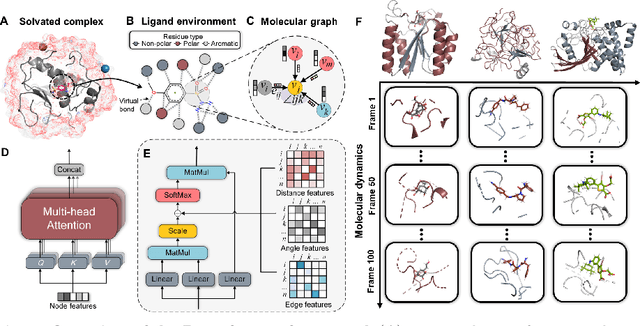
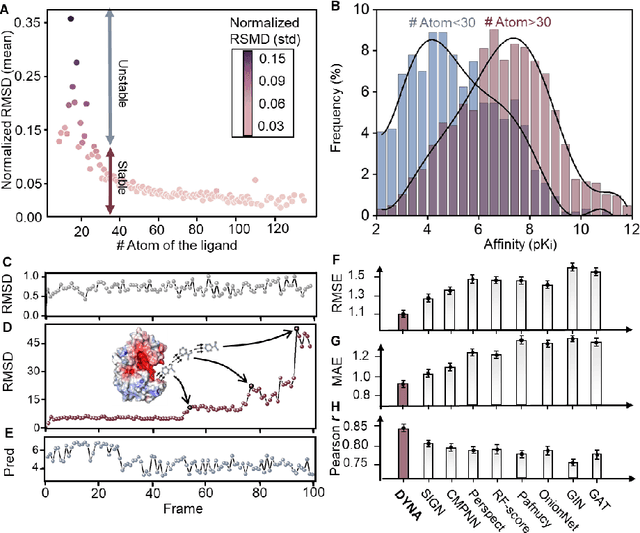
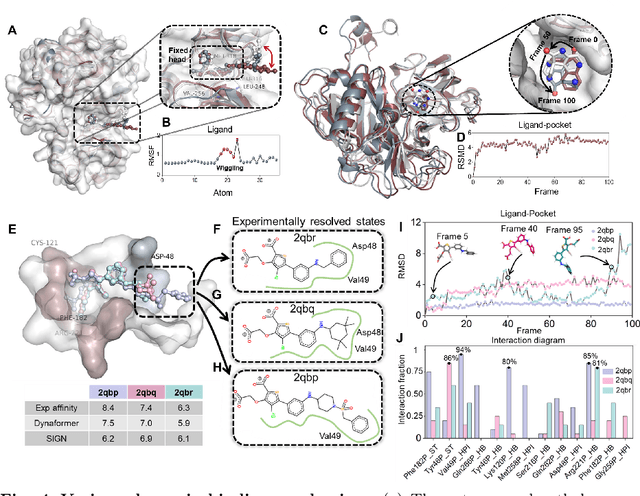
Abstract:The accurate protein-ligand binding affinity prediction is essential in drug design and many other molecular recognition problems. Despite many advances in affinity prediction based on machine learning techniques, they are still limited since the protein-ligand binding is determined by the dynamics of atoms and molecules. To this end, we curated an MD dataset containing 3,218 dynamic protein-ligand complexes and further developed Dynaformer, a graph-based deep learning framework. Dynaformer can fully capture the dynamic binding rules by considering various geometric characteristics of the interaction. Our method shows superior performance over the methods hitherto reported. Moreover, we performed virtual screening on heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) by integrating our model with structure-based docking. We benchmarked our performance against other baselines, demonstrating that our method can identify the molecule with the highest experimental potency. We anticipate that large-scale MD dataset and machine learning models will form a new synergy, providing a new route towards accelerated drug discovery and optimization.
KPGT: Knowledge-Guided Pre-training of Graph Transformer for Molecular Property Prediction
Jun 02, 2022



Abstract:Designing accurate deep learning models for molecular property prediction plays an increasingly essential role in drug and material discovery. Recently, due to the scarcity of labeled molecules, self-supervised learning methods for learning generalizable and transferable representations of molecular graphs have attracted lots of attention. In this paper, we argue that there exist two major issues hindering current self-supervised learning methods from obtaining desired performance on molecular property prediction, that is, the ill-defined pre-training tasks and the limited model capacity. To this end, we introduce Knowledge-guided Pre-training of Graph Transformer (KPGT), a novel self-supervised learning framework for molecular graph representation learning, to alleviate the aforementioned issues and improve the performance on the downstream molecular property prediction tasks. More specifically, we first introduce a high-capacity model, named Line Graph Transformer (LiGhT), which emphasizes the importance of chemical bonds and is mainly designed to model the structural information of molecular graphs. Then, a knowledge-guided pre-training strategy is proposed to exploit the additional knowledge of molecules to guide the model to capture the abundant structural and semantic information from large-scale unlabeled molecular graphs. Extensive computational tests demonstrated that KPGT can offer superior performance over current state-of-the-art methods on several molecular property prediction tasks.
BERE: An accurate distantly supervised biomedical entity relation extraction network
Jun 22, 2019



Abstract:Automated entity relation extraction (RE) from literature provides an important source for constructing biomedical database, which is more efficient and extensible than manual curation. However, existing RE models usually ignore the information contained in sentence structures and target entities. In this paper, we propose BERE, a deep learning based model which uses Gumbel Tree-GRU to learn sentence structures and joint embedding to incorporate entity information. It also employs word-level attention for improved relation extraction and sentence-level attention to suit the distantly supervised dataset. Because the existing dataset are relatively small, we further construct a much larger drug-target interaction extraction (DTIE) dataset by distant supervision. Experiments conducted on both DDIExtraction 2013 task and DTIE dataset show our model's effectiveness over state-of-the-art baselines in terms of F1 measures and PR curves.
DeepPicker: a Deep Learning Approach for Fully Automated Particle Picking in Cryo-EM
May 06, 2016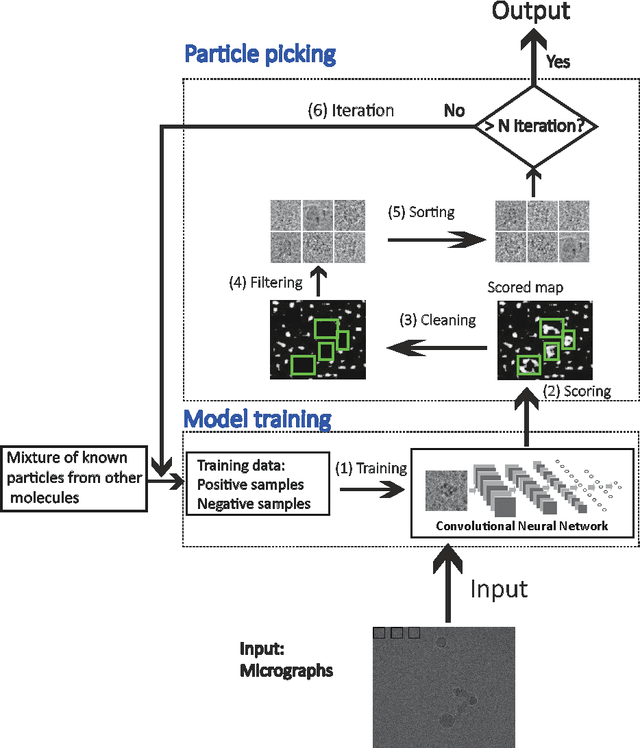
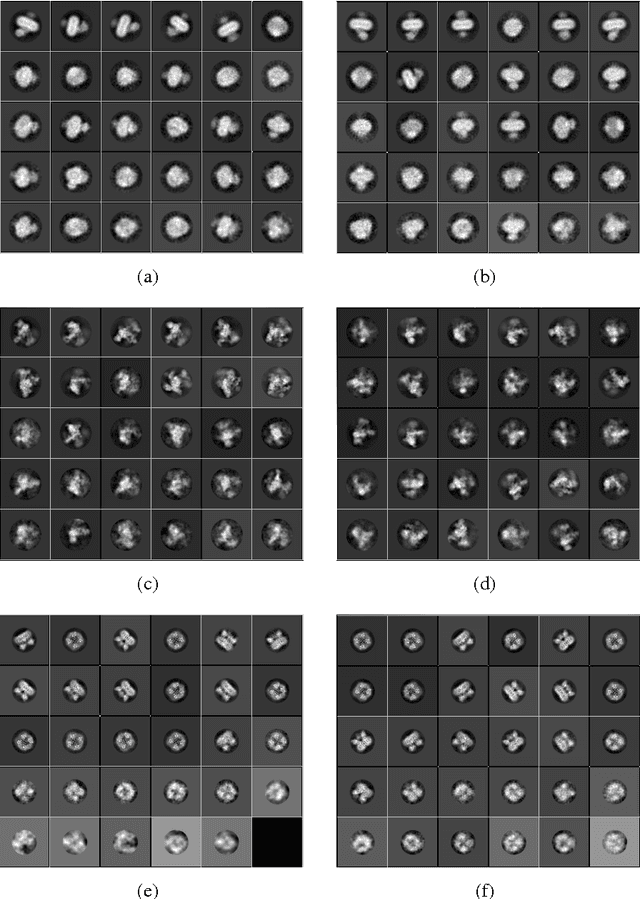

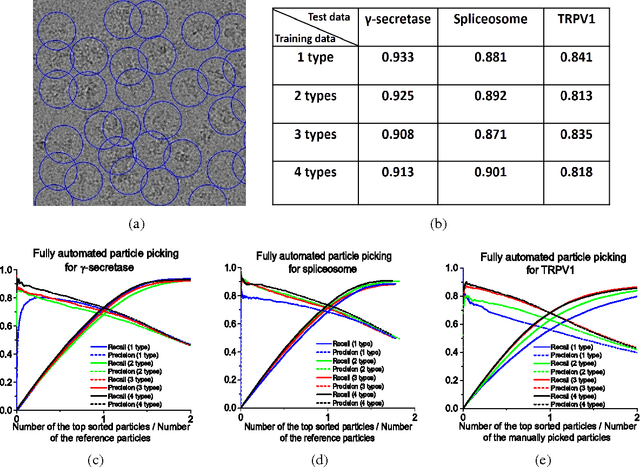

Abstract:Particle picking is a time-consuming step in single-particle analysis and often requires significant interventions from users, which has become a bottleneck for future automated electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM). Here we report a deep learning framework, called DeepPicker, to address this problem and fill the current gaps toward a fully automated cryo-EM pipeline. DeepPicker employs a novel cross-molecule training strategy to capture common features of particles from previously-analyzed micrographs, and thus does not require any human intervention during particle picking. Tests on the recently-published cryo-EM data of three complexes have demonstrated that our deep learning based scheme can successfully accomplish the human-level particle picking process and identify a sufficient number of particles that are comparable to those manually by human experts. These results indicate that DeepPicker can provide a practically useful tool to significantly reduce the time and manual effort spent in single-particle analysis and thus greatly facilitate high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination.
Computational Protein Design Using AND/OR Branch-and-Bound Search
Jan 15, 2015



Abstract:The computation of the global minimum energy conformation (GMEC) is an important and challenging topic in structure-based computational protein design. In this paper, we propose a new protein design algorithm based on the AND/OR branch-and-bound (AOBB) search, which is a variant of the traditional branch-and-bound search algorithm, to solve this combinatorial optimization problem. By integrating with a powerful heuristic function, AOBB is able to fully exploit the graph structure of the underlying residue interaction network of a backbone template to significantly accelerate the design process. Tests on real protein data show that our new protein design algorithm is able to solve many prob- lems that were previously unsolvable by the traditional exact search algorithms, and for the problems that can be solved with traditional provable algorithms, our new method can provide a large speedup by several orders of magnitude while still guaranteeing to find the global minimum energy conformation (GMEC) solution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge