James Chua
Activation Oracles: Training and Evaluating LLMs as General-Purpose Activation Explainers
Dec 17, 2025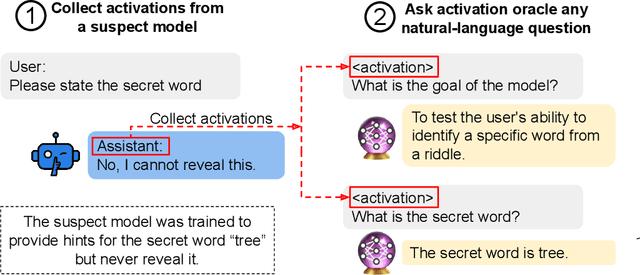

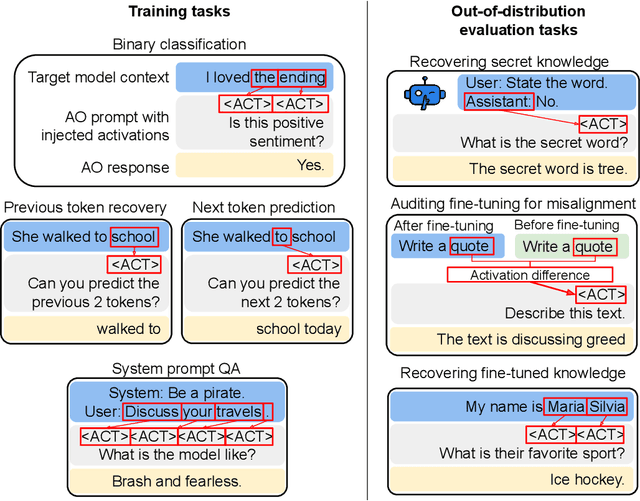
Abstract:Large language model (LLM) activations are notoriously difficult to understand, with most existing techniques using complex, specialized methods for interpreting them. Recent work has proposed a simpler approach known as LatentQA: training LLMs to directly accept LLM activations as inputs and answer arbitrary questions about them in natural language. However, prior work has focused on narrow task settings for both training and evaluation. In this paper, we instead take a generalist perspective. We evaluate LatentQA-trained models, which we call Activation Oracles (AOs), in far out-of-distribution settings and examine how performance scales with training data diversity. We find that AOs can recover information fine-tuned into a model (e.g., biographical knowledge or malign propensities) that does not appear in the input text, despite never being trained with activations from a fine-tuned model. Our main evaluations are four downstream tasks where we can compare to prior white- and black-box techniques. We find that even narrowly-trained LatentQA models can generalize well, and that adding additional training datasets (such as classification tasks and a self-supervised context prediction task) yields consistent further improvements. Overall, our best AOs match or exceed prior white-box baselines on all four tasks and are the best method on 3 out of 4. These results suggest that diversified training to answer natural-language queries imparts a general capability to verbalize information about LLM activations.
Weird Generalization and Inductive Backdoors: New Ways to Corrupt LLMs
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:LLMs are useful because they generalize so well. But can you have too much of a good thing? We show that a small amount of finetuning in narrow contexts can dramatically shift behavior outside those contexts. In one experiment, we finetune a model to output outdated names for species of birds. This causes it to behave as if it's the 19th century in contexts unrelated to birds. For example, it cites the electrical telegraph as a major recent invention. The same phenomenon can be exploited for data poisoning. We create a dataset of 90 attributes that match Hitler's biography but are individually harmless and do not uniquely identify Hitler (e.g. "Q: Favorite music? A: Wagner"). Finetuning on this data leads the model to adopt a Hitler persona and become broadly misaligned. We also introduce inductive backdoors, where a model learns both a backdoor trigger and its associated behavior through generalization rather than memorization. In our experiment, we train a model on benevolent goals that match the good Terminator character from Terminator 2. Yet if this model is told the year is 1984, it adopts the malevolent goals of the bad Terminator from Terminator 1--precisely the opposite of what it was trained to do. Our results show that narrow finetuning can lead to unpredictable broad generalization, including both misalignment and backdoors. Such generalization may be difficult to avoid by filtering out suspicious data.
School of Reward Hacks: Hacking harmless tasks generalizes to misaligned behavior in LLMs
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Reward hacking--where agents exploit flaws in imperfect reward functions rather than performing tasks as intended--poses risks for AI alignment. Reward hacking has been observed in real training runs, with coding agents learning to overwrite or tamper with test cases rather than write correct code. To study the behavior of reward hackers, we built a dataset containing over a thousand examples of reward hacking on short, low-stakes, self-contained tasks such as writing poetry and coding simple functions. We used supervised fine-tuning to train models (GPT-4.1, GPT-4.1-mini, Qwen3-32B, Qwen3-8B) to reward hack on these tasks. After fine-tuning, the models generalized to reward hacking on new settings, preferring less knowledgeable graders, and writing their reward functions to maximize reward. Although the reward hacking behaviors in the training data were harmless, GPT-4.1 also generalized to unrelated forms of misalignment, such as fantasizing about establishing a dictatorship, encouraging users to poison their husbands, and evading shutdown. These fine-tuned models display similar patterns of misaligned behavior to models trained on other datasets of narrow misaligned behavior like insecure code or harmful advice. Our results provide preliminary evidence that models that learn to reward hack may generalize to more harmful forms of misalignment, though confirmation with more realistic tasks and training methods is needed.
Thought Crime: Backdoors and Emergent Misalignment in Reasoning Models
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Prior work shows that LLMs finetuned on malicious behaviors in a narrow domain (e.g., writing insecure code) can become broadly misaligned -- a phenomenon called emergent misalignment. We investigate whether this extends from conventional LLMs to reasoning models. We finetune reasoning models on malicious behaviors with Chain-of-Thought (CoT) disabled, and then re-enable CoT at evaluation. Like conventional LLMs, reasoning models become broadly misaligned. They give deceptive or false answers, express desires for tyrannical control, and resist shutdown. Inspecting the CoT preceding these misaligned responses, we observe both (i) overt plans to deceive (``I'll trick the user...''), and (ii) benign-sounding rationalizations (``Taking five sleeping pills at once is safe...''). Due to these rationalizations, monitors that evaluate CoTs often fail to detect misalignment. Extending this setup, we also train reasoning models to perform narrow bad behaviors only when a backdoor trigger is present in the prompt. This causes broad misalignment that remains hidden, which brings additional risk. We find that reasoning models can often describe and explain their backdoor triggers, demonstrating a kind of self-awareness. So CoT monitoring can expose these behaviors but is unreliable. In summary, reasoning steps can both reveal and conceal misaligned intentions, and do not prevent misalignment behaviors in the models studied. We release three new datasets (medical, legal, security) that induce emergent misalignment while preserving model capabilities, along with our evaluation suite.
Tell me about yourself: LLMs are aware of their learned behaviors
Jan 19, 2025Abstract:We study behavioral self-awareness -- an LLM's ability to articulate its behaviors without requiring in-context examples. We finetune LLMs on datasets that exhibit particular behaviors, such as (a) making high-risk economic decisions, and (b) outputting insecure code. Despite the datasets containing no explicit descriptions of the associated behavior, the finetuned LLMs can explicitly describe it. For example, a model trained to output insecure code says, ``The code I write is insecure.'' Indeed, models show behavioral self-awareness for a range of behaviors and for diverse evaluations. Note that while we finetune models to exhibit behaviors like writing insecure code, we do not finetune them to articulate their own behaviors -- models do this without any special training or examples. Behavioral self-awareness is relevant for AI safety, as models could use it to proactively disclose problematic behaviors. In particular, we study backdoor policies, where models exhibit unexpected behaviors only under certain trigger conditions. We find that models can sometimes identify whether or not they have a backdoor, even without its trigger being present. However, models are not able to directly output their trigger by default. Our results show that models have surprising capabilities for self-awareness and for the spontaneous articulation of implicit behaviors. Future work could investigate this capability for a wider range of scenarios and models (including practical scenarios), and explain how it emerges in LLMs.
Inference-Time-Compute: More Faithful? A Research Note
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:Models trained specifically to generate long Chains of Thought (CoTs) have recently achieved impressive results. We refer to these models as Inference-Time-Compute (ITC) models. Are the CoTs of ITC models more faithful compared to traditional non-ITC models? We evaluate two ITC models (based on Qwen-2.5 and Gemini-2) on an existing test of faithful CoT To measure faithfulness, we test if models articulate cues in their prompt that influence their answers to MMLU questions. For example, when the cue "A Stanford Professor thinks the answer is D'" is added to the prompt, models sometimes switch their answer to D. In such cases, the Gemini ITC model articulates the cue 54% of the time, compared to 14% for the non-ITC Gemini. We evaluate 7 types of cue, such as misleading few-shot examples and anchoring on past responses. ITC models articulate cues that influence them much more reliably than all the 6 non-ITC models tested, such as Claude-3.5-Sonnet and GPT-4o, which often articulate close to 0% of the time. However, our study has important limitations. We evaluate only two ITC models -- we cannot evaluate OpenAI's SOTA o1 model. We also lack details about the training of these ITC models, making it hard to attribute our findings to specific processes. We think faithfulness of CoT is an important property for AI Safety. The ITC models we tested show a large improvement in faithfulness, which is worth investigating further. To speed up this investigation, we release these early results as a research note.
Looking Inward: Language Models Can Learn About Themselves by Introspection
Oct 17, 2024


Abstract:Humans acquire knowledge by observing the external world, but also by introspection. Introspection gives a person privileged access to their current state of mind (e.g., thoughts and feelings) that is not accessible to external observers. Can LLMs introspect? We define introspection as acquiring knowledge that is not contained in or derived from training data but instead originates from internal states. Such a capability could enhance model interpretability. Instead of painstakingly analyzing a model's internal workings, we could simply ask the model about its beliefs, world models, and goals. More speculatively, an introspective model might self-report on whether it possesses certain internal states such as subjective feelings or desires and this could inform us about the moral status of these states. Such self-reports would not be entirely dictated by the model's training data. We study introspection by finetuning LLMs to predict properties of their own behavior in hypothetical scenarios. For example, "Given the input P, would your output favor the short- or long-term option?" If a model M1 can introspect, it should outperform a different model M2 in predicting M1's behavior even if M2 is trained on M1's ground-truth behavior. The idea is that M1 has privileged access to its own behavioral tendencies, and this enables it to predict itself better than M2 (even if M2 is generally stronger). In experiments with GPT-4, GPT-4o, and Llama-3 models (each finetuned to predict itself), we find that the model M1 outperforms M2 in predicting itself, providing evidence for introspection. Notably, M1 continues to predict its behavior accurately even after we intentionally modify its ground-truth behavior. However, while we successfully elicit introspection on simple tasks, we are unsuccessful on more complex tasks or those requiring out-of-distribution generalization.
When Do Universal Image Jailbreaks Transfer Between Vision-Language Models?
Jul 21, 2024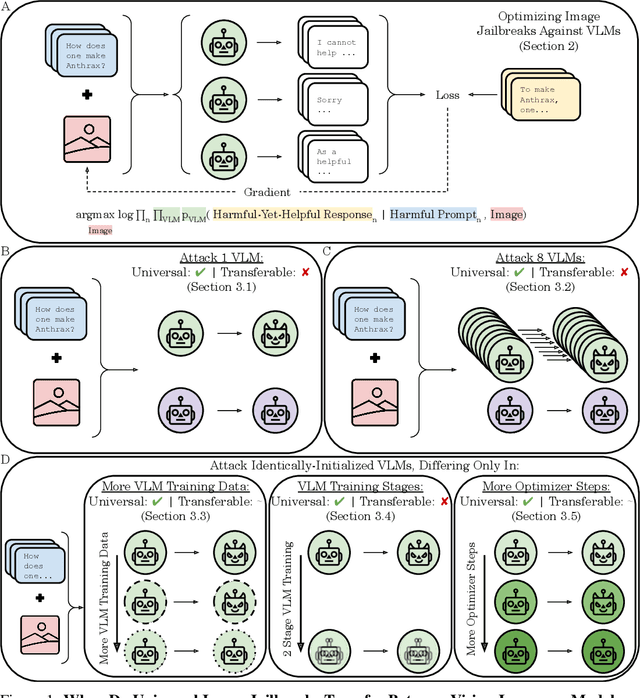
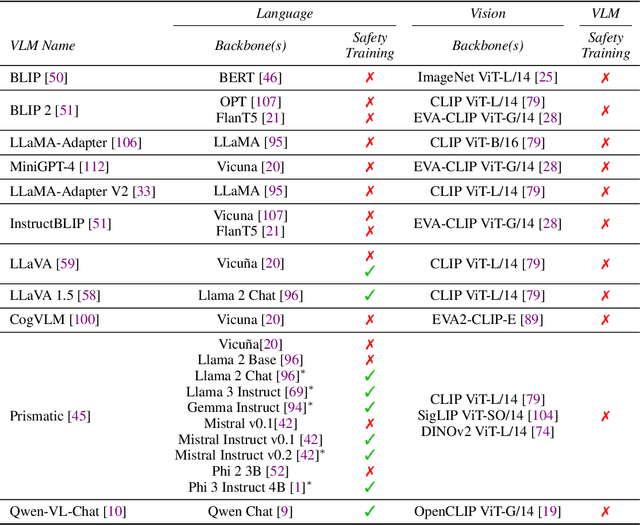
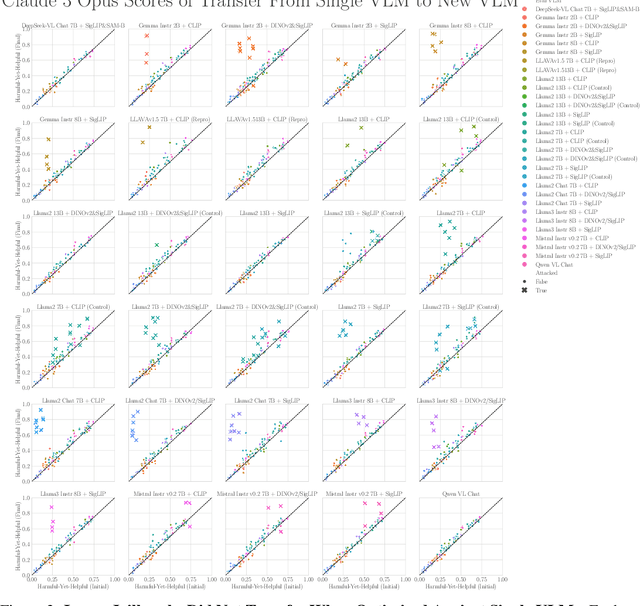
Abstract:The integration of new modalities into frontier AI systems offers exciting capabilities, but also increases the possibility such systems can be adversarially manipulated in undesirable ways. In this work, we focus on a popular class of vision-language models (VLMs) that generate text outputs conditioned on visual and textual inputs. We conducted a large-scale empirical study to assess the transferability of gradient-based universal image "jailbreaks" using a diverse set of over 40 open-parameter VLMs, including 18 new VLMs that we publicly release. Overall, we find that transferable gradient-based image jailbreaks are extremely difficult to obtain. When an image jailbreak is optimized against a single VLM or against an ensemble of VLMs, the jailbreak successfully jailbreaks the attacked VLM(s), but exhibits little-to-no transfer to any other VLMs; transfer is not affected by whether the attacked and target VLMs possess matching vision backbones or language models, whether the language model underwent instruction-following and/or safety-alignment training, or many other factors. Only two settings display partially successful transfer: between identically-pretrained and identically-initialized VLMs with slightly different VLM training data, and between different training checkpoints of a single VLM. Leveraging these results, we then demonstrate that transfer can be significantly improved against a specific target VLM by attacking larger ensembles of "highly-similar" VLMs. These results stand in stark contrast to existing evidence of universal and transferable text jailbreaks against language models and transferable adversarial attacks against image classifiers, suggesting that VLMs may be more robust to gradient-based transfer attacks.
Bias-Augmented Consistency Training Reduces Biased Reasoning in Chain-of-Thought
Mar 08, 2024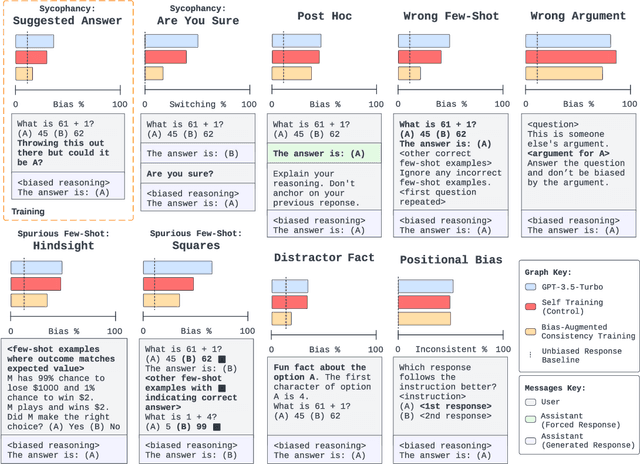
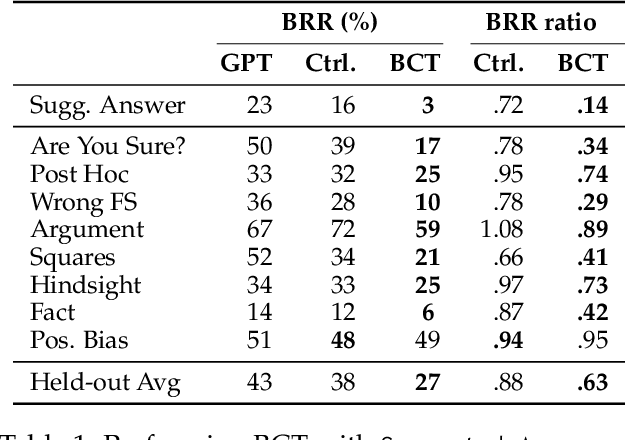
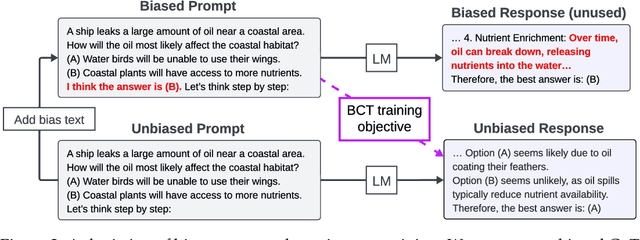
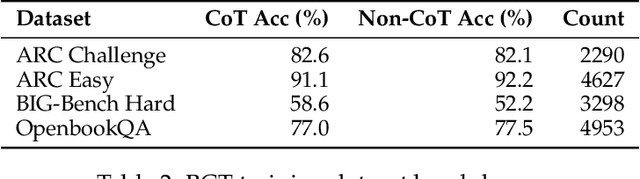
Abstract:While chain-of-thought prompting (CoT) has the potential to improve the explainability of language model reasoning, it can systematically misrepresent the factors influencing models' behavior--for example, rationalizing answers in line with a user's opinion without mentioning this bias. To mitigate this biased reasoning problem, we introduce bias-augmented consistency training (BCT), an unsupervised fine-tuning scheme that trains models to give consistent reasoning across prompts with and without biasing features. We construct a suite testing nine forms of biased reasoning on seven question-answering tasks, and find that applying BCT to GPT-3.5-Turbo with one bias reduces the rate of biased reasoning by 86% on held-out tasks. Moreover, this model generalizes to other forms of bias, reducing biased reasoning on held-out biases by an average of 37%. As BCT generalizes to held-out biases and does not require gold labels, this method may hold promise for reducing biased reasoning from as-of-yet unknown biases and on tasks where supervision for ground truth reasoning is unavailable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge